Imagine if your life began in a tiny, cozy ball of food. That’s pretty much what a dung beetle egg experiences. The lifecycle of a dung beetle is a remarkable process, and it all starts with these little eggs. From there, they grow into larvae, pupae, and then emerge as adults. Each stage is like a chapter in a book, filled with unique challenges and discoveries. So grab your favorite drink, and let’s explore this incredible journey!
The Egg Stage: A Hidden Beginning
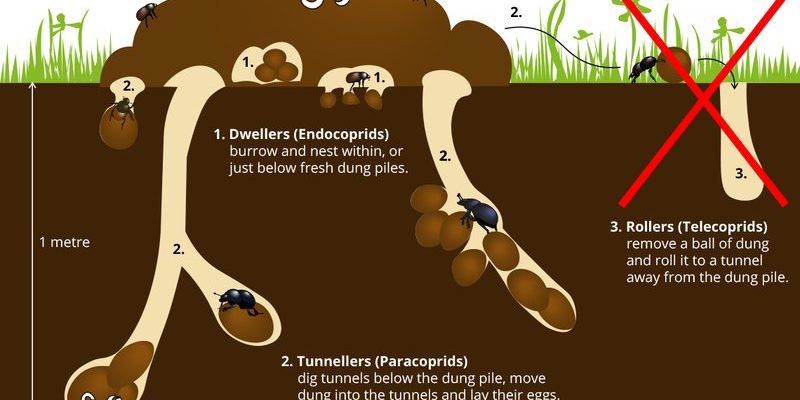
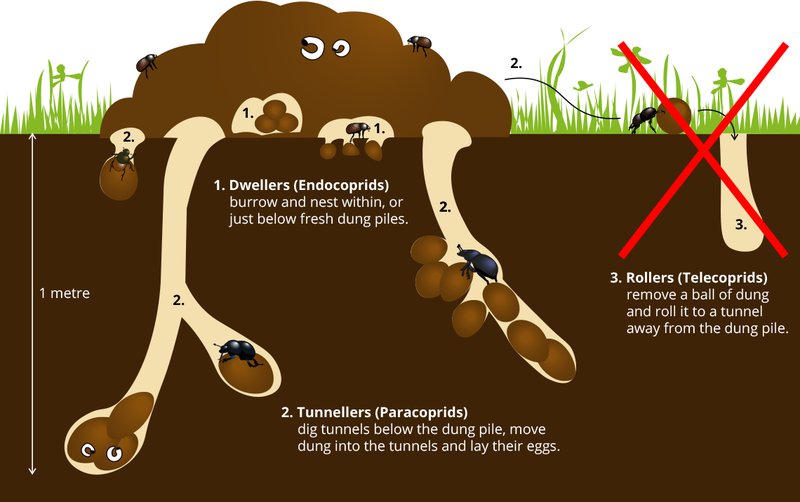
The lifecycle of a dung beetle starts when a female lays her eggs in a dung ball. It’s like she’s planting a garden in a nutrient-rich patch. The dung serves not just as a food source but also as a protective environment for her eggs. Each egg is tiny, about the size of a pinhead, and is safely nestled within the dung.
You might be wondering why dung beetles choose dung for their eggs. Here’s the thing: the nutrients found in animal waste are perfect for the larvae when they hatch. Once the eggs are laid, they face a crucial waiting game. Depending on the species and environmental conditions, the eggs may take about a week to hatch. During this time, the female dung beetle guards her precious dung ball from predators and competitors.
After about a week, these tiny larvae emerge. They’re quite different from what we might think of when we picture a beetle. Instead of legs and wings, they look more like small, white grubs. This stage is when they’ll start to dig into the dung, feeding and growing fast.
The Larval Stage: Growing Up in Dung
As the larvae munch through the nutrient-rich dung, they undergo significant growth. This stage lasts anywhere from a few weeks to several months, depending on factors like temperature and food availability. You can think of them as little sponge-like creatures soaking up all the nutrients they need to thrive.
