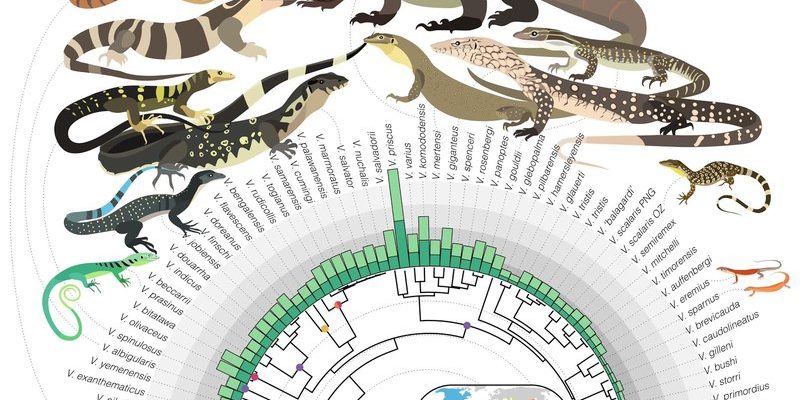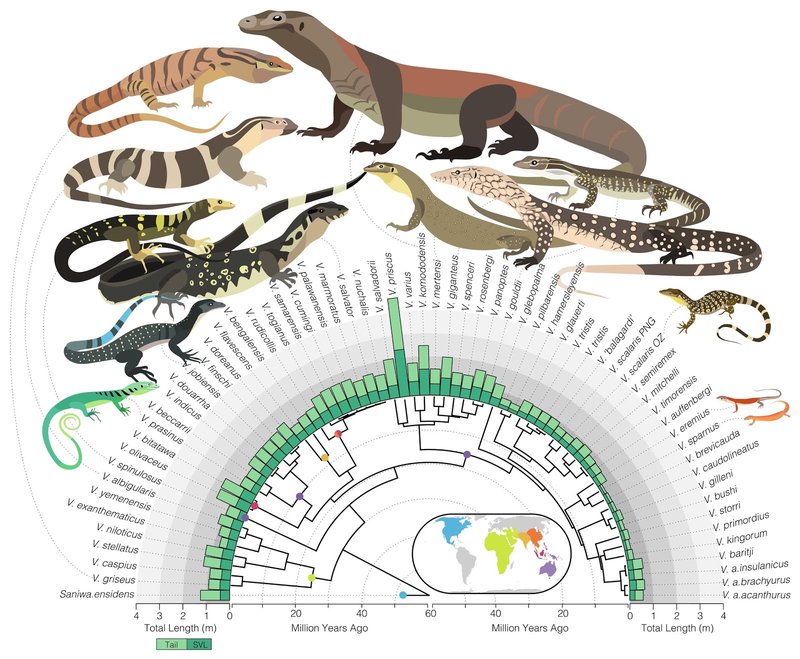
Monitor lizards belong to the Varanidae family, and their lineage goes back to a time when dinosaurs still roamed the Earth. You might be wondering how these lizards managed to survive through so many changes in the planet’s climate and landscape. Let’s take a closer look at their evolutionary journey, how they came to be the adaptable creatures we see today, and why understanding this history is essential for appreciating their role in our ecosystems.
Origins of Monitor Lizards
The story of monitor lizards begins in the late Cretaceous period, around 70 million years ago. During this time, the Earth was a vastly different place, teeming with diverse dinosaur species and primitive mammals. Monitor lizards are believed to have evolved from a group of ancient reptiles known as the lacertilians, which also gave rise to some of today’s lizard species.
These early ancestors had characteristics that helped them thrive in various habitats. They were likely small, agile creatures, which allowed them to hunt insects and small animals. Over time, as environmental conditions changed—such as the extinction of the dinosaurs—monitor lizards began to diversify. They adapted to different environments, from tropical forests to arid deserts, leading to a variety of species that we recognize today.
You may find it fascinating that the Varanus genus, which includes monitor lizards, eventually branched out into over 70 different species. This adaptability is partly due to their keen senses and hunting prowess. They became efficient predators, capable of consuming everything from insects to larger mammals, depending on the species.
Physical Adaptations Through Time
One of the most remarkable things about monitor lizards is their physical adaptations. Over millions of years, they developed traits that allowed them to thrive in specific environments. For instance, the Komodo dragon, the largest species, evolved to be a formidable predator with excellent camouflage and the ability to take down large prey like deer.
In contrast, species like the savannah monitor are smaller and have different adaptations for their environment. They have stout bodies and powerful limbs that help them dig burrows, providing shelter from predators and extreme weather conditions. This variation in physical traits is a testament to their ability to survive and flourish in diverse habitats.
It’s also worth mentioning their impressive tongue. Monitor lizards have long, forked tongues that they use to gather scent particles from the air, somewhat like snakes. This adaptation helps them track prey and navigate through their environment. It’s almost like having a built-in GPS system!
Geographical Distribution and Diversity
Monitor lizards are found across various continents, which reflects their incredible adaptability. You can spot them in Africa, Asia, Australia, and even on some Pacific islands. Each region hosts different species, each uniquely adapted to their surroundings.
For example, the Asian water monitor thrives in aquatic habitats, while the Timor monitor prefers dry, rocky environments. This wide distribution illustrates how monitor lizards have capitalized on different ecological niches throughout their evolutionary history.
The fact that they can live in both mountainous regions and lowland swamps speaks volumes about their adaptability. In essence, monitor lizards can occupy multiple ecological roles—from predators to scavengers—making them an important part of their ecosystems. Their presence helps maintain the balance of populations within their habitats.
Behavior and Intelligence
When it comes to behavior, monitor lizards are surprisingly intelligent. They have complex social behaviors and are known for their problem-solving abilities. For instance, some species have been observed using tools, like digging sticks, to extract prey from holes.
They also engage in intricate social interactions, including displays of dominance and territoriality. You might find it interesting that some monitor lizards establish social hierarchies, similar to what you’d see in various animal communities. These interactions can even influence their reproduction and survival, showcasing the depth of their social structures.
You might be wondering how all this intelligence ties into their evolutionary journey. Simply put, the ability to learn and adapt is crucial for survival. Monitor lizards that can solve problems or adjust their behaviors in response to environmental changes are more likely to thrive.
Conservation Status and Challenges
Despite their fascinating history, many monitor lizard species are facing threats today. Habitat destruction, climate change, and poaching for the pet trade are significant challenges. Some species, like the Komodo dragon, are classified as vulnerable, raising concerns for their future survival.
Conservation efforts are crucial for ensuring that these incredible reptiles continue to thrive. Organizations are working hard to protect their natural habitats and raise awareness about the importance of biodiversity. It’s essential to understand that the loss of monitor lizards would not only affect their species but also disrupt the ecosystems they help maintain.
You might feel inspired to contribute to conservation efforts or support organizations that work to protect these fascinating creatures. After all, understanding and advocating for their survival is a way to honor their long evolutionary journey.
The evolutionary history of monitor lizards is a captivating story of adaptability and survival. From their origins millions of years ago to their diverse species found around the world today, these reptiles have shown remarkable resilience. Their physical adaptations, intelligence, and varied behaviors highlight just how fascinating they are—and why they deserve our attention and protection.
As you reflect on their journey, remember that understanding these creatures is more than just appreciating their unique characteristics. It’s about recognizing the role they play in our ecosystems and the importance of preserving their habitats for future generations. So next time you spot a monitor lizard, think about the millions of years of history behind that sleek, scaly exterior.