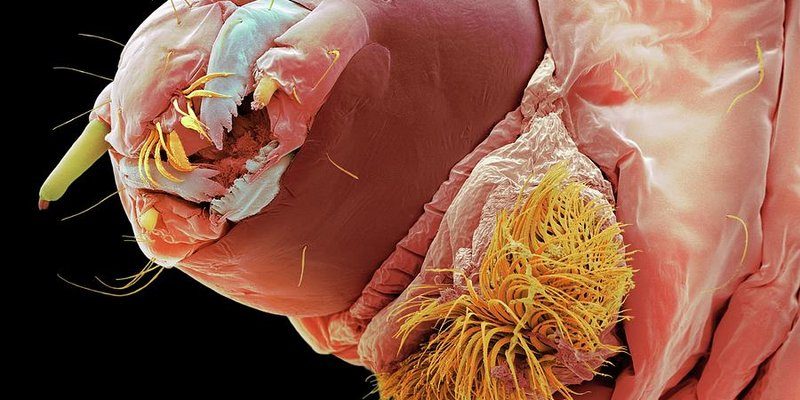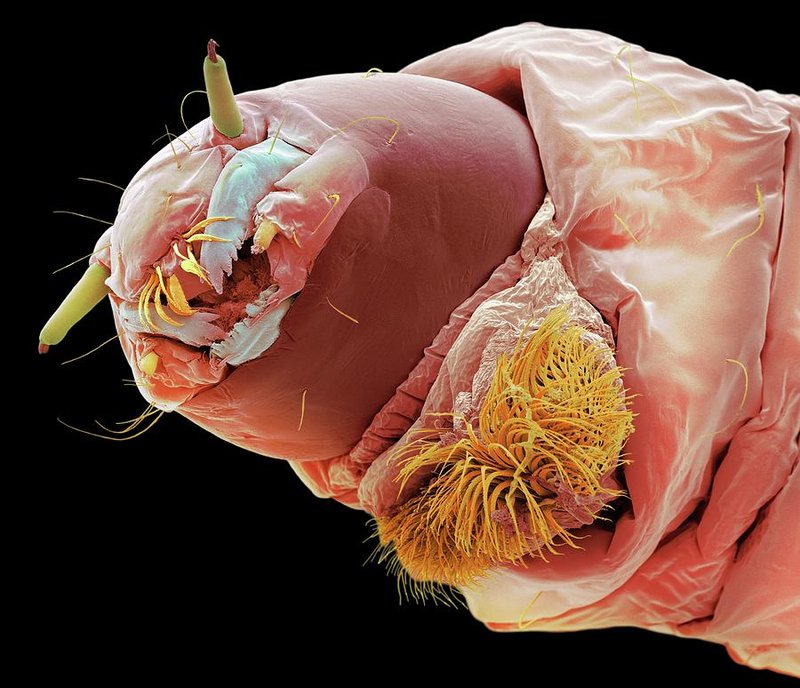
Bloodworms are the larval stage of midge flies, and they thrive in various habitats, ranging from muddy ponds to marshes. Just like how a chef selects ingredients based on what’s fresh and available, the habitat these little guys choose greatly influences their size, color, and abundance. So, whether you’re a fish enthusiast or just curious about these remarkable creatures, understanding their global distribution will give you a clearer picture of their importance in the aquatic food chain.
What Are Bloodworms?
Before we delve into their range and distribution, let’s clarify what exactly bloodworms are. These creatures often get their name from their reddish color, which comes from the high amount of hemoglobin in their bodies—yes, just like in our blood! Bloodworms can vary in size, but they generally grow to about 1-4 inches long. They’re often found in stagnant or slow-moving waters where they can burrow into the mud, making them a reliable food source for various fish species.
Here’s the thing: bloodworms aren’t just a snack for fish. They play a significant role in fish farming and even aquaponics, where fish and plants grow together symbiotically. They help recycle nutrients in the water, which benefits both fish and plants. So, understanding their range and distribution is crucial for anyone interested in aquaculture or simply maintaining a healthy aquarium.
