When we talk about the evolutionary history of the turtle, we’re diving into a timeline that stretches back to the time of dinosaurs. These remarkable reptiles have been around for approximately 220 million years, making them one of the oldest living groups of vertebrates. Their journey through time is not just a tale of survival; it’s a testament to how life evolves and adapts. So, let’s take a fascinating stroll through the ages and explore how turtles came to be.
How Turtles Fit into the Evolutionary Tree
Understanding the evolutionary history of turtles starts with looking at their place on the evolutionary tree. They belong to a group called reptiles, which also includes snakes, lizards, and crocodiles. Within this group, turtles form their own special category known as Testudines. The cool part? Turtles are more closely related to birds and crocodiles than they are to other reptiles like snakes.
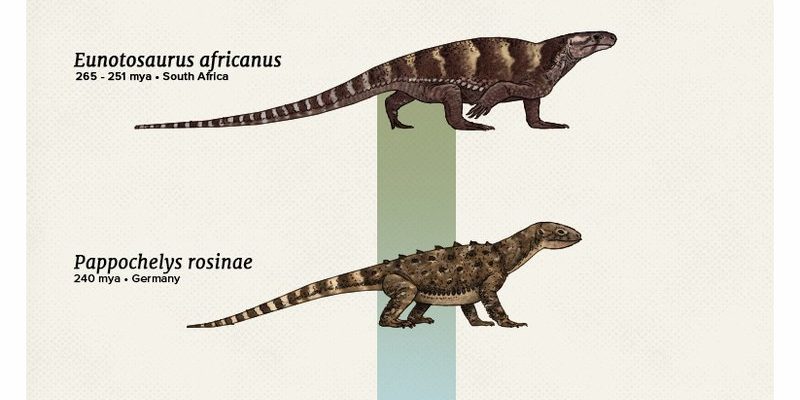
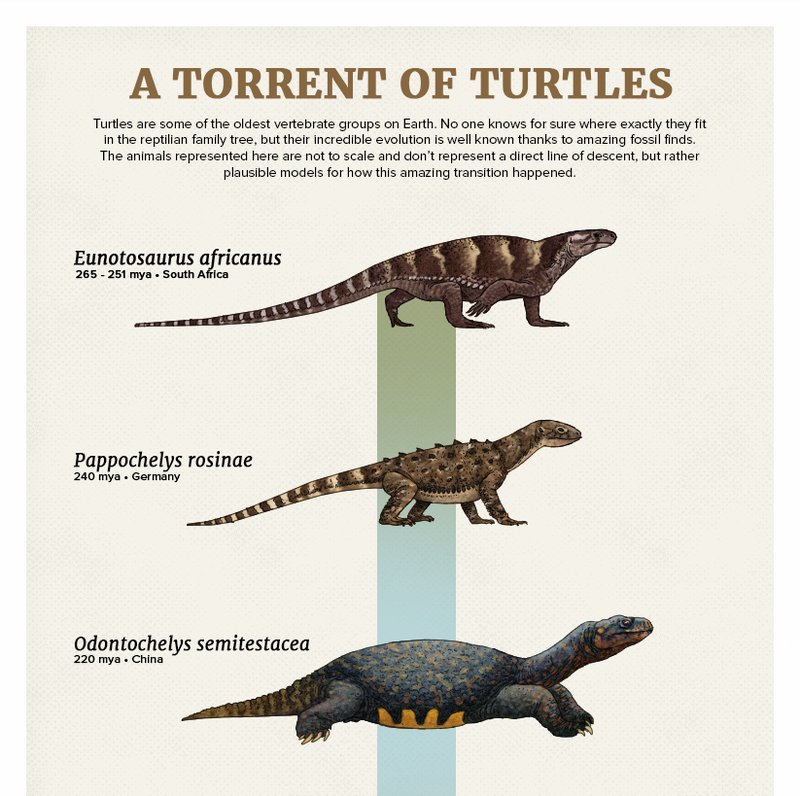
Here’s the thing: the unique shell structure of turtles—made of bone and cartilage—sets them apart. Imagine their shell as a mobile home that protects them from predators. This adaptation is believed to have originated around the Late Triassic period, roughly 220 million years ago. If you think about it, that’s a long time for any creature to survive and adapt!
Additionally, turtles are often described as “living fossils.” This means they showcase traits that haven’t changed much over millions of years. Their hard protective shells and slow movement have proven to be effective survival strategies. It’s like they’ve found a formula that works and decided to stick with it.
