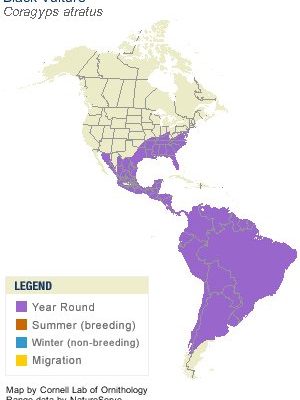
Understanding Vulture Habitats
Vultures typically thrive in open environments where they can soar gracefully on thermals, or columns of warm air. These birds are keen-eyed scavengers, often seen gliding over fields, grasslands, forests, and even urban areas. But their habitat choice isn’t just random—it’s closely related to their food sources.
Depending on the species, vultures may prefer specific environments. For example, the **Turkey Vulture**, one of the most common types, is often found in forests, fields, and even along roadsides. They have a wide range and can adapt to various landscapes across North America, from coastal regions to mountainous areas.
In contrast, the **African White-backed Vulture** enjoys the expansive savannas and grasslands of sub-Saharan Africa. These areas provide the open space needed to spot carcasses from above. You might be wondering, how do these birds know where to find food? Well, they have an incredible sense of smell and excellent eyesight, which helps them locate meals from high in the sky.
Geographical Distribution of Vultures
Vultures are distributed across multiple continents, each species preferring different climates and terrains. In North America, you’ll find the Turkey Vulture and the California Condor, which has a very limited range. Meanwhile, in Europe, the **Griffon Vulture** can be spotted soaring over mountainous terrains like the Alps and the Pyrenees.
In Asia, the **Himalayan Vulture** resides in high-altitude regions, while in South America, the **Greater Yellow-headed Vulture** prefers coastal areas. With such varied habitats, vultures have adapted over time to thrive in different ecosystems, relying on a wide array of food sources, from livestock to wild animals.
To give you a clearer picture, here’s a quick overview of some notable vulture species and their habitats:
| Vulture Species | Habitat | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Turkey Vulture | Forests, grasslands, urban areas | North America |
| Griffon Vulture | Mountains, cliffs | Europe |
| Himalayan Vulture | High-altitude regions | Asia |
| Greater Yellow-headed Vulture | Coastal areas | South America |
The Role of Habitat in Vulture Conservation
Vultures play a vital role in their ecosystems, acting as nature’s recyclers by consuming carcasses that could spread disease. However, as you might guess, their habitats are under threat. Urban development, agriculture, and climate change are leading to habitat loss, endangering these essential birds.
In some regions, such as India and parts of Africa, the decline in vulture populations due to habitat destruction and poisoning poses a serious environmental issue. Without vultures, ecosystems struggle to maintain balance, leading to increased instances of disease from rotting carcasses.
That’s why understanding where vultures live is crucial for conservation efforts. Protecting their natural habitats means ensuring that they continue to thrive. Organizations worldwide are working hard to restore habitats and educate communities about the importance of vultures, often highlighting their unique role in maintaining ecosystem health.
Common Habitats Vultures Occupy
Let’s look at some common habitats vultures occupy in more detail:
- Grasslands: These open areas provide ample food sources. Vultures can spot carcasses from great heights. Think of it as their buffet!
- Forests: While less common, some vultures adapt to wooded areas. They often nest in trees, taking advantage of the cover to raise their young.
- Deserts: Surprisingly, some species thrive in arid regions where food may be scarce, relying on their excellent foraging skills to find meals.
- Urban Areas: Increased urbanization has led vultures to adapt and find food in cities, scavenging safely in parks and open areas.
Each habitat comes with its own challenges and opportunities. For instance, while grasslands offer plenty of open space, they also face threats from farming and land development.
How Vultures Adapt to Their Environments
Vultures are truly remarkable when it comes to adaptation. They have a keen ability to adjust to different climates and food availability, which is essential for their survival. Think of them as nature’s optimizers, finding ways to thrive no matter the conditions.
For example, their strong wings provide excellent soaring capabilities, allowing them to travel long distances with minimal energy. This ability is crucial when searching for food across vast landscapes. Additionally, vultures have developed a unique digestive system that can handle bacteria and pathogens found in decaying meat, which protects them from diseases that could harm other scavengers.
Their keen eyesight helps them spot potential meals from miles away. Interestingly, some species have a limited sense of smell, which means they often rely on sight rather than scent to find carcasses. You might be thinking, how do they know when to eat? Vultures are also social birds, often following each other to find food. When one vulture spots something tasty, others quickly join in for the feast.
The Future of Vulture Habitats
Looking ahead, the future of vulture habitats depends on our willingness to protect them. As we face climate change and increasing human encroachment, conserving these crucial ecosystems is more important than ever.
Efforts are underway to set aside protected areas, ensuring vultures have safe places to nest and feed. Community education programs also aim to reduce misconceptions about these birds and demonstrate their role in maintaining healthy environments. By fostering a better understanding of vultures, we can encourage people to coexist peacefully with these vital scavengers.
In conclusion, vultures are more than just scavengers; they’re essential players in our ecosystems, and their habitats matter. Understanding where they live and how they adapt is the first step toward their conservation. So, the next time you see a vulture soaring in the sky, remember the important role it plays in our natural world. Together, we can help protect their homes for future generations.