The seasonal behavior of bone-eating worms is more complex than it might seem. It’s not just about finding food; it’s about adapting to a world that changes with the seasons, much like how we adjust our wardrobes for winter or summer. Understanding these patterns helps researchers gain insights not only into the worms themselves but also into the broader marine ecosystem. So, grab your coffee, and let’s explore the fascinating life of *Osedax*, including their feeding habits and how seasonal changes affect them.
What Are Bone-Eating Worms?
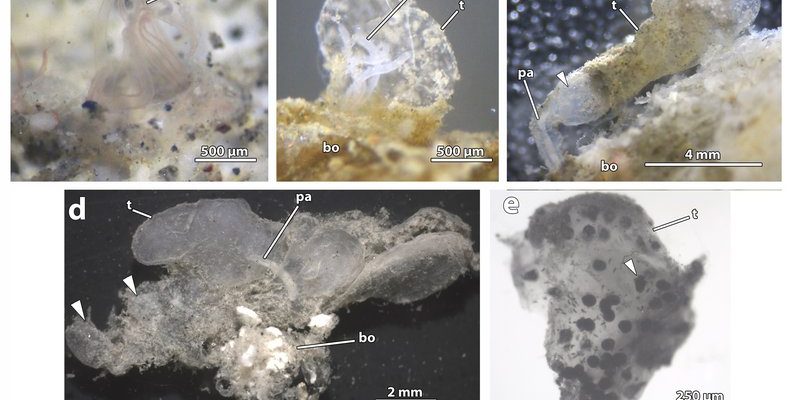
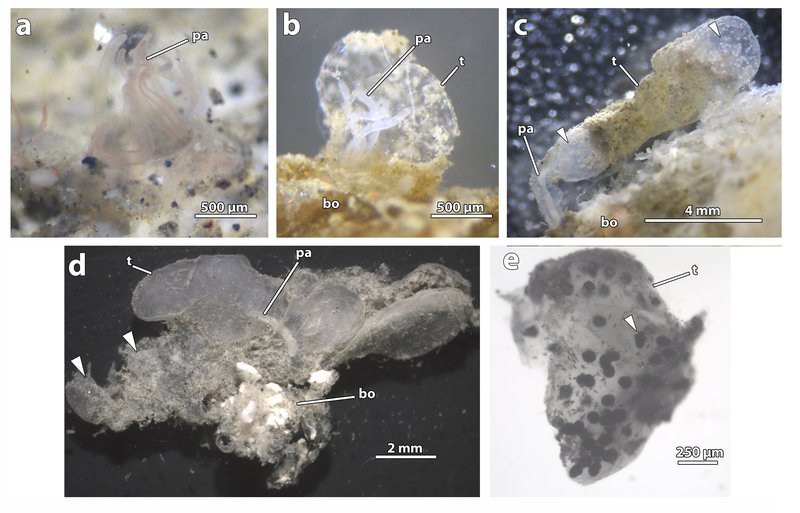
Bone-eating worms are a type of marine annelid that thrive on the ocean floor. These worms are particularly known for their unique feeding strategy—they consume the bones of dead animals, like whales, that have sunk to the seabed. Imagine a hidden treasure chest full of bones just lying there, and these worms are like treasure hunters, utilizing specialized enzymes to break down the bone and absorb the nutrients within.
They first caught researchers’ attention back in 2002, when scientists discovered their remarkable ability to survive in nutrient-poor environments. This adaptation allows them to thrive where most other organisms would struggle. With a soft, pink body and feathery structures known as “plumules” that filter food, these worms can seem almost delicate. But don’t let their appearance fool you—they’re tough survivors in a harsh environment.
You might be wondering how these worms find their meals. It turns out they have a superb sense of smell, which helps them locate food sources from a distance. Once they find a suitable snack, they latch onto the bone and get to work, digesting it leisurely over time. Talk about a slow food movement!
