These creatures belong to the phylum Platyhelminthes, and they can be found in various environments, from oceans to freshwater and even on land. Their bodies are flat and ribbon-like, which contributes to their name. What’s particularly interesting is how they manage to consume food in their own peculiar way. So, grab a cup of coffee, sit back, and let’s explore the step-by-step feeding process of flatworms.
Understanding Flatworms’ Anatomy
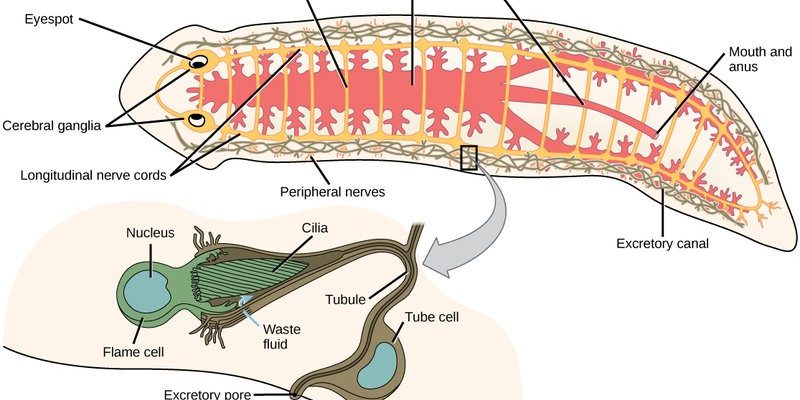
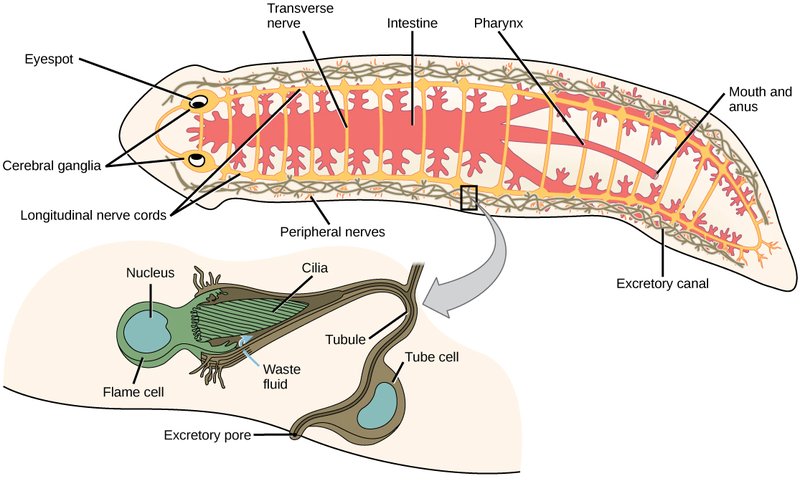
Before we get into how flatworms eat, it’s essential to know a bit about their anatomy. Flatworms have a simple body structure lacking complex organs. They have a soft body and no bones, which makes them quite flexible. This adaptability allows them to navigate through narrow spaces and explore their environment.
The most vital part of their anatomy when it comes to feeding is the gastrovascular cavity. This is like their stomach and intestine rolled into one. Instead of having a separate mouth and anus, flatworms only have one opening that serves both functions. This means that food goes in one end, and waste comes out the same way. It’s a bit like a bag with one opening—everything enters and exits through the same spot.
Another key feature is the presence of a pharynx, which is a tube-like structure that extends out of their body. Think of it as a straw they use to suck up their food. The pharynx is crucial for their feeding mechanism, so let’s look at how it all works.
The Feeding Process of Flatworms
Okay, now that we have a grasp of their anatomy, let’s break down how flatworms actually feed step-by-step.
1. Locating Food: Flatworms are predators and scavengers, so they look for small organisms like tiny crustaceans, worms, or even decaying organic material. They use their senses to detect food, often finding it by smell.
