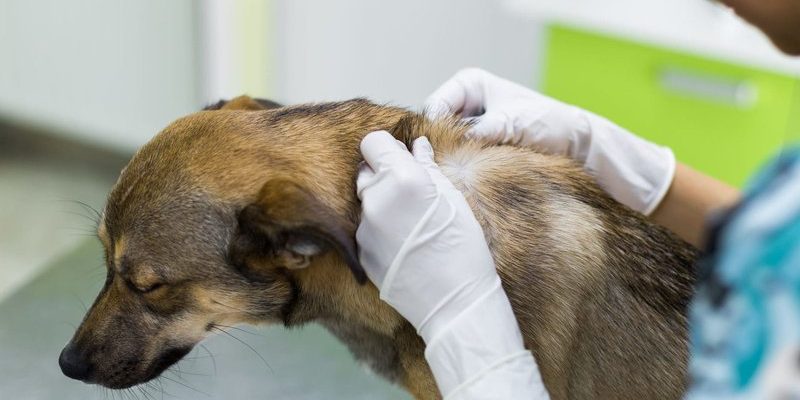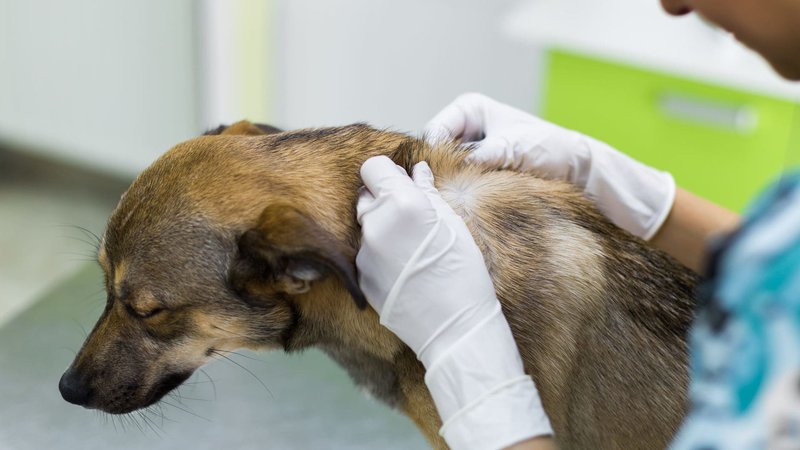
Wolf worms, specifically the larvae of the *Dermatobia hominis* fly, can inflict quite the toll on their hosts, which often include animals like wolves, coyotes, and even domestic pets. As these larvae make themselves comfortable, the hosts may start to behave differently—kind of like that feeling you get when you’ve caught a nasty cold. You might wonder how to spot these changes and why they happen. Let’s dive into the world of animal behavior and find out what we can learn about these fascinating creatures.
What Are Wolf Worms?
Before we dig into the behavior changes, it’s essential to understand what wolf worms really are. These parasites develop inside the skin of their hosts, feeding off their blood and tissue until they’re ready to emerge. Wolf worms can be likened to uninvited guests that won’t leave, hanging around until they’re fully grown.
Wolf worms are particularly notorious because they manipulate their hosts’ behavior. Think of it like a director taking control of a movie—these worms change how the animal acts to ensure their survival. They create discomfort, urging the animal to seek out environments that benefit the worms’ development.
You might find it surprising, but wolf worms can affect a variety of hosts, not just wolves. They can infest anything from wild canines to domesticated pets. This adaptability is part of why they can be such a concern in both wild and urban settings.
How Do Animals Respond to Infestation?
Once an animal becomes infested with wolf worms, you’ll notice changes in behavior that can be pretty alarming. For starters, the affected animals often display signs of distress. They may start scratching or grooming excessively in an attempt to rid themselves of the irritation caused by the larvae. Imagine an itch you can’t scratch—frustrating right?