Global Distribution of Bloodworms
Bloodworms can be found in many parts of the world, but their range is notably extensive across North America, Europe, and parts of Asia. They tend to inhabit areas with specific environmental conditions, which helps explain their widespread distribution. Typically, these areas are rich in organic materials, like decaying leaves, where bloodworms can thrive.
In North America, you’ll find them in freshwater lakes, ponds, and marshes, especially during the warmer months when the conditions are just right. In Europe, they’ve made their mark in wetlands and even in some coastal areas. As for Asia, places like China and India support diverse habitats where bloodworms can flourish, showing just how adaptable they are.
Factors Influencing Distribution
Several factors influence where bloodworms are found.
- Water Quality: Bloodworms thrive in clean or moderately polluted waters. Too much pollution can kill them off, so their presence often indicates a healthy ecosystem.
- Temperature: These creatures prefer warmer waters. In cooler climates, they’re more likely to hide out during winter months, returning as the temperatures rise.
- Oxygen Levels: Since they live in muddy substrates, low oxygen levels can also affect where they can be found. They need some oxygen to survive, but too much can be a problem.
Understanding these factors can help us appreciate why bloodworms are more abundant in some regions than others.
Habitat Preferences
Bloodworms are fascinating not just for their appearance but also for their specific habitat preferences. They tend to burrow in soft, muddy substrates, where they can find plenty of organic material to feast on. This habitat choice makes them easily accessible to many fish species that rely on them for nutrition.
In still or slow-moving waters, bloodworms can be found in various aquatic environments. You’ll often find them in:
- Ponds and Lakes: These calm waters provide a perfect setting for bloodworms to thrive and multiply.
- Marshes: The rich organic matter in marshy areas allows bloodworms to burrow and grow.
- Wetlands: Like marshes, wetlands are a hotspot for bloodworm populations due to their nutrient-rich environments.
Because they occupy multiple habitats, bloodworms can easily adapt to different conditions, which is a big advantage in the wild.
Bloodworm Species and Subspecies
While you might think of bloodworms as a singular entity, there’s actually a variety of species and subspecies that exist under this umbrella. The most common bloodworm is the Chironomus midge, but there are others, like Procladius and Tanytarsus, each with unique characteristics and distribution patterns.
These species can vary in size, coloration, and habitat preferences. For example, some might thrive in warmer waters while others prefer cooler environments. Knowing the species can help aquarists or fish farmers better understand which kind of bloodworms to use for their needs.
Honestly, the diversity is astounding! Each of these species plays a role in the ecosystem, contributing to the overall health of their environments.
The Importance of Bloodworms in Aquatic Ecosystems
You might be wondering why understanding the distribution of bloodworms matters. The simple answer is that they’re a crucial component of many aquatic food webs. Fish, birds, and even some amphibians rely on these larvae as a primary food source. Without bloodworms, these animals would struggle to find enough nutrition.
Additionally, bloodworms help maintain the quality of water ecosystems. By breaking down organic matter, they assist in nutrient recycling, which is essential for the growth of aquatic plants. This symbiotic relationship nurtures the balance in aquatic environments.
Benefits to Fish Farmers
For fish farmers, bloodworms are more than just a food source; they’re an asset. Using bloodworms in fish farming can improve growth rates and overall health in fish populations. They’re packed with nutrients, making them a top-choice feed. When fish are well-fed with high-quality bloodworms, they grow faster and are more resilient to disease.
This practicality makes bloodworms an ideal option for aquaculturists aiming to maximize production while ensuring healthy ecosystems. Incorporating them into feeding regimens can also lead to less waste and more sustainable practices overall.
In summary, bloodworms are more than just creepy little creatures lurking in muddy waters; they’re vital components of freshwater ecosystems worldwide. Their documented range and distribution span various habitats across continents, highlighting their adaptability and importance. Whether you’re a fish enthusiast, a farmer, or simply someone interested in the wonders of nature, knowing more about bloodworms can enrich your understanding of aquatic life.
By appreciating their role in the ecosystem, we can better protect these fascinating creatures and ensure that the aquatic environments they inhabit remain healthy and vibrant. So next time you’re near a pond or a lake, remember the crucial role that bloodworms play just beneath the surface.