These incredible animals roam the forests of Central Africa, but their habitat isn’t just any old forest. It’s a delicate ecosystem that provides everything they need to thrive. Understanding their habitat and distribution is essential, not only for the well-being of the gorillas themselves but also for the health of our planet. So, let’s dive into where these magnificent creatures live and what makes their habitat so special.
Understanding the Range of Western Gorillas
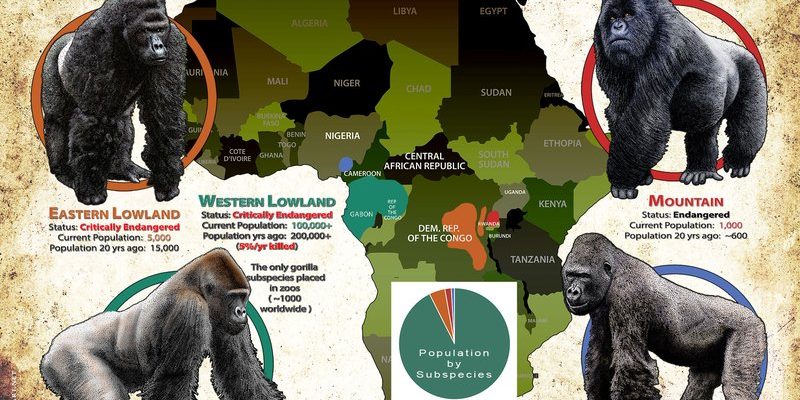
Western gorillas are found primarily in two different regions: Western lowland gorillas and Cross River gorillas. The western lowland gorilla has the largest population and resides in lowland forests, swamps, and even some rural areas. On the flip side, the Cross River gorilla lives in a more isolated and mountainous environment along the Nigeria-Cameroon border, making it one of the rarest primates in the world.
Here’s the thing: the distinction between these sub-species isn’t just academic. The differences in their habitats affect their behavior, diet, and even their interactions with humans. While the western lowland gorilla is more adaptable to various forest types, the Cross River gorilla is significantly more endangered, with fewer than 300 individuals remaining in its natural habitat—yikes!
Western Lowland Gorillas
The western lowland gorilla’s territory spans several countries including the Republic of Congo, Gabon, and Cameroon. They thrive in dense tropical rainforests, which provide them with ample food and shelter. These forests are rich in fruiting trees, vines, and leafy plants, which are staples in their diet. Imagine wandering through a park filled with delicious snacks at your fingertips—that’s what their habitat is like!
Furthermore, these gorillas are known to be social animals, often seen in family groups. This social structure not only helps them in finding food but also in protecting one another. Their ability to adapt to various types of environments, including disturbed forests, has helped them maintain a relatively stable population, despite facing threats from hunting and habitat destruction.
Cross River Gorillas
In contrast, the Cross River gorilla’s habitat is more fragmented and challenging to navigate. They inhabit hilly, rugged terrains and dense forests that are often surrounded by agricultural land. This means that they have become isolated from larger populations, leading to an even greater risk of extinction.
The living conditions are tough. The dense underbrush makes it harder for them to find enough food, and their limited range leads to competition with local farmers, who often clear land for crops. This conflict can be detrimental not just to the gorillas but also to local communities trying to coexist with wildlife. It’s a complex relationship that shows just how delicate these ecosystems can be.
The Importance of Forest Ecosystems
You might be wondering why the forests where western gorillas live are so significant. Well, these forests play a crucial role in the overall health of our planet. They act as carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide and helping to mitigate climate change. Additionally, they support a wide array of wildlife, not just gorillas. Birds, reptiles, insects, and countless other animals rely on these habitats for survival.
Furthermore, these forests have deep-rooted relationships within their ecosystems. The plants that grow in the forests provide food not only for gorillas but also for other animals that, in turn, help with pollination and seed dispersal. This interconnectedness means that protecting gorilla habitats is essential for preserving biodiversity.
Threats to Their Habitat
Sadly, despite how important these habitats are, they face numerous threats. Deforestation, driven mainly by logging, agriculture, and infrastructure development, is a significant issue. When trees are cut down, gorillas lose their homes, food sources, and safety.
Another critical threat is poaching. Illegal hunting for bushmeat continues to pose a significant risk to western gorillas. Not only is this practice harmful directly, but it also disrupts the social structures within gorilla groups. Imagine if your neighborhood was suddenly turned upside down by hunters—how would that feel for you and your community?
In addition to these, disease is a real concern. Gorillas share about 98% of their DNA with humans, making them susceptible to many human diseases. Outbreaks like Ebola can devastate gorilla populations.
Conservation Efforts
Luckily, many organizations are working hard to protect western gorillas and their habitats. Conservation efforts focus on habitat preservation, anti-poaching initiatives, and community education. By engaging local communities and providing alternative livelihoods, these efforts help reduce pressure on the forests.
For instance, eco-tourism can be a powerful tool. By encouraging people to visit these regions responsibly, communities can earn a living while protecting the gorillas. It’s a win-win—people get to experience the beauty of these animals up close, and the gorillas have a better chance of survival.
How You Can Help
You might think, “I’m just one person—what can I do?” Here’s the thing: every little bit counts! Supporting conservation organizations is one way to make a difference. Donations, awareness-raising campaigns, and even volunteering can help protect these incredible creatures.
Also, consider making environmentally sustainable choices in your daily life. Using less paper, reducing your waste, and supporting sustainable products can all contribute to preserving gorilla habitats. Remember, a healthy planet is a shared responsibility, and we all play a part.
So, where do western gorillas live? They inhabit the lush, vibrant forests of Central Africa, with each sub-species facing its unique challenges. From the adaptable western lowland gorillas to the critically endangered Cross River gorillas, these magnificent creatures remind us of the interconnectedness of life on Earth.
Protecting their habitats is not just about saving gorillas; it’s about safeguarding our planet’s health and biodiversity. By understanding their needs and supporting conservation efforts, we can ensure that future generations get to experience the beauty of western gorillas in their natural habitat. Let’s work together to make a positive impact!