Let’s dive into the dual nature of Trichinella spiralis populations. On one hand, they contribute to food webs and help control other species. On the other, they pose risks to wildlife and human health. So, grab your coffee, and let’s unpack the ecological benefits and drawbacks of these fascinating, if sometimes troubling, parasites.
What Is Trichinella Spiralis?
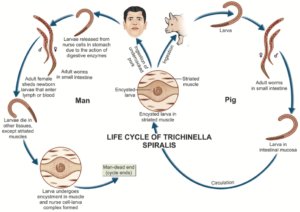
Before we discuss the ecological impacts, it’s essential to understand what Trichinella spiralis really is. This tiny roundworm is a parasite that primarily infects mammals, including pigs and humans. When humans eat undercooked meat containing these larvae, they can end up with a disease called trichinosis. Here’s the real kicker: while it may sound scary, these worms have intriguing roles in their ecosystems.
Trichinella is part of a larger group of organisms that help regulate populations in nature. When animals get infected—whether it’s a wild boar or a domestic pig—it’s like nature’s way of keeping things in check. In that way, they contribute to the balance of their ecosystems. However, this balance can be quite delicate. If Trichinella spiralis populations get out of hand, they can cause serious issues for their hosts.
Ecological Benefits of Trichinella Spiralis
You might be surprised to learn that Trichinella spiralis can have some positive impacts on ecosystems. Here are a few ways they contribute:
- Controlling Wildlife Populations: Trichinella can help manage animal populations by affecting the health and survival rates of their hosts. Healthy populations of certain species can keep ecosystems functioning smoothly.
- Nutrient Cycling: When infected animals die, their bodies decompose, returning nutrients to the soil. This is crucial for plant life, which supports the entire food web.
- Biodiversity: In a way, Trichinella spiralis adds to biodiversity by existing in various host species. A healthy mix of species can lead to more resilient ecosystems.
These benefits might not be obvious at first glance, but they play a significant role in the big picture. An ecosystem is like a spider web—remove one strand, and the whole structure can weaken.
Drawbacks of Trichinella Spiralis
Now let’s shift gears and talk about the downsides of Trichinella spiralis. While they have some ecological benefits, they also bring significant challenges:
- Health Risks: Trichinella can cause serious health issues in humans. Trichinosis can lead to symptoms like nausea, diarrhea, and muscle pain. It’s a clear reminder that these parasites are more than just ecological players—they’re also a threat.
- Impact on Wildlife: In wildlife, high infection rates can lead to population declines. This can disrupt local food chains and alter ecosystems permanently.
- Economic Costs: For farmers, dealing with Trichinella means increased management costs. There are regulations to prevent human infection, which adds layers of complexity to livestock farming.
These drawbacks are significant. While nature often finds a balance, human interaction can tip the scales in a way that leads to ecological disruption.
The Role in Food Webs
Understanding how Trichinella spiralis fits into food webs is crucial. Think of food webs as intricate networks of who-eats-who. Trichinella spiralis affects numerous species, particularly carnivores and omnivores that consume infected animals.
These worms can impact the health and survival of their hosts, which can ripple through the food web. For example, if a carnivore eats an infected animal, it might become less effective at hunting or reproducing. This could lead to a decline in that predator’s population, which in turn affects its prey species.
Maintaining a healthy balance is vital here. As the hosts and their predators interact, it creates a dynamic system that can adapt or crumble, depending on various factors, including Trichinella spiralis populations.
Managing Trichinella Spiralis Populations
With the benefits and drawbacks in mind, how can we manage Trichinella spiralis populations effectively? Here are some strategies:
- Education: Teaching people about safe food practices is crucial. Proper cooking techniques can help prevent trichinosis in people and livestock alike.
- Wildlife Management: Monitoring wildlife populations and their health can help control the spread of Trichinella. This might include managing hunting regulations or habitat conditions.
- Research: Understanding the biology of Trichinella and its interactions with hosts can inform better management practices. Science can be a useful ally.
These strategies show that while Trichinella spiralis can pose challenges, they’re not insurmountable. With the right approaches, we can harness the positive aspects while minimizing the negative impacts.
Trichinella spiralis is more than just a pesky parasite; it plays a complex role in ecosystems. While it contributes to nutrient cycling and controlling animal populations, its potential health risks and economic impacts cannot be ignored. The key is finding that middle ground. By understanding the ecological benefits and drawbacks, we can manage these populations more effectively.
In a world where everything is interconnected, it’s essential to see the bigger picture. Nature often balances itself out, but human actions can tip that balance one way or another. So next time you think about Trichinella spiralis, remember it’s a small player with a big impact—just like many of us in the grand scheme of things.
