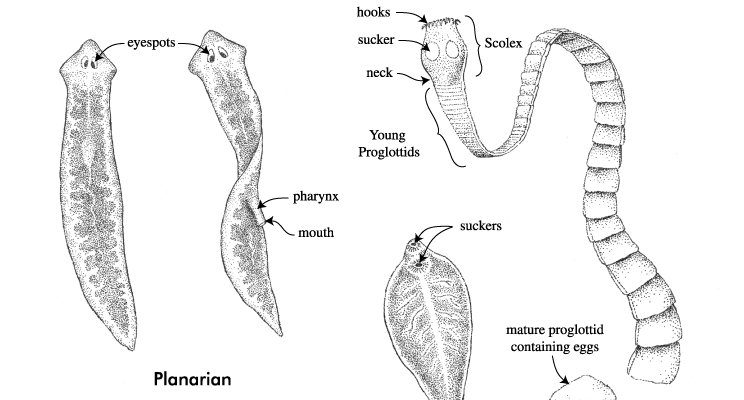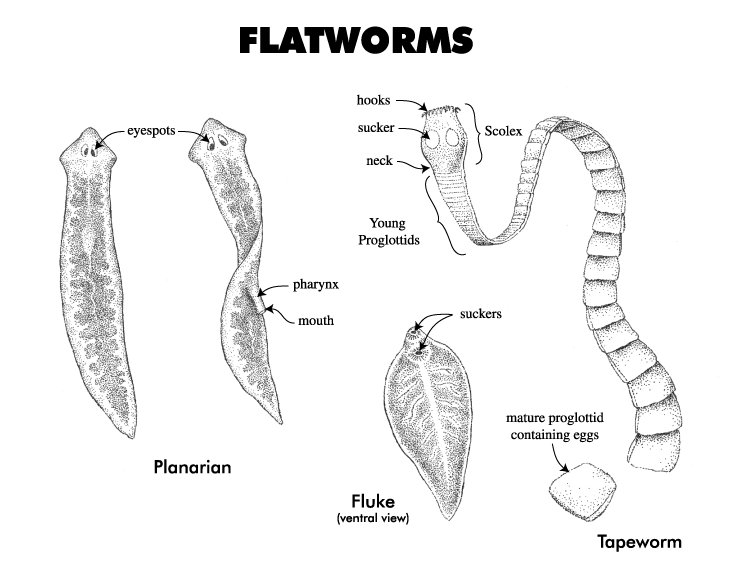
When we talk about flatworm reproduction, it’s not just about the act of mating—there’s a whole lot of biology and behavior that goes into it. Picture a dance where each partner has to play their role just right to ensure the survival of their species. Flatworms have some interesting reproductive strategies—some are hermaphroditic, meaning they have both male and female sex organs, while others have different roles during mating. Let me explain how this works, what happens during mating, the incredible journey of their eggs, and the lives of their larvae.
Understanding Flatworm Mating Habits
Flatworms are like relationship experts in the animal kingdom with their unique mating rituals. Most species are hermaphroditic, which means they can produce both eggs and sperm. Imagine attending a party where everyone can dance with everyone else—that’s a bit like how flatworms mate!
During mating, these little creatures engage in a process called copulation. Here’s how it generally goes down:
- Two flatworms line up side by side in a** dance of compatibility**.
- They exchange sperm, which can take several hours. It’s like a long, intimate conversation that leads to something beautiful.
- After this exchange, each flatworm can use the received sperm to fertilize their own eggs later. Talk about getting creative!
You might be wondering how they know who’s who during this exchange. Well, flatworms use chemical cues in the water and touch to find mates. Some even engage in courtship behaviors, like rubbing against each other. It’s all part of the attraction game!
Flatworm Eggs: The Next Generation
Once mating has occurred, it’s time for the flatworms to lay some eggs. But how does this happen? Here’s where it gets interesting. The eggs of flatworms are typically laid in clusters and surrounded by a protective coating, which helps keep them safe from predators and environmental factors.
The egg-laying process varies among species. For example, some flatworms can lay up to 1,000 eggs at a time! These eggs can be found in two main forms:
- Cocoon-like structures that act like a cozy bedroom for the developing embryos.
- Single or clustered eggs that float or stick to surfaces. Think of them as tiny jelly beans sprinkled across their habitat.
After laying eggs, it can take anywhere from a few days to several weeks for the eggs to hatch, depending on the species and environmental conditions. This waiting period is crucial as flatworm eggs undergo development until they’re ready to make their grand entrance into the world.
Journey of Flatworm Larvae
When the eggs hatch, out come the larvae, and it’s a whole new adventure for these tiny flatworms. In many cases, the larvae that emerge from flatworm eggs are quite different from adult flatworms. They often belong to a stage called thelminthic larvae, which can swim freely.
This early life stage is vital for survival because it allows the larvae to find new habitats where they can mature. Here’s what typically happens:
- The larvae are usually free-swimming and can travel significant distances in search of food and shelter.
- During this time, they might encounter various predators, which is why they develop a few tricks to stay safe.
- Eventually, they undergo transformations, adapting to their new environment until they settle down and develop into adult flatworms.
The cute little larvae don’t stay small forever. As they grow, they start to resemble the flatworms we’re familiar with. It’s like watching a caterpillar transform into a butterfly, just with a bit less glamour!
Reproductive Strategies in Flatworms
Flatworms really bring a lot to the table when it comes to reproductive strategies. As mentioned earlier, many are hermaphroditic, which means they can be both *male* and *female*. This versatility helps them find mates more easily, especially in environments where flatworms may be scarce.
Some flatworm species have developed a practice called sperm trading, where they mate multiple times to ensure they’re not just relying on one partner’s sperm. Others even engage in a behavior known as penis fencing. Imagine two flatworms literally fencing with their penises to inject sperm into each other! This unique strategy allows them to ensure fertilization, and it’s quite fascinating to watch.
Here’s a quick rundown of the types of reproduction seen in flatworms:
- Asexual reproduction: In some cases, flatworms can reproduce by dividing themselves in half and regenerating into two new individuals. It’s like cloning but in the natural world!
- Sexual reproduction: Most notably seen in hermaphroditic species, where both partners exchange sperm for fertilization.
Each strategy has its advantages and challenges, but they all aim to ensure the survival of their species.
The Importance of Flatworm Reproduction to Ecosystems
Flatworms may seem small, but their role in ecosystems is huge. They contribute to the balance of aquatic environments and help control populations of smaller organisms. Here’s why their reproduction is crucial:
- Flatworms feed on a variety of prey, including smaller invertebrates and organic matter, helping to recycle nutrients back into the ecosystem.
- Their larvae stages can serve as food for a range of aquatic animals, linking them to the broader food web.
- Healthy flatworm populations indicate good water quality, as they thrive in clean, well-oxygenated environments.
By ensuring their populations thrive through effective reproduction strategies, flatworms support the intricate balance within their habitats. It’s a remarkable contribution for creatures that many overlook!
Flatworm reproduction is a rich and complex subject, full of intrigue and fascinating behaviors. From their unique mating rituals to the life cycles of their eggs and larvae, these creatures have a lot to teach us about resilience and adaptability. Whether they’re trading sperm like seasoned pros or laying thousands of eggs, flatworms play an essential role in maintaining the health of their ecosystems.
So, the next time you come across a flatworm, take a moment to appreciate their incredible journey—from tiny larvae to fully-fledged adults. Who knew that such small creatures could lead such big lives? Flatworms remind us that even the simplest beings can have captivating stories worth telling.