As the infestation progresses, the animal might become lethargic or withdraw from its usual activities. Predators like wolves usually rely on agility and coordination to hunt, but an infested wolf might avoid hunting altogether. This can significantly affect its survival and that of its pack.
Changes in social behavior are also common. Some animals might become more aggressive due to discomfort, while others may go into hiding, becoming less social. Essentially, these behavior shifts are survival strategies. When an animal feels unwell, it’s only natural to try and protect itself by retreating from potential threats or interactions.
Physical Symptoms of Infestation
Recognizing the physical signs of wolf worm infestation can provide insight into behavioral changes. Typically, you’ll notice swelling or raised bumps on the skin where the larvae are located. These bumps might be itchy and inflamed, leading the animal to scratch or bite at the site.
Additionally, the presence of a small hole or opening in the skin can indicate that the larvae are emerging. This can create an even more uncomfortable experience, causing the animal to act out more aggressively or become increasingly wary of others.
Pay attention to changes in grooming habits, too. While animals are usually meticulous about their appearance, infested animals may over-groom or neglect their coats entirely. This can lead to further health complications, potentially leading to infections as they try to manage the discomfort.
Impact on Daily Activities
When an animal is dealing with a wolf worm infestation, its daily activities can drastically change. Think about how you feel when you’ve got a headache—sometimes, just getting out of bed seems daunting. Similarly, infested animals may struggle to carry out their usual routines, whether that’s hunting, foraging, or simply interacting with other animals.
Hunting, for instance, requires energy and focus, and an infested wolf might not have either. This can lead to changes in pack dynamics, with others stepping in to hunt while the infested animal takes a backseat. This shift can affect social hierarchy and the overall well-being of the group.
Moreover, animals may alter their territory. An infested animal might instinctively seek out safer, quieter areas where they can minimize stress. This change isn’t just a temporary fix; it can alter their habitat use significantly. Just like humans might choose a cozy couch over a party when feeling unwell, animals do the same.
The Role of Stress in Behavior Changes
Stress plays a significant role in how animals respond to wolf worm infestations. When an animal is under stress from both physical discomfort and environmental changes, its body reacts in various ways. Behavioral responses can include aggression, withdrawal, and even changes in vocalizations, like howling or whining.
Stress hormones like cortisol spike in response to such infestations. This hormonal reaction can cloud judgment and alter instincts. A normally confident wolf might become skittish, making choices that aren’t typical of its usual behavior. This can also affect feeding strategies and social interactions within its pack.
It’s essential to understand that stress doesn’t just affect the individual animal; it can ripple through the entire ecosystem. When predators like wolves change their behavior, it can impact the prey population and the overall balance of the ecosystem.
Prevention and Management of Infestation
Preventing wolf worm infestations is always better than dealing with the aftermath. Keep your pets healthy and regularly check for any signs of parasites. Keeping up with vaccinations and health check-ups can be a great way to reduce risks.
If you do suspect an infestation, acting quickly is crucial. Consulting a veterinarian can ensure proper treatment to remove the larvae. This is similar to going to the doctor when you’re feeling unwell—early intervention can minimize discomfort.
Here’s a quick rundown of steps you can take:
- Regularly check your pets for signs of skin issues.
- Maintain a clean living environment to reduce the risk of attracting parasites.
- Consult professionals for preventative treatments.
Being proactive can save your pet from a lot of discomfort and help maintain a healthy environment for all animals involved.
Understanding how animals react during a wolf worm infestation opens the floor to discussions about health, ecosystems, and the delicate balance of nature. It’s amazing how something so small can have such a big impact on behavior, right? Just like humans, animals respond to discomfort in ways that are instinctive and aimed at survival.
Whether you’re a wildlife enthusiast or a concerned pet owner, being aware of these changes can empower you to take action—whether that means keeping a close eye on your pets or better understanding the animals around you in nature. The world of wildlife is complex, and awareness is a crucial step in protecting these fascinating creatures. Remember, staying informed helps not just the animals, but the ecosystems they inhabit.