Imagine a cozy underground home filled with soft, cool earth—this is the secret world where aardvarks thrive. Known scientifically as *Orycteropus afer*, these nocturnal mammals roam the plains and savannas of Africa, primarily searching for their favorite meal: ants and termites. While they may be elusive to spot, understanding their habitat can help us appreciate the role they play in the ecosystem.
So, grab your coffee, and let’s explore the fascinating habitat and distribution of aardvarks!
Aardvark Habitats: A Closer Look
Aardvarks are primarily found in a range of habitats across sub-Saharan Africa. From arid deserts to lush woodlands, they are surprisingly adaptable. They prefer areas where they can easily dig into the ground to create burrows. This digging ability not only provides them with a place to sleep but also helps aerate the soil and create tunnels for other creatures.
– Savannas: The vast grasslands of the savanna offer a buffet of ants and termites, which is why aardvarks thrive in these regions. The open space allows them to forage easily at night, avoiding predators while searching for food.
– Woodlands: Aardvarks can also be found in wooded areas where they have access to both insects and the shelter of trees. These environments provide them with a little more cover during their nighttime excursions.
– Deserts: Believe it or not, some aardvarks have adapted to life in arid desert conditions. They dig deep burrows to escape the heat during the day and come out at night to hunt for food.
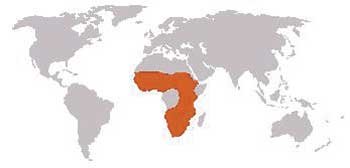
Distribution Across Africa
Aardvarks inhabit various regions across Africa, which impacts their lifestyle and behavior. They are predominantly found in southern and eastern regions, but the exact distribution can vary. Here’s a breakdown:
– Southern Africa: Countries like South Africa, Namibia, and Botswana host many aardvarks. The diverse habitats here, including grasslands and bushveld, provide ample foraging opportunities.
– Eastern Africa: In countries like Kenya, Tanzania, and Zambia, aardvarks thrive in various ecosystems. The availability of termites in both park reserves and rural areas ensures they have a sufficient food source.
– Central and West Africa: Although less common, aardvarks can still be spotted in areas like Cameroon and the Central African Republic. However, they tend to be more isolated due to habitat destruction and hunting.
You might be wondering how they manage to survive in such different climates. Their ability to adapt to various environments is mainly due to their nocturnal lifestyle, which allows them to avoid daytime heat and find cooler places to dig.
Aardvark Burrows: Home Sweet Home
One of the most fascinating aspects of an aardvark’s lifestyle is its burrowing behavior. Aardvarks dig intricate tunnels that can be quite extensive. Typically, these burrows can reach up to 3 meters deep and 10 meters long!
Here’s why their burrows are so essential:
– Protection: The underground homes protect aardvarks from predators and extreme weather conditions.
– Temperature Control: Burrows maintain a stable temperature, which is crucial for the aardvark’s well-being, especially in hotter climates.
– Living Space for Others: When aardvarks abandon their burrows, other animals like rodents, snakes, and insects often move in, benefiting the ecosystem.
They use strong, shovel-like claws to dig, which makes their burrowing quite efficient. You can think of them as nature’s builders, shaping the underground environment for the broader community.
Impact of Habitat Loss on Aardvarks
Sadly, the fascinating life of aardvarks is under threat due to habitat loss. Urbanization, agriculture, and deforestation are taking away their homes and food sources. Here’s how this affects them:
– Food Scarcity: As their habitats shrink, so do their food sources. With fewer ants and termites, aardvarks struggle to find enough to eat.
– Reduced Burrowing Areas: Less land means fewer places to dig, leaving them vulnerable to predators and harsh weather.
– Isolation: Fragmented habitats can lead to isolated populations. This isolation can reduce genetic diversity, making it harder for the species to adapt to changes.
Conservation efforts are essential to protect these unique animals. Understanding where aardvarks live helps us appreciate their role in the ecosystem and the need to safeguard their habitats.
How Do Aardvarks Fit into Their Ecosystem?
Aardvarks are more than just cute and quirky creatures; they play a significant role in their ecosystems. Here’s how:
– Soil Aeration: Their burrowing habits help break up the earth, allowing air and water to penetrate deeper into the soil. This process benefits various plant species and promotes healthy growth.
– Pest Control: By consuming large quantities of ants and termites, aardvarks help control these insect populations. If left unchecked, these pests can cause significant damage to crops and vegetation.
– Food Source: Aardvarks also serve as a food source for larger predators like lions, leopards, and hyenas, contributing to the food chain.
You might not have thought about how interconnected each species is, but aardvarks highlight the delicate balance of nature. Their presence, or absence, can significantly impact their local environment.
Why Should We Care About Aardvarks?
You might be wondering why we should care about a seemingly obscure animal like the aardvark. Well, here’s the thing: every creature plays a role in the grand tapestry of our planet. By protecting aardvarks, we’re also taking steps to preserve their habitats and the ecosystems they support.
Conservation efforts can boost biodiversity and help maintain ecological balance. Each species, no matter how small or odd, has its part to play. By fostering a healthy environment for aardvarks, we can ensure a healthier planet for ourselves and future generations.
In conclusion, understanding where aardvarks live and the challenges they face helps us appreciate these unusual mammals. Their unique adaptations, fascinating burrowing behaviors, and significant ecological roles make them a species worth protecting. So the next time you hear about aardvarks, remember: these remarkable creatures are a vital part of the African landscape, deserving of our attention and care.
