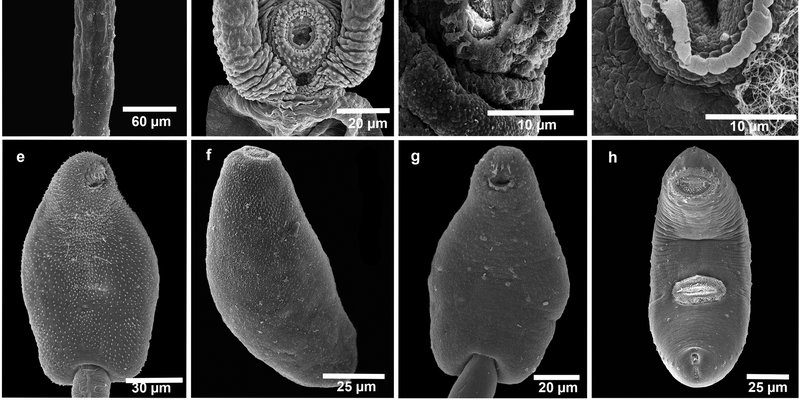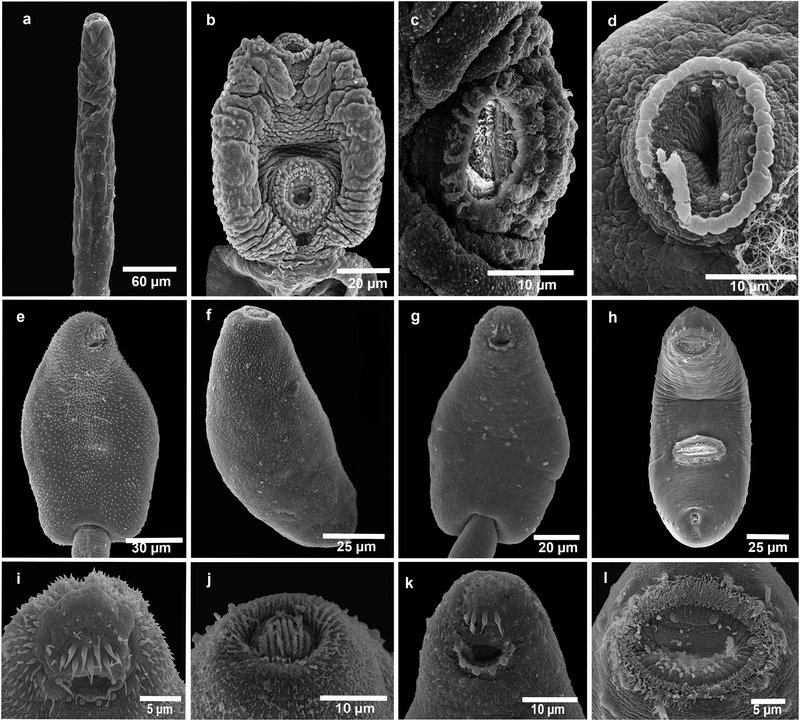
In this article, we’ll dive into how you can effectively use field cameras to observe trematodes. We’ll explore which types of cameras work best for this kind of research, how to set them up, and what you might discover. Think of it as your go-to guide for embarking on this little adventure in the world of parasitology. A popular choice among researchers is the Bushnell Trophy Cam, known for its reliability and image quality. So let’s get started!
Why Study Trematodes?
You might be asking, “Why should I care about trematodes?” These little guys play a significant role in ecosystems. Trematodes affect not just their host animals, like fish or mammals, but they also influence the environment around them. By studying their behavior and interactions, we can learn more about biodiversity and even the health of ecosystems.
Moreover, understanding how trematodes operate can shed light on larger issues, like disease spread. For example, certain trematodes can affect fish populations, which in turn can impact those who rely on fishing for their livelihood. So, when we document their behavior, we’re not just observing bugs; we’re connecting the dots in a much larger ecological puzzle.
Selecting the Right Field Camera
When it comes to capturing the behavior of trematodes, having the right equipment is crucial. You’ll want a field camera that can withstand the elements and provide clear images. Here are a few key features to consider:
- Resolution: Look for cameras with at least 12 megapixels for good-quality images.
- Night Vision: Since many trematodes are more active in low light, infrared night vision is important.
- Battery Life: Choose a camera with long battery life, ideally several months, so you don’t have to check it often.
- Waterproofing: Your camera should be able to withstand rain and moisture since you’ll likely be placing it outdoors.
The Bushnell Trophy Cam meets many of these criteria, making it a solid choice for researchers and nature enthusiasts alike. For added flexibility, consider whether the camera has Wi-Fi capabilities, allowing you to sync and download images directly to your device.
Setting Up Your Field Camera
Now that you’ve chosen your camera, it’s time to set it up in the field. When you’re documenting trematodes, placement is key. Here’s how to do it effectively:
1. Choose the Right Location: Look for areas where trematodes are likely to be found, such as near water sources or in areas with host animals.
2. Mounting: Use a sturdy strap to secure your camera to a tree or pole at a height that captures the ground level. This angle will give you the best chance of observing these creatures in action.
3. Test the Angle: Before leaving the camera for an extended period, do a quick test shot to make sure it’s capturing the desired area. Adjust as necessary.
4. Timing: Set the camera to take pictures or videos during peak activity times, often early morning or dusk, to maximize your chances of capturing trematodes.
Remember to check your camera regularly to ensure it’s functioning properly and to change the batteries if needed.
What To Expect When Documenting Trematodes
Documenting trematodes isn’t just about clicking away and hoping for the best—it’s more of a discovery process. Here’s what you might find:
– Feeding Behavior: Trematodes often feed on tissues or fluids from their hosts. You might observe how they latch on or move within their host.
– Life Cycle Stages: Many trematodes have complex life cycles involving multiple hosts. Your camera might catch glimpses of these stages, showing how they develop over time.
– Interactions with Hosts: Watch for behavior changes in host animals. For instance, trematodes can sometimes manipulate their hosts’ behavior, leading to scenarios that might surprise you.
Each of these observations can lead to deeper insights into the role of trematodes within their ecosystems, helping you contribute to ongoing research in this fascinating field.
Analyzing Your Findings
Once you’ve collected a healthy amount of footage or images, the next step is analyzing your findings. Here’s how to go about it:
1. Organize Your Data: Create folders on your computer for different locations or dates. This will make it easier to sift through your findings.
2. Identify Patterns: Look for recurring behaviors or interactions. Take notes on anything unusual or interesting you observe.
3. Document Your Observations: Create a simple report summarizing your findings, which can be useful for your personal record or for sharing with others interested in trematode research.
4. Share Your Insights: Engage with online communities or local research groups to discuss your findings. You might inspire others to join the field of trematode research!
Analyzing your findings can be just as rewarding as capturing them. You might even uncover new knowledge that adds to the existing literature on these intriguing organisms.
Common Challenges and Troubleshooting
While documenting trematodes can be thrilling, there are challenges you might face along the way. Let’s tackle some common problems:
– Camera Malfunctions: If your camera isn’t capturing images, check the battery, memory card, and settings. A simple reset can often fix these issues.
– Poor Image Quality: If your images are blurry or dim, ensure that the camera lens is clean and that it’s set to the appropriate resolution and night vision mode.
– Wild Animal Interference: Sometimes, larger animals or humans may trigger your camera and waste battery life or memory. Adjust the camera’s angle or sensitivity settings to minimize this.
Remember, troubleshooting is part of the process, and each issue is a learning opportunity.
Using field cameras to document the behavior of trematodes is an exciting and fulfilling endeavor. It requires patience and observation, much like waiting for the perfect photo of a sunset. But the rewards—understanding the complex lives of these tiny creatures—make it all worthwhile.
As you embark on this journey, remember that every observation contributes to the larger picture of biodiversity and ecological health. So grab your field camera, and enjoy capturing the secret lives of trematodes. You never know what fascinating discoveries await you!