The Earliest Turtles and Their Environment
The first turtles, like *Proganochelys*, emerged during the Late Triassic period. These ancient turtles looked quite different from our familiar modern-day tortoises and sea turtles. For instance, they had very long tails and lacked the flexible necks we associate with today’s turtles. Imagine a reptile that still had dinosaur-like features but was starting to adapt to a new way of life.
During this period, Earth was a vastly different place. The climate was generally warmer, and ecosystems were filled with lush vegetation and diverse animal life. Early turtles thrived in both freshwater and terrestrial environments, showcasing their versatility. This ability to adjust to different habitats helped them survive against evolving predators and changing landscapes.
What’s intriguing is how these early turtles began to develop the traits we associate with them today. As they adapted to various niches, certain species started to develop more robust shells, which provided better protection. This design innovation was crucial for surviving in a world full of danger, from fierce dinosaurs to changing environments.
The Great Extinction and Turtle Survival
Fast forward to about 66 million years ago—the time of the mass extinction that wiped out the dinosaurs. You might be wondering how turtles managed to survive this cataclysm. Well, as it turns out, their hardy nature and adaptability played a significant role.
Turtles were able to thrive during this tumultuous time largely because of their ability to live in various habitats. While many species went extinct, some turtles found refuge in areas less affected by the catastrophic events, such as floods or wildfires. Their burrowing habits and aquatic lifestyles allowed them to escape the worst of the consequences.
After this extinction, turtles rapidly diversified. New species emerged, adapting to life in oceans, rivers, and on land. For example, the marine turtles we see today belong to a lineage that adapted to life in the open sea. This adaptability opened up a range of new opportunities for turtles, allowing them to fill ecological gaps left by extinct species.
The Diversity of Turtles Today
Today, there are over 350 recognized turtle species, all showcasing the amazing adaptability of this ancient group. Turtles can be found in almost every corner of the planet—from the depths of the ocean to the driest deserts. Just think about how varied they are: some turtles are tiny, like the Eastern Box Turtle, while others, like the Leatherback Sea Turtle, can weigh over 2,000 pounds!
One of the most exciting aspects of turtles is their specialized adaptations. For example, sea turtles have flippers that make them excellent swimmers, enabling them to navigate vast ocean waters. In contrast, tortoises have thick, sturdy legs and strong shells, perfect for a life of grazing on land. Each species reflects a unique story of survival and evolution based on the environments in which they live.
However, despite their fascinating adaptability, turtle populations are under threat today due to habitat loss, pollution, and climate change. Each turtle carries the legacy of millions of years of evolution, making their survival all the more crucial.
Conservation Efforts and Their Importance
As we explore the evolutionary history of turtles, we find ourselves in a critical conversation about conservation. Many turtle species are endangered or facing threats, and protecting them is essential not just for their survival, but for the ecosystems they inhabit. Efforts like habitat preservation, legal protection, and public education are vital in the fight to save these ancient reptiles.
Conservationists often focus on specific species, like the Loggerhead Sea Turtle and the Gopher Tortoise, which play significant roles in their ecosystems. For example, sea turtles help maintain the health of seagrass beds and coral reefs. By protecting turtles, we’re not just saving a beloved animal; we’re also preserving entire ecosystems that depend on their presence.
Additionally, advances in technology and research are helping conservation efforts. Tracking turtle migrations and studying their habits allow scientists to understand their needs better and develop effective strategies to protect them. It’s like gathering pieces of a puzzle to see the complete picture of their survival.
The Future of Turtles
Looking ahead, the future of turtles is a mixed bag. On one hand, their long history shows incredible resilience and adaptability. On the other hand, the challenges they face from human activity and climate change are significant. You might be wondering what we can do to help.
Simple actions can make a big difference, like reducing plastic use, supporting turtle-friendly products, and raising awareness about their plight. Each small effort contributes to a larger movement to protect these majestic creatures. It’s a team effort, reminding us that we are all connected to the natural world.
In conclusion, the evolutionary history of the turtle is a remarkable journey of survival, adaptation, and resilience. From their ancient ancestors to the diverse species we see today, turtles have a story that deserves to be told. As stewards of the Earth, let’s commit to ensuring that this story continues for generations to come. After all, turtles are not just relics of the past; they are living symbols of the beauty and complexity of evolution.