You might be surprised to learn that bootlace worms are not just long; they’re also quite unique in their feeding habits. Living in the cold waters of Europe, these worms have developed some interesting strategies to meet their energy needs. Understanding their feeding frequency is essential, especially if you’re a marine enthusiast or just curious about the wonders of underwater life. Let’s unravel the mystery of bootlace worm feeding habits!
What Are Bootlace Worms?
Bootlace worms belong to the genus *Lineus* and are part of the ribbon worm family. These elongated, often brightly colored creatures capture attention with their striking appearance. You can find them lurking in shallow coastal waters, often hiding beneath rocks or seaweed.
One of the most fascinating things about bootlace worms is their **body structure**. They’re made of a soft, flexible material that allows them to stretch and contract, which is handy for both movement and feeding. Plus, they have a remarkable ability to regenerate lost body parts, which makes them even more interesting. This regeneration capability is just one reason bootlace worms are studied by scientists.
To put it simply, bootlace worms are like the superheroes of the marine world: long, resilient, and full of surprises. So, how do they fuel their unique lives?
The Bootlace Worm’s Diet
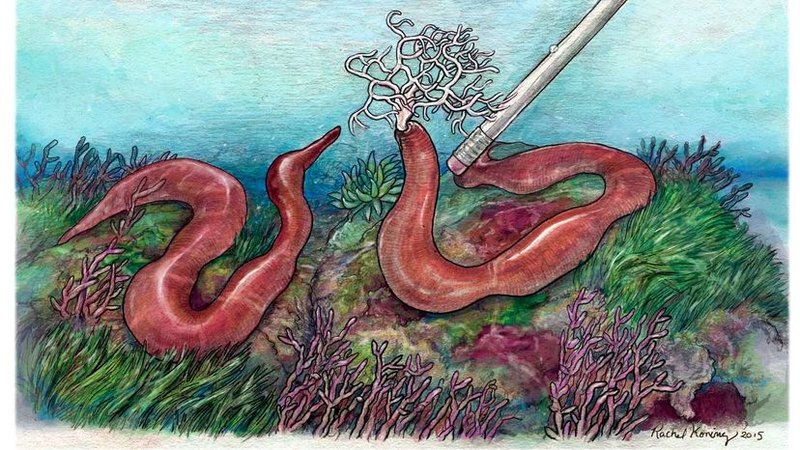
Bootlace worms are carnivorous, preying on smaller marine animals. Their diet mainly consists of crustaceans and other tiny creatures found in their habitats. But here’s the kicker—bootlace worms have a unique feeding method. They use a long, sticky proboscis, which is like a fancy tongue, to catch their prey. Imagine using a super long spaghetti noodle to snag a meatball; that’s kind of how they do it.
When a bootlace worm senses prey nearby, it extends its proboscis to snag the unsuspecting animal. This is where the worm’s energy needs come into play. They don’t need to eat all the time; they may go for days without a meal, relying on their stored energy from previous feedings. This adaptability allows them to thrive in environments where food might not always be abundant.
Now, you might wonder: how often do they actually need to eat?
Feeding Frequency of Bootlace Worms
The **feeding frequency** of bootlace worms isn’t set in stone; it varies based on several factors. Generally, they might consume food every few days. In optimal conditions with plenty of prey, they may feast more frequently, perhaps every 2–3 days. However, if food is scarce, they can slow down their metabolism and stretch out their meals.
This ability to adjust their feeding habits is crucial for survival. It’s similar to how we might skip a meal when we’re busy or when the fridge is bare. Bootlace worms can survive on less food when necessary, which helps them manage their energy reserves efficiently.
Overall, understanding their feeding frequency gives insight into how bootlace worms have adapted to their environments. When food is plentiful, they can afford to eat more often, but when it’s limited, they thrive by using their stored energy wisely.
Energy Needs and Metabolism
Bootlace worms have relatively **low energy needs** compared to many other marine creatures, primarily because of their unique feeding strategy. When they eat, they consume a significant amount, helping them maintain their long, squiggly bodies. Their metabolism can slow down, which is why they can go for days without food.
– **Stored energy** is key.
– They have specialized cells that help store nutrients effectively.
This energy management technique is like a squirrel storing nuts for the winter—bootlace worms prepare for lean times by building up reserves.
The temperature of their environment also plays a significant role in their metabolism. Cooler waters can slow their metabolic rate, meaning they need less energy. In warm waters, their metabolism speeds up, leading to a higher food intake to match their increased energy demand.
Comparison with Other Marine Life
When thinking about how bootlace worms fit into the larger picture of marine life, it’s interesting to compare them to other creatures. For example, many fish eat daily, needing constant nourishment to keep their energy levels up. In contrast, bootlace worms enjoy a more “easy-going” approach, allowing them to go longer between meals.
– **Fish vs. Bootlace Worms**:
– Fish typically need to eat several times a day.
– Bootlace worms can stretch their meals over days, adapting based on food availability.
This difference in feeding habits highlights the bootlace worm’s unique approach to survival. It showcases how various marine creatures have adapted to their environments in different ways.
Factors Affecting Bootlace Worm Feeding
Several factors influence how often bootlace worms eat and their overall energy needs.
1. **Prey Availability**: If there’s plenty of food around, they’ll eat more frequently. Think of it like having a buffet versus a sparse snack selection.
2. **Water Temperature**: As mentioned earlier, cooler waters slow their metabolism and, consequently, their need for food.
3. **Seasonal Changes**: During certain times of the year, like spawning seasons, their feeding habits may change due to shifts in prey availability.
Understanding these factors helps explain why bootlace worms are so resilient. They can adjust their feeding frequency and energy consumption based on what’s happening in their environment, ensuring they survive and thrive.
In summary, bootlace worms are fascinating creatures that adapt their feeding frequency and energy needs to suit their environment. They manage to survive on a diet of smaller marine animals, using their unique feeding method to capture prey efficiently. Their ability to go days without food showcases their resilience and adaptability.
When we compare them to other marine life, it’s clear that each species has found its niche in the ocean, using different strategies to thrive. Bootlace worms may not be the most glamorous of marine creatures, but they sure have a lot to teach us about survival and adaptation. So, the next time you think of the ocean, remember these incredible worms that remind us how diverse and resourceful life can be!