During this phase, they’re not just eating; they’re also developing. As they consume the dung, their bodies transform. They grow in size and energy, preparing for their next big change. Interestingly, some dung beetles may even have siblings sharing the same dung ball, all growing together in this rich environment.
The larval stage is not without its dangers. Predators such as ants and other insects often seek out these vulnerable larvae. Because of this, they rely on the safety of the dung ball, which acts as a fortress. Here, they can grow without too much risk of being eaten. Imagine a hidden treasure chest where these grubs are stockpiling their energy for the challenges that lie ahead.
Pupal Stage: The Transformation
After the larval stage, the dung beetle enters the pupal stage. This is where the real magic happens. The larvae find a safe spot, usually within the dung or sometimes in the soil, and form a protective casing around themselves. It’s like they’re wrapping up for a long nap, but this isn’t just any snooze—this is a transformation.
During the pupal stage, which can last for weeks to several months, the larva morphs into a beetle. Inside that cozy little cocoon, their body parts rearrange and develop into the recognizable shape of an adult beetle. It’s a fascinating process, often compared to a butterfly’s transformation.
But it’s not all smooth sailing. The pupae are still vulnerable to predators. So, finding the right location is crucial for their survival. Once the transformation process is complete, they’ll be ready to break out of their pupal casing and enter the world as fully formed adults.
After weeks of waiting, the moment finally arrives. The adult dung beetle breaks free from its pupal case, emerging into the world ready to find food, a mate, and a suitable place to lay its own eggs. Adult dung beetles can vary in size and color, but they generally have a robust body and strong legs designed for burrowing into dung.
As adults, these beetles play a vital role in their ecosystem. Not only do they help recycle nutrients back into the soil, but they also help control parasites that would otherwise thrive in animal waste. By breaking down dung, they aerate the soil and reduce the buildup of waste in their environment.
You might wonder how long they live after emerging. Adult dung beetles can live anywhere from a few weeks to several years, depending on the species and conditions. They spend their lives sampling different types of dung, forming dung balls, and, of course, mating.
The Importance of Dung Beetles in Ecosystems
You might be thinking, “Why should I care about dung beetles?” Well, their role in the ecosystem is actually pretty significant. Here’s what they do:
- Nutrient Recycling: Dung beetles break down dung into smaller pieces, returning nutrients to the soil and promoting plant growth.
- Soil Aeration: By burying dung, they aerate the soil, helping water and nutrients reach plant roots more effectively.
- Pest Control: Dung beetles help reduce the population of pest species such as flies that can breed in animal waste.
- Habitat for Other Species: Their activities create habitats for other organisms, promoting overall biodiversity.
In short, dung beetles are unsung heroes in our ecosystems, cleaning up waste and ensuring that nutrients are available for plants and animals alike. Their lifecycle may seem simple, but it’s a crucial part of maintaining balance in nature.
Fun Facts About Dung Beetles
Dung beetles are more interesting than you might think! Here are a few fun facts to spice up your knowledge:
- Speedy Rollers: Some dung beetle species can roll dung balls that are over 50 times their body weight!
- Navigation Skills: Dung beetles can navigate using the Milky Way. How amazing is that?
- Diverse Species: There are over 8,000 species of dung beetles worldwide, each with unique behaviors and adaptations.
These little facts highlight just how unique and adaptable dung beetles are in our world.
The lifecycle of a dung beetle is a remarkable journey from a tiny egg nestled in dung to an adult that plays an essential role in the ecosystem. Each stage—egg, larva, pupa, and adult—has its own challenges and contributions. By recycling nutrients and helping maintain soil health, dung beetles are vital to our environment, though often overlooked.
So, the next time you think about beetles, don’t just picture them scurrying around. Remember the journey they’ve taken, and appreciate the important work they’re doing for our planet. Dung beetles may be small, but they make a big difference!