So, what exactly happens when wolf worms decide to take up residence in a host? It’s a bit like a surprise party gone wrong. The host is often blissfully unaware of the invasion until things start to get uncomfortable. As we dig deeper into wolf worm behavior, especially how they interact with host tissues, you’ll understand why this unusual phenomenon is both captivating and, at times, alarming.
What Are Wolf Worms?
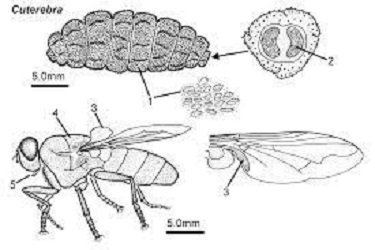
To set the stage, let’s clarify what wolf worms actually are. These critters are the larval form of **botflies**, primarily from the genus *Cuterebra*. They can be found in various environments, often preying on small mammals like rodents or rabbits. Once an adult botfly lays its eggs near a potential host, the larvae hatch and wiggle their way into the host’s skin. It’s as if they’re waiting for the right moment to sneak in.
This sneaky entry typically happens through wounds or when the host brushes against the eggs. At this point, you might be wondering just how these little guys manage once they’re inside. Well, think of them as houseguests who are not just staying for the weekend—they’re settling in for quite a while!
How Do Wolf Worms Interact with Host Tissues?
Once the wolf worm is inside the host, it doesn’t just hang out idly. It engages in some pretty fascinating behaviors as it interacts with the host’s tissues. Initially, the larva starts to burrow into the skin, creating a small cavity where it can develop. This is where the party truly begins.
The larva feeds on the host’s tissues and fluids, and while this sounds a bit gruesome, it’s a survival mechanism for the worm. As the larva grows, it releases certain substances that can manipulate the host’s immune response. This is like a magician’s trick, where the worm distracts the host’s immune system—making it less likely to attack.
Alongside that, the larva creates a unique breathing hole to the outside world, allowing it to take in air while remaining snug in its cozy home inside. Isn’t that something? It’s a complex relationship, one that raises questions about the balance of life and survival.
The Stages of Wolf Worm Development
The life cycle of a wolf worm is fascinating and consists of several stages. Initially, after entering the host’s tissue, the larva will go through a rapid growth phase. During this period, it can grow significantly in size, sometimes as much as 2 inches long.
1. **Egg Stage**: This is when the adult botfly lays eggs, usually near the host.
2. **Larval Stage**: After hatching, the larvae enter the host tissue. This stage can last several weeks.
3. **Pre-Pupal Stage**: Once fully grown, the larvae will exit the host to pupate in the soil.
4. **Adult Stage**: Finally, they emerge as adult flies, ready to continue the cycle.
Each stage of their development is finely tuned to ensