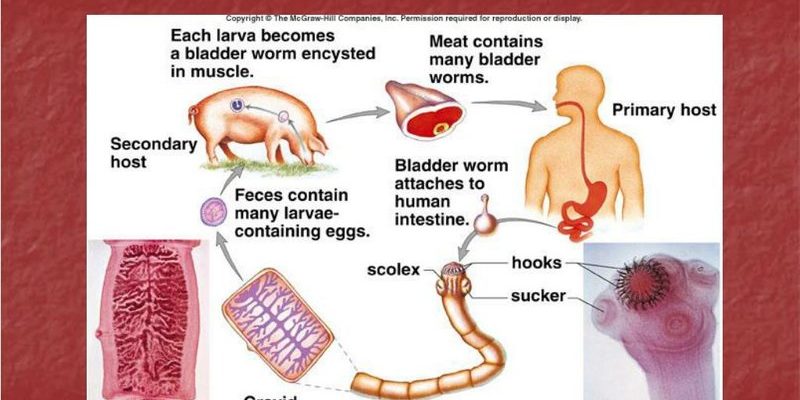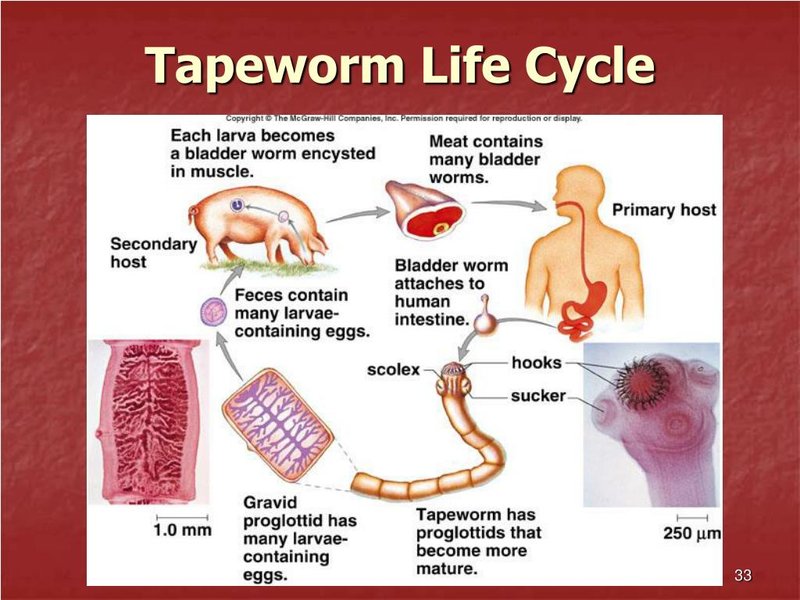
Imagine sitting in a café and discussing how these creatures begin their lives as tiny larvae, transforming into the fascinating adults we often overlook. The life cycle of flatworms is a blend of unique stages, each bringing out different behaviors and adaptations. So, grab a cup of coffee, and let me take you through the captivating journey of flatworms from start to finish!
What are Flatworms?
Flatworms, or *Platyhelminthes*, are soft-bodied invertebrates that come in many shapes and sizes. You might find them in marine, freshwater, or even moist terrestrial environments. Their flat shape—hence the name—allows them to thrive in various habitats. These creatures can be as small as a few millimeters or grow to impressive lengths, like the tapeworms that can span several meters in a host’s intestines.
There are three main classes of flatworms: Turbellaria (mostly free-living), Trematoda (parasitic flukes), and Cestoda (tapeworms). Most people encounter flatworms when they observe aquatic ecosystems or even when dealing with parasite infections in animals and humans. Understanding their life cycle is essential not just for biology enthusiasts but also for anyone interested in the balance of ecosystems and the health of both animals and humans.
The Stages of Flatworm Development
Flatworms go through distinct stages in their life cycle, each marked by changes in form and behavior. Typically, these include the egg stage, larval stage, and adult stage. Let’s break down each one:
1. Egg Stage
The life of a flatworm begins when an adult lays eggs. These eggs are often encased in a protective layer, which helps safeguard the developing embryos from predators and environmental stressors. Depending on the species, you might find individual eggs or clusters that look like tiny jellybeans.
These eggs can take several days to weeks to hatch, influenced by temperature and water conditions. Here’s the thing: the environment they hatch into can significantly affect their survival. If conditions are favorable, the embryos develop into larvae, ready to embark on their next stage.
2. Larval Stage
Once the eggs hatch, flatworm larvae emerge. The most common form of larva you’ll encounter is the miracidium, which is often ciliated, allowing it to swim through water. This stage is crucial, especially for parasitic flatworms. They seek out specific host organisms to continue their development.
Think about it: if you’re a larva looking for a host, it’s like trying to find the right place to crash at a party! Once they find a suitable host, the larvae can transform into a more complex form, like sporocysts or rediae, depending on their species.
3. Juvenile Stage
After the larval stage, flatworms transition into their juvenile phase. This stage often involves dramatic changes in structure and behavior. The flatworm starts to develop the characteristics of an adult but is not yet fully mature. They’ll begin to feed more actively, often on detritus or small organisms, as they grow larger.
During this phase, they may also start to exhibit some turf battles with others of their species or different aquatic organisms. It’s a fascinating sight—like a miniature battlefield, with flatworms asserting their dominance in their little world.
4. Adult Stage
The final stage is adulthood. Adult flatworms have fully developed reproductive systems. Depending on their environment, they can be hermaphroditic, meaning each individual has both male and female reproductive organs. This adaptability is crucial, especially in environments where mates might be scarce.
Adult flatworms are often predators or scavengers, consuming a variety of small organisms. Their behaviors can vary widely; some species are more active hunters, while others might prefer to remain hidden and ambush their prey.
Behavioral Traits of Flatworms
Flatworms are not just passive creatures drifting through their environments; they exhibit some interesting behaviors. Here’s a look at a few key traits:
Movement
Flatworms have a unique way of moving that can be mesmerizing to watch. They use muscle contractions to glide across surfaces, pushing their bodies in a wave-like motion. This movement not only helps them navigate their environment but also aids in the search for food and the evasion of predators.
Some species can even regenerate lost body parts, which is extraordinary! Imagine losing a part of your arm and growing it back. It’s part of their survival strategy, especially when faced with danger.
Feeding Habits
Flatworms are diverse in their feeding habits. Some are carnivorous, actively hunting down smaller organisms, while others are more opportunistic, consuming decomposing matter. They often have a pharynx that they extend to suck food into their bodies, kind of like a mini vacuum cleaner.
Here’s an interesting tidbit: some flatworms can survive in low-oxygen environments. They’ve adapted to eat whatever nutrients are available, which is essential for their survival in harsh habitats.
Reproductive Behavior
Reproduction is another area where flatworms show fascinating behavior! Many flatworm species are hermaphroditic, which means they can mate with any other flatworm they encounter. This ability increases their chances of finding partners, especially in environments where population density may be low.
During mating, flatworms engage in a unique ritual that includes intertwining their bodies. After successful mating, each flatworm can lay eggs in protective capsules. This reproductive strategy ensures the continuation of their species, regardless of environmental challenges.
The life cycle of flatworms is an incredible journey filled with unique stages and behaviors. From tiny eggs to vibrant adults, each phase contributes to the overall survival and adaptability of these fascinating creatures. Whether they’re cruising through freshwater ponds or hiding in the sand, flatworms play essential roles in their ecosystems.
Understanding their life cycle not only deepens our appreciation for them but also highlights their importance in the natural world. So, next time you encounter a flatworm, remember the remarkable journey it has traveled to become the creature you see!