The Role of Seasons in Feeding Behavior
As we move deeper into the ocean’s mysteries, we find that the behavior of bone-eating worms changes with the seasons. In many locations, the ocean undergoes shifts in temperature, food availability, and even light exposure throughout the year. These changes can significantly affect how *Osedax* worms behave.
For instance, during warmer months, the increased biological activity in the ocean leads to a richer food supply. This can mean more dead animals sinking to the seabed, providing ample meals for *Osedax*. In these conditions, researchers have noted that the worms tend to reproduce more actively, ensuring that their population can take advantage of the plentiful food.
On the flip side, during colder months, food supply may dwindle. The worms have to adapt to survive. They often slow their metabolism, conserving energy, and can even enter a state of dormancy. This seasonal adaptation is a brilliant example of how organisms meet the challenges of their environment.
Reproductive Patterns and Seasonal Changes
Reproduction in bone-eating worms also shows a seasonal pattern. When conditions are right, typically during warmer months, the worms engage in more successful mating. They release gametes into the water, where fertilization occurs. Researchers have observed that the timing of this reproductive surge corresponds with the peak availability of food resources, allowing for the highest chance of survival for the offspring.
Let’s think of it this way: if you’re planning a big party, you’d want good food and a vibrant atmosphere, right? Similarly, these worms time their reproduction to ensure that their babies have the best chance of thriving in a plentiful environment.
Interestingly, when food is scarce, the worms might delay reproduction. This decision helps ensure that they don’t waste energy on offspring that might not survive. Evolution has fine-tuned this balance of energy expenditure—kind of like how we might hold off on planning a big trip if we know our budget is tight.
Feeding Strategies Throughout the Year
The feeding habits of *Osedax* worms can also vary with the seasons. In warmer months, when food is more abundant, they can afford to eat more frequently. They actively scout for bones and can consume large quantities. Imagine going on a buffet binge when your favorite dishes are available!
In contrast, during winter months, the situation changes. The worms may conserve their energy and feed less often, focusing only on the most nutrient-rich bones. This selective feeding ensures that they make the most of what’s available, much like how we might decide to splurge on a nice dinner when money allows but scale back when necessary.
Moreover, researchers have noted that even the types of bones consumed can change with the seasons. During different times of the year, certain prey may be more abundant, leading the worms to adapt their feeding strategies accordingly. They’re like culinary adventurers, trying different flavors as the seasons shift.
Field Studies and Observations
Field studies have played a crucial role in observing these seasonal behavior patterns. Scientists often deploy devices that monitor the ocean floor to track the activities of *Osedax* worms in their natural environment. These studies provide valuable insights into how seasonal changes affect their feeding and reproductive behaviors.
For example, researchers might use remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) equipped with cameras to observe these captivating worms in action. By observing them in their natural habitat, scientists can gather data on their reproductive cycles, feeding rates, and population dynamics throughout different seasons.
Such detailed observations help paint a clearer picture of the bone-eating worm’s life cycle and its ecological role. Researchers can also analyze how environmental factors, such as temperature and food availability, influence these behaviors year-round.
The Importance of Understanding Seasonal Behaviors
So, why should we care about the seasonal behavior patterns of bone-eating worms? Well, understanding these behaviors gives us insight into the overall health of marine ecosystems. These worms play a pivotal role by recycling nutrients from dead animals back into the ocean. This process supports a web of life in deep-sea environments.
Additionally, studying *Osedax* can help scientists monitor the impacts of climate change on ocean ecosystems. As sea temperatures rise and environments change, knowing how these worms adapt can provide clues to the resilience of marine life.
In essence, by observing the seasonal habits of these worms, scientists can gather important information that may help us protect and manage ocean resources more effectively.
The bone-eating worm, with its unique adaptations and seasonal behaviors, serves as a fascinating example of life in the ocean. From its impressive feeding strategies to its reproductive patterns, *Osedax* demonstrates how life can thrive even in the most challenging environments.
By diving into the study of these peculiar creatures, we not only learn more about their world but also gain valuable insights into the health of our oceans. So, next time you think about the vast seas, remember the bone-eating worm—a tiny but mighty player in the grand story of marine life.

