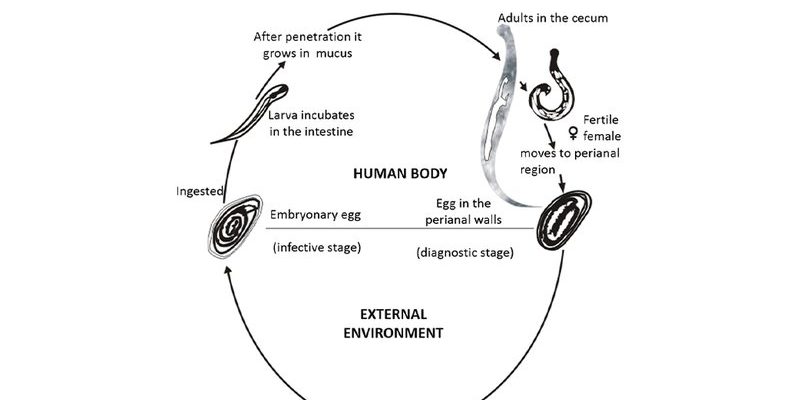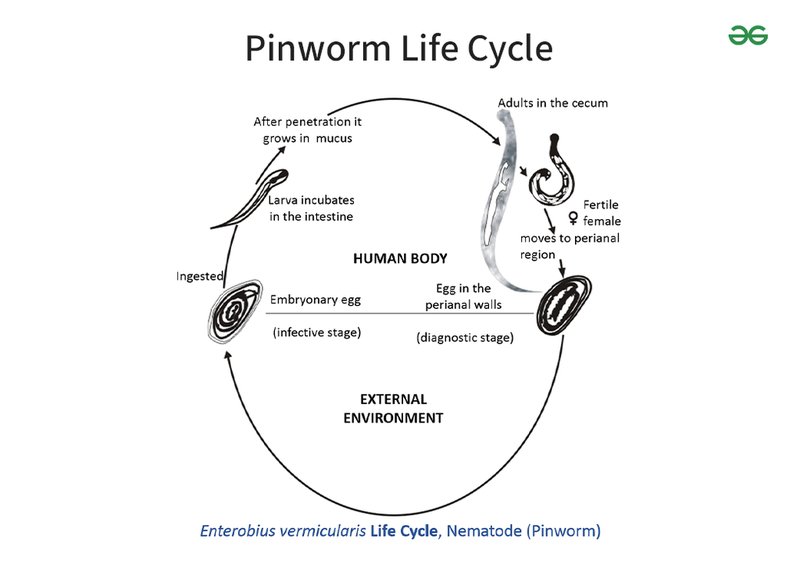
Pinworms, also known scientifically as *Enterobius vermicularis*, are small intestinal parasites primarily affecting people, especially children. If you’ve ever been curious about how pinworms reproduce and thrive, you’re in the right place. I’ll guide you through their mating rituals, egg-laying practices, and the journey of their larvae in a way that’s simple, engaging, and informative, just like a chat over coffee.
What Are Pinworms?
Before diving into reproduction, it’s essential to understand what pinworms really are. Picture a thin, white thread, about the size of a staple—that’s a pinworm! These worms are typically found in the human intestines, particularly in the colon and rectum. They’re most commonly known for causing itching and discomfort, especially at night when the female worms come out to lay their eggs.
You might be wondering, “How do these worms end up in our bodies?” Well, they often spread through contaminated surfaces, like bedding or clothing. Children are particularly susceptible since they’re not always the best at washing their hands. Just a tiny egg can hitch a ride on a finger and make its way to a mouth, starting the cycle all over again.
How Do Pinworms Mate?
Now, let’s talk about the mating process. Pinworm reproduction is pretty straightforward, but it’s also quite unique. Male pinworms are smaller than females and have a curved tail, which helps them hang onto the female during mating. Here’s where it gets interesting: mating usually occurs in the intestines, where the males swim around looking for females, like a tiny underwater dance party.
After mating, the female pinworm does something amazing. She’ll migrate to the anal area at night to lay her eggs. It’s almost as if she knows it’s the perfect time since her unsuspecting host is fast asleep. Each female can lay around 10,000 to 15,000 eggs in one night! That’s quite a prolific party, don’t you think?
The Egg-Laying Process
Once the female pinworm reaches the anal area, she releases her eggs into the folds of skin. But these eggs aren’t just dropped and left alone; they’re sticky! This stickiness helps them adhere to surfaces, increasing the chances of being transferred to another host. You might picture it like a tiny sticky note, waiting to be picked up.
The warmth and moisture of the environment help these eggs develop rapidly. In just a few hours, they’re ready for the next stage of their life cycle. It’s a strategic move, considering the eggs can survive outside the human body for several weeks. This durability is a big reason why pinworm infections are so common.
Lifecycle of a Pinworm
To fully grasp pinworm reproduction, you need to understand the life cycle. Think of it as a well-orchestrated routine that keeps going as long as conditions are favorable. Here’s how it unfolds:
1. Eggs: After being laid, the sticky eggs can be transferred to hands, clothing, or surfaces.
2. Ingestion: Someone unknowingly ingests the eggs, often by touching their mouth after contact with contaminated surfaces.
3. Hatching: Inside the intestines, the eggs hatch into larvae, starting the cycle all over again.
This life cycle highlights why pinworm infections are easily transmitted, especially in crowded places like schools or daycare centers. Each phase is carefully designed to ensure the survival and spread of pinworms.
The Role of Larvae in the Life Cycle
Let’s take a closer look at the larval stage of pinworms. Once the eggs hatch in the intestines, they emerge as tiny larvae. These larvae are hungry and eager to grow, feeding on the host’s intestinal contents. This stage is crucial for their development; they must prepare to mature into adult worms.
The larvae will develop into adult pinworms within about two to six weeks. Once they reach maturity, they can reproduce, continuing the cycle. It’s a classic case of “the circle of life,” but with a rather unwelcome twist!
Prevention and Treatment Options
So, why does understanding pinworm reproduction matter? It helps in prevention and treatment. Knowing how pinworms spread can equip you to take measures to stop them. Here are some effective strategies:
- Handwashing Regularly wash your hands, especially after using the restroom and before eating.
- Wash Bedding: Change and wash bedding and pajamas frequently to remove potential eggs.
- Treat Infections: If someone in your household has pinworms, consider treatment for everyone, as they can spread quickly.
Pinworm treatments usually include over-the-counter medications. These medications work by killing the adult worms and preventing them from laying more eggs. However, it’s always best to consult a healthcare provider for the most effective approach.
Why Understanding Pinworm Reproduction Matters
Understanding the reproduction of pinworms isn’t just for trivia—it’s crucial for anyone dealing with these pesky infections. Knowledge empowers you to take action and protect yourself and your family. By grasping their life cycle and habits, you can implement better hygiene practices, reducing the risk of infection.
In addition, awareness of the symptoms—like itching or discomfort—can lead to prompt treatment, preventing the spread to others. It’s all about being proactive rather than reactive.
Pinworms may be small, but they can have a significant impact on daily life. So, knowing how they reproduce, spread, and develop helps you stay one step ahead.
In closing, while pinworms might not be the most charming topic, understanding their reproduction and life cycle makes the subject much less intimidating. It’s about grasping the bigger picture: the importance of hygiene, awareness, and prompt action can lead to healthier lives. Who knew that such tiny creatures could teach us so much?