Imagine you’re in a cozy coffee shop, chatting about the fascinating life cycles and roles of worms in our ecosystems. You might be surprised to learn that roundworms are not just random squiggly creatures—they play a vital role in soil health and are vital for decomposing organic material. So, if you’ve ever wondered how roundworms compare to other worm species living in the same environment, you’re in for a treat. Let’s explore some of their most notable comparisons, diving deep into the lives of these squishy little organisms.
What Are Roundworms?
Roundworms are part of the phylum Nematoda and are a huge group of worms known for their cylindrical bodies. Unlike flatworms or segmented worms, roundworms have a smooth, elongated shape that gives them a unique appearance. You might find them in soil, fresh water, and even saltwater, making them incredibly versatile.
One fascinating aspect of roundworms is their *size diversity*. They can range from microscopic to several inches long. For example, the famous Caenorhabditis elegans, a tiny roundworm, is only about 1 millimeter long! Despite their small size and sometimes transparent appearance, they have a significant role in nutrient cycling, helping decompose organic matter. This might make you think about how tiny creatures can have such a big impact on ecosystems.
Honestly, if you took a closer look at the soil in your garden, you’d probably find thousands of roundworms hanging out. They help aerate the soil, allowing roots to access water and nutrients. This makes them crucial players in maintaining healthy plant growth!
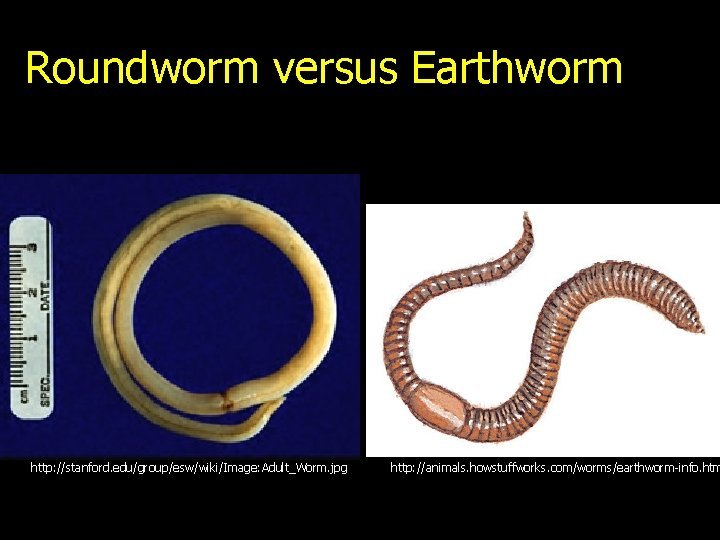
Roundworms vs. Earthworms
When comparing roundworms to earthworms, also known as annelids, you’re stepping into a world of differences. Earthworms are probably the most well-known type of worm out there, and for a good reason! They have segmented bodies, which gives them a distinct look and feel.
So, why does this matter? Segmentation allows earthworms to move with a unique flexibility. They can burrow deep into the soil, which helps aerate and enrich it. On the other hand, roundworms, lacking these segments, move through soil more like a slinky, wiggling along in a smooth motion.
Another key difference is their diet. Earthworms primarily eat decaying organic matter, while roundworms have a broader range of diets. Some are herbivores, eating plant roots, while others can be parasitic, living off hosts like animals or humans. It’s a wild world in the soil, and these dietary choices significantly impact their interactions with the environment.
You might also be surprised to learn that while both types of worms contribute to soil health, they do so in different ways. Earthworms focus on breaking down organic material, whereas roundworms help control pest populations by feeding on various microorganisms. Together, they maintain a balanced ecosystem, showcasing the beauty of biodiversity!
Roundworms vs. Flatworms
Looking at flatworms, or platyhelminthes, we see another layer of diversity in the worm family. Flatworms are, as the name suggests, flat and often come with a more complicated structure than roundworms. They can be found in freshwater, saltwater, and even as parasites within other animals. Think about those creepy tapeworms you hear about—that’s a type of flatworm!
One major difference lies in their body structure. Flatworms are often hermaphroditic, meaning they have both male and female reproductive organs, which makes reproduction fascinating and complex. Roundworms, on the other hand, typically have separate sexes—male and female.
Here’s the thing: while flatworms can have incredible regenerative abilities, like growing back lost body parts, roundworms are more resilient when it comes to tough environments. Some roundworms can survive extreme temperatures and pressures, making them some of the hardiest organisms on Earth. This resilience allows them to thrive in diverse habitats, from the deepest oceans to the soil in your backyard.
Understanding the differences between these worm types helps us appreciate their specific roles in ecosystems. While flatworms may dabble in parasitism, roundworms serve as essential players in nutrient cycling, showing how varied life can be down there in the dirt.
Roundworms and Their Intriguing Habitats
Roundworms can be found in various habitats, leading to fascinating interactions with other organisms. You might think the garden soil is their home ground, but they also thrive in marshes, ocean floors, and even compost heaps. These varied habitats provide a range of food sources, contributing to their adaptability and resilience.
In aquatic environments, roundworms play a crucial role in maintaining the health of ecosystems. They help decompose organic material—think dead fish or fallen leaves—turning it into nutrients that plants can use. In freshwater habitats, they often coexist with other microorganisms, participating in a complex food web that keeps the ecosystem balanced.
You might be surprised by how many roundworm species exist. Some estimates suggest there could be over a million species of nematodes, with thousands yet to be discovered. This incredible diversity means that they can adapt to almost any environment, making them a vital component of ecosystems across the globe.
The Role of Roundworms in Soil Fertility
Let’s talk about the nitty-gritty details of how roundworms contribute to soil health. You might not realize this, but these tiny creatures are like the unsung heroes of the gardening world. They help break down organic materials, speeding up decomposition. This process enriches the soil with nutrients, making it more fertile for plants to grow.
When roundworms feed on bacteria and fungi, they release nutrients such as nitrogen back into the soil. This not only benefits plants but also helps maintain a balanced microbial community. With their help, your garden can thrive, potentially leading to better yields and healthier plants.
You could think of roundworms as nature’s recyclers. They ensure that nothing goes to waste. By breaking down dead plant and animal matter, they contribute to a cycle that keeps the soil rich and full of life. If you’re ever in doubt about the importance of these little worms, just look at the plants thriving in well-maintained gardens—they owe a lot to roundworms!
In exploring the lives of roundworms and how they compare to other worm species, we uncover a rich tapestry of life that thrives beneath our feet. From their unique characteristics and habitats to their vital roles in ecosystems, roundworms are fascinating creatures worthy of our attention.
So, the next time you see a roundworm wriggling through the soil, remember that it’s more than just a squishy little thing. It’s a key player in maintaining the balance of our ecosystems. Whether they’re working alongside earthworms or competing with flatworms, roundworms continue to show us just how interconnected life is. Let’s appreciate these small yet mighty creatures that make our world a better place, one nutrient at a time!

