Imagine living in a place where temperatures can drop to minus thirty degrees Fahrenheit, and sunlight might be scarce for months at a time. That’s the world of polar bears. They’ve adapted to life in freezing conditions, but their homes are changing due to climate shifts. So, let’s take a closer look at where polar bears live and why their habitat matters.
Understanding Polar Bear Habitats
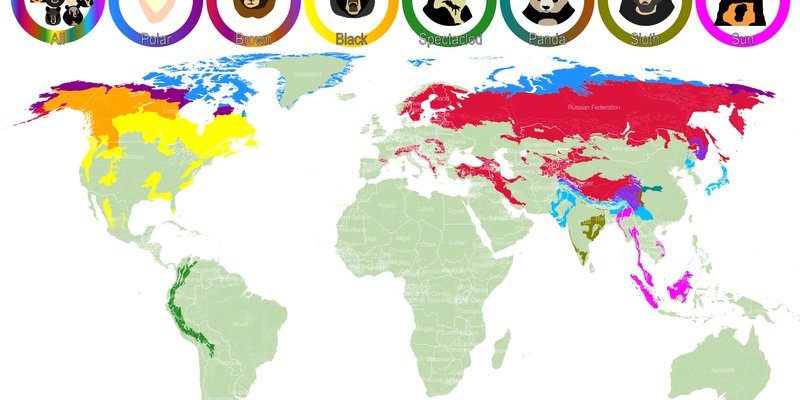
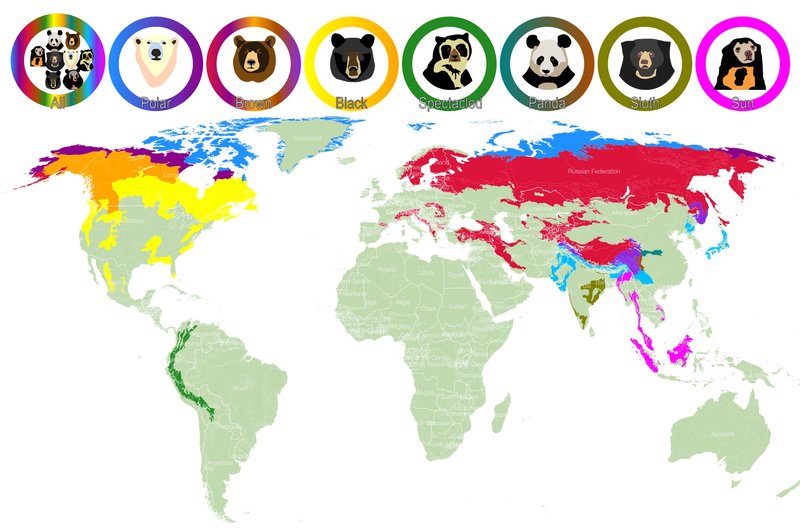
Polar bears primarily inhabit the Arctic region. Their territory stretches across several countries, including Canada, the United States (specifically Alaska), Russia, Greenland, and Norway. These bears are typically found on sea ice, which forms over the ocean and provides them with access to their main food source: seals. Picture a giant ice puzzle, with various pieces forming platforms where polar bears can hunt and rest.
The sea ice is crucial for hunting seals, their favorite meal. As seals come to breathe through holes in the ice, polar bears lie in wait, ready to pounce. But it’s not just their food source that makes this habitat essential; it’s also their breeding ground. Female polar bears often dig dens in the snow to give birth to their cubs, providing them a safe space to grow until spring arrives.
Climate Zones and Distribution
Polar bears thrive in two main climate zones: the Arctic Ocean and the surrounding coastlines. These regions experience extreme conditions, with long, cold winters and short summers. While sea ice is foundational to their survival, polar bears can also be found on land during the summer months when the ice melts. This typically occurs in places like Hudson Bay in Canada, where bears might wander onto land for food if ice is scarce.
Interestingly, polar bear populations are not evenly distributed across their habitat. They tend to gather in areas with the highest seal populations. Think of it like a group of friends choosing a restaurant based on where the best food is. This means that certain regions, like the Beaufort Sea and Chukchi Sea, are hotspots for polar bears due to abundant seals. Understanding where to find these ice giants is key to their conservation.
The Impact of Climate Change on Polar Bear Habitats
You might be wondering how climate change affects polar bears. Well, it’s a big deal. As global temperatures rise, sea ice is melting at an alarming rate. This not only reduces the hunting grounds for polar bears but also alters their migratory patterns. Imagine having your favorite ice rink gradually disappearing—frustrating, right?
With less ice, polar bears have to travel farther to find food. This can lead to malnutrition or starvation, especially for pregnant females who need extra energy. Unfortunately, as their habitat shrinks, polar bears increasingly come into contact with humans, leading to conflicts and challenges for both species.
Polar Bear Habitats Around the World
Let’s break down the primary regions where polar bears thrive. Each area has its unique characteristics:
- Canada: Home to approximately two-thirds of the world’s polar bear population, especially in Nunavut and the Northwest Territories.
- Alaska: Various populations of polar bears roam the northern coast, particularly around the Beaufort Sea.
- Russia: The Chukchi Sea north of Siberia is another critical area for these bears.
- Greenland: The eastern and western coasts provide excellent hunting grounds.
- Norway: The Svalbard archipelago is a frequently visited spot for polar bears.
Each of these regions offers distinct environments that help define the polar bears’ lifestyles. By studying where they live, we gain valuable insights into their needs and how to help preserve their habitats.
Why Polar Bear Habitats Matter
Understanding where polar bears live is more than just knowing about a cute, cuddly creature. It’s about recognizing the intricate web of life that relies on the Arctic ecosystem. Polar bears are often seen as indicator species, meaning their health reflects the condition of their environment. When polar bears struggle, it’s a signal that changes in climate or disturbances in their habitat are occurring.
Preserving their habitat is essential for maintaining the delicate balance of the Arctic ecosystem. If polar bears face extinction, it could lead to unforeseen consequences for other species and even the global climate. Protecting these magnificent creatures can help ensure the survival of countless other animals and plants that share their environment.
Conservation Efforts
So, what efforts are being made to protect polar bears and their habitats? Various organizations and governments are working tirelessly to create strategies for polar bear conservation. Some key approaches include:
- Habitat Protection: Establishing protected areas to preserve critical habitats.
- Fuel Reduction: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions to combat climate change and its impact on polar ice.
- Research: Conducting studies to monitor polar bear populations and health through tracking and observing behaviors.
Every small action contributes to a larger mission. Whether it’s supporting conservation organizations or advocating for policies that address climate change, we all play a part in keeping polar bears and their habitats safe.
In conclusion, polar bears are incredible creatures that depend on a delicate Arctic habitat for survival. Their living spaces are not just icy expanses; they are crucial ecosystems that reflect the health of our planet. As we’ve explored, these majestic animals face significant challenges due to climate change and habitat loss.
By understanding where polar bears live and why their habitats are under threat, we can all work towards solutions that protect these stunning animals and the natural world they inhabit. Remember, every effort counts in ensuring that future generations can enjoy the sight of these magnificent beings roaming the Arctic.