2. Extending the Pharynx: Once a flatworm spots its meal, it extends its pharynx out of its body. This can be a fascinating sight! Think of it like a vacuum cleaner hose ready to gobble up food. The flatworm can extend this pharynx to grab onto its prey.
3. Ingesting Food: After the pharynx grabs the food, the flatworm sucks it through the pharynx into the gastrovascular cavity. Here, the food is broken down by enzymes. It’s like a mini digestive factory inside their body!
4. Absorbing Nutrients: The broken-down food is then absorbed through the walls of the gastrovascular cavity into the flatworm’s body. This is where the nutrients get distributed, giving the worm energy to move and grow.
5. Excreting Waste: Finally, any waste is expelled through the same opening they used to eat. It’s a simple but effective system that allows flatworms to survive in various habitats.
Types of Flatworm Feeding Strategies
Flatworms aren’t one-size-fits-all when it comes to feeding strategies. Different species have adapted to their environments in unique ways. Let’s explore a few of these strategies.
1. Predatory Flatworms: Some flatworms, like planarians, actively hunt their prey. They can even regenerate lost body parts, allowing them to recover from injuries sustained during hunting. This helps them stay on top of their game when searching for food.
2. Scavengers: Others take on the role of scavengers. They feed on decaying organic matter, cleaning up their habitats. This is essential for the ecosystem because it helps recycle nutrients.
3. Parasitic Flatworms: Then there are parasitic flatworms, like tapeworms, that live inside the bodies of other animals. They absorb nutrients from their hosts without causing noticeable harm at first. This type of feeding strategy showcases how adaptable and varied flatworm feeding mechanisms can be.
4. Symbiotic Relationships: Lastly, some flatworms form symbiotic relationships with other organisms. They coexist and benefit from each other, finding food sources through their interactions.
Importance of Flatworms in the Ecosystem
Now, you might be asking, “Why should I care about flatworms?” Well, these little guys play important roles in their ecosystems, and their feeding mechanisms are a big part of it.
1. Nutrient Recycling: By feeding on decomposing matter, flatworms help break down organic material, returning nutrients to the soil. This supports plant growth and encourages the health of their ecosystems.
2. Food Source for Other Animals: Flatworms are also a food source for various animals, including fish and birds. Their position in the food chain is vital, helping to maintain balance in ecosystems.
3. Indicators of Environmental Health: Because flatworms are sensitive to pollution and environmental changes, they can serve as indicators of ecosystem health. Scientists often study them to assess the quality of water and habitat.
4. Research Opportunities: Flatworms, particularly planarians, are of interest in scientific research. Their ability to regenerate body parts provides insights into cellular processes and potential applications in medicine.
Challenges Flatworms Face
Despite their resilience, flatworms also face challenges in their environments. Understanding these can give us a better perspective on their existence.
1. Habitat Loss: Pollution and habitat destruction can harm flatworm populations. When their environments get damaged, it affects their ability to find food and reproduce.
2. Climate Change: Changes in temperature and water quality due to climate change also impact flatworms. They are sensitive creatures, and shifts in their habitats can disrupt their feeding mechanisms and overall survival.
3. Competition: Increased competition for food sources with other species can lead to declines in flatworm populations. If they cannot find enough to eat, their numbers may dwindle.
4. Human Impact: Activities like overfishing and water pollution contribute to their struggles. Addressing these issues is crucial for maintaining flatworm populations and healthy ecosystems.
Flatworms might be small, but they are mighty in their roles within the ecosystem. Their unique feeding mechanisms—using a pharynx to inhale nutrients—showcase the wonders of adaptation in nature. Whether they hunt prey, scavenge for decaying matter, or exist as parasites, flatworms remind us just how interconnected life is.
By understanding flatworms and their feeding processes, we gain appreciation for the intricate balance of ecosystems. Protecting these mini marvels is essential for the health of our planet. So, next time you come across a flatworm, take a moment to consider the fascinating journey it has taken to find its next meal, and the valuable role it plays in its home.