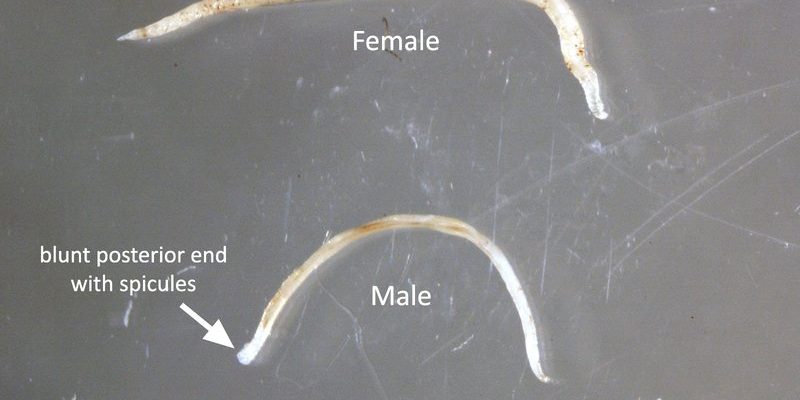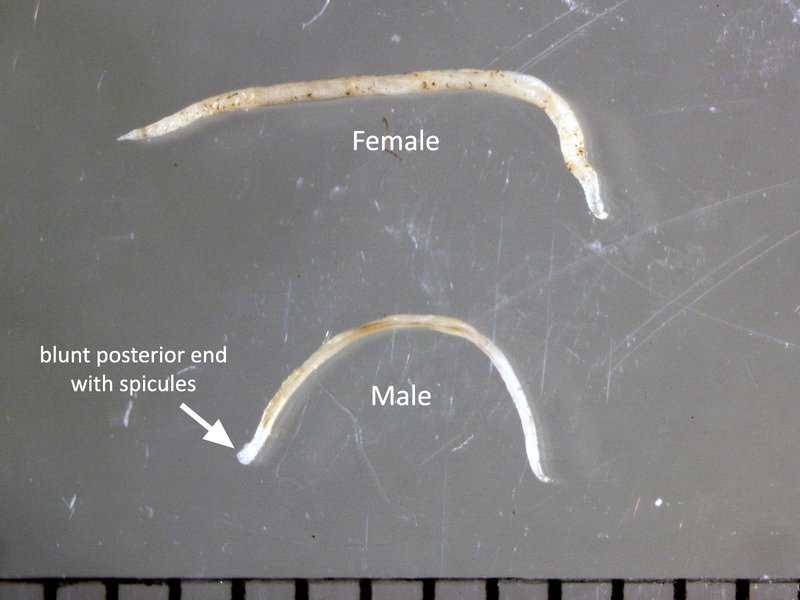
You might be wondering, can we actually study or even farm hookworms in captivity? The short answer is yes, but it’s not as simple as it sounds. Like any living organism, hookworms require specific conditions and care to thrive. Let’s dig deeper into how these creatures can be raised and researched in a controlled environment.
Understanding Hookworms
Hookworms are parasitic worms that primarily inhabit the intestines of their hosts, feeding on their blood. They belong to the family Ancylostomatidae, with two of the most notable species being *Ancylostoma duodenale* and *Necator americanus*. These worms are a bit like unwanted guests; they can cause significant health issues, especially in areas where sanitation is poor.
Their life cycle is quite interesting. Hookworms begin as eggs, which hatch in the soil. The larvae can then penetrate the skin of a host, usually through bare feet. Once inside, they migrate to the intestines, where they latch on and start feeding. Sadly, this can lead to anemia and other health problems for the host.
You might think, “Why would anyone want to study such a harmful creature?” Well, the truth is that understanding these parasitic worms can lead to better treatments and prevention methods for those affected by them.
