So, what exactly is a bone-eating worm? Picture a tiny, brightly colored worm that can consume bone material—yes, bones! They latch onto dead marine creatures, burrowing into the remains and extracting nutrients. This unique ability allows them to live in some of the harshest conditions on Earth, turning what would otherwise be waste into a source of energy. Now, let’s dive deeper into their documented range and distribution across the globe.
What Are Bone-Eating Worms?
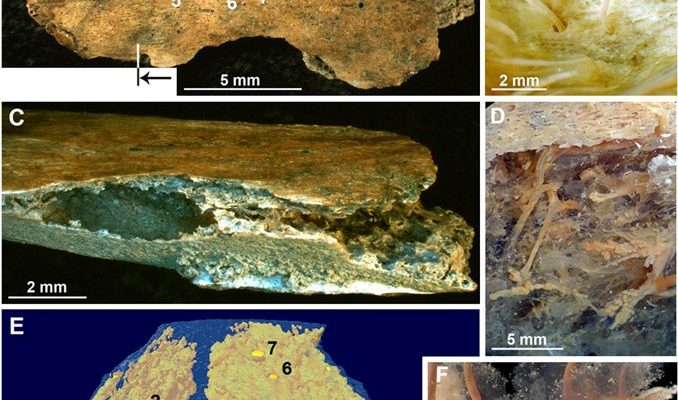
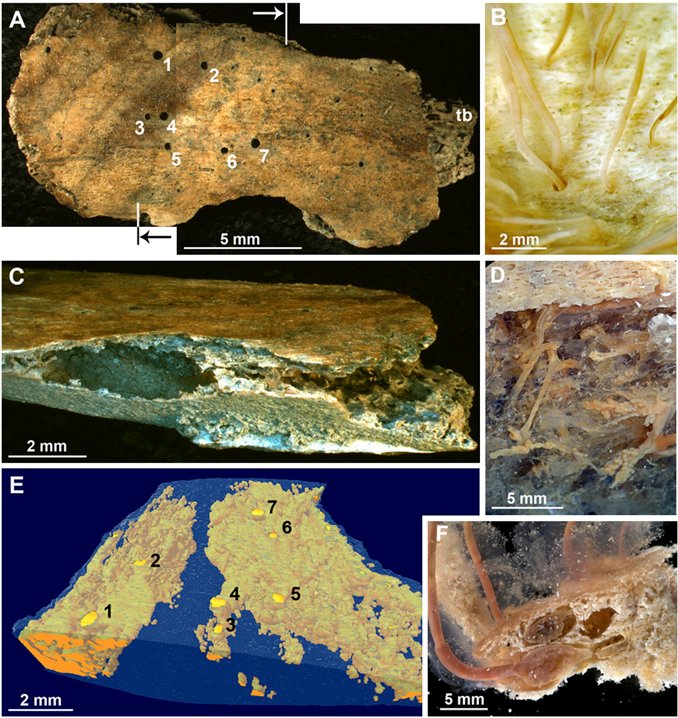
Bone-eating worms, belonging to the genus *Osedax*, are part of a family called Siboglinidae. They’re often found on the ocean floor, where they feast on the bones of large marine animals like whales. These worms have specialized roots that allow them to penetrate bone and absorb lipids and other nutrients. They don’t just munch on any old bone, either; they prefer those enriched with oils, which are packed with energy.
You might be wondering how they find these bones in the vast ocean. Well, *Osedax* worms are smart. They release chemical signals that attract other organisms, creating a mini-ecosystem around the remains. Once they latch onto a bone, they can sometimes produce enzymes that help break down the material further, making it easier to digest. It’s like nature’s very own recycling program!
What’s even more surprising is their color. These worms often boast vibrant hues of pink, yellow, or green, which is due to symbiotic bacteria living in their tissues. This partnership helps them process nutrients, making the worms even more efficient at bone digestion. Isn’t that cool?
Global Distribution of Bone-Eating Worms
Bone-eating worms can be found across the globe, but their habitat is mainly concentrated in deep-sea environments. They thrive at various depths, from shallow coastal waters to the abyssal plains of the ocean. This wide distribution is largely due to the availability of food sources, like whale falls, where large marine animals die and their bodies sink to the seabed.
Different species of *Osedax* occupy different regions. For instance, the *Osedax mucofloris* has been found off the coast of California, while *Osedax roseus* has been observed near Japan. Researchers have even discovered new species in unique locations, expanding our understanding of their range.
These worms often congregate in large numbers around bone deposits, creating vibrant communities. You might imagine a bustling city of worms feasting together, each playing a part in their shared environment. This is fascinating because it shows us how interconnected life is in the deep sea.
The Unique Ecosystems of Bone-Eating Worms
The ecosystems surrounding bone-eating worms are incredibly diverse. When a large animal like a whale dies and its body sinks to the ocean floor, it becomes a feast for many organisms. Bone-eating worms are just one part of this complex food web. As they consume the bones, they provide nutrients for other creatures, including scavenging fish, crustaceans, and various microorganisms.
In these ecosystems, *Osedax* worms create a microhabitat. The areas around whale falls can host dozens of other species that depend on the bones as a food source. Essentially, bone-eating worms act as a bridge between the dead animals and the living organisms that rely on those resources to thrive.
This relationship highlights the importance of bone-eating worms in our oceans. If they didn’t play their part in recycling nutrients, we could see significant changes in the biodiversity of these underwater ecosystems. It’s a reminder of how every creature, no matter how small, has a role to play in the health of our planet.
How Do Bone-Eating Worms Survive?
You might be thinking, “How do these worms manage to live in such extreme conditions?” Well, bone-eating worms have several adaptations that allow them to thrive in deep-sea environments. First off, their ability to digest bone is quite a feat. They possess specialized enzymes that break down the hard material, allowing them to extract nutrients that many other organisms can’t access.
Moreover, these worms have a unique mechanism for respiration. They don’t rely on oxygen in the same way that land animals do. Instead, they can use dissolved sulfide found in the water around hydrothermal vents. This adaptation enables them to flourish in areas where other life forms might struggle.
Their reproductive strategies are fascinating, too. Some species of *Osedax* are hermaphroditic, meaning they have both male and female reproductive organs. This increases their chances of finding a mate in the sparse environment of the ocean floor. When conditions are right, they can release eggs into the water, creating new generations of bone-eating worms.
Conservation and Importance of Bone-Eating Worms
With the ongoing changes in our oceans, it’s essential to understand the role bone-eating worms play in marine ecosystems. Although they may seem obscure, they are vital for nutrient recycling. Their ability to break down complex organic materials helps sustain other marine life and supports biodiversity.
Unfortunately, deep-sea habitats are threatened by human activities like deep-sea mining and climate change. Disturbances to these unique ecosystems can have cascading effects on the species that rely on them, including bone-eating worms. Protecting their habitats is crucial for maintaining the health of our oceans.
Additionally, studying these worms provides insights into evolution and adaptation under extreme conditions. Researchers can learn how life can flourish in environments previously thought inhospitable, which could inform our understanding of life on other planets, too.
Bone-eating worms may not be the most glamorous creatures in the ocean, but they play a significant role in the health of marine ecosystems. Their ability to thrive on bones, thrive in extreme conditions, and contribute to the recycling of nutrients showcases the incredible diversity of life beneath the waves. From their global distribution to their fascinating adaptations, these worms help us understand the complex relationships within our oceans.
As we learn more about these unique organisms, it’s essential to appreciate their contributions to biodiversity and the delicate balance of marine ecosystems. By protecting their habitats, we ensure a healthier ocean for future generations. So next time you think of worms, remember the amazing bone-eating worm and its vital role in the underwater world!