Challenges of Captive Hookworm Studies
Studying hookworms in captivity comes with its own set of challenges. First off, creating the right environment is crucial. Hookworms thrive in specific temperatures and humidity levels. Without these ideal conditions, they might not develop properly or could even die. It’s a bit like trying to keep a tropical plant alive in a cold climate.
Additionally, keeping these parasites in captivity poses ethical questions. Researchers must ensure that their methods align with humane treatment practices. This often means creating conditions that mimic their natural habitat as closely as possible. You can’t just throw them into a plastic tub and expect them to flourish!
Moreover, feeding hookworms their preferred nutrients can be tricky. These parasites feed on blood, which can pose a problem for researchers. Finding a sustainable and ethical way to provide this nutrient is essential.
Can Hookworms Be Farmed?
Now, let’s get to the juicy part: can hookworms be farmed? In theory, yes! Hookworms can be bred in controlled environments, which can help researchers understand their biology better. There are ongoing studies exploring the potential benefits of hookworms, particularly in treating autoimmune diseases. The idea is that introducing these parasites into the human gut may help modulate the immune response, similar to how some people use probiotic bacteria.
Farming hookworms is also essential for educational purposes. Schools and universities might want to study these organisms to teach students about parasitology. However, farming them requires strict regulations and protocols to ensure safety and ethical considerations.
One fascinating aspect of farming hookworms is how it can aid in research about soil health and ecosystems. As researchers learn more about how these organisms interact with their environment, they can contribute to broader ecological understanding.
The Role of Hookworms in Medicine
Researchers are increasingly looking into hookworms for their potential *medicinal benefits*. Believe it or not, these pesky parasites might actually help in treating certain conditions! There’s a growing body of evidence suggesting that hookworms could play a role in reducing autoimmune diseases like asthma and allergies. The theory is that hookworms trick the immune system into a more balanced response, thus reducing overreactions often seen in these conditions.
This emerging field is often referred to as “helminth therapy.” Despite the potential advantages, the *idea of introducing* parasites into our bodies can be pretty daunting for many. This is where studying hookworms in captivity becomes crucial – researchers can conduct extensive testing and trials to ensure safety and efficacy.
Ethical Considerations
When talking about farming or studying hookworms, we can’t ignore the ethical implications. Each study or farming initiative must prioritize humane treatment and the welfare of the organisms involved. Researchers should aim to replicate natural conditions as closely as possible, ensuring the hookworms can thrive without suffering.
It’s also essential to consider the potential risks of using hookworms for treatment in humans. Any medical approach must be carefully regulated and monitored to avoid unintended consequences. Proper guidelines should be established to protect both the patients and the parasites.
Future Directions in Hookworm Research
Looking ahead, the future of hookworm research in captivity holds exciting possibilities. Scientists are continuously exploring new methods to study these parasites safely. Advances in technology, such as genomic studies, allow researchers to understand hookworm biology on a much deeper level.
Additionally, with the global focus on mental and physical health, there’s a growing interest in the *therapeutic potential* of hookworms. The concept of using them to treat various health issues will likely be pursued further. New studies might even emerge that focus on innovative ways to use hookworm farming to improve soil health or even contribute to biodiversity.
As this research progresses, it will be crucial to ensure that any applications are evidence-based and ethically sound. Collaborative research across different fields – from medicine to environmental science – can help unlock the secrets of hookworms while respecting their role in our ecosystems.
So, can hookworms be studied or farmed in captivity? Absolutely! While there are challenges and ethical considerations, understanding these fascinating creatures offers valuable insights into both human health and ecosystems. Their potential benefits and the fundamental science surrounding them are worth exploring. As research evolves, who knows what remarkable discoveries might emerge from studying these tiny, resilient survivors?
Next time you think about hookworms, remember that beneath their parasitic reputation lies a world of possibilities that could teach us much about healing and nature. Whether they’re helping us tackle health issues or enlightening us about ecosystems, hookworms are more than just parasites—they’re a gateway to understanding life in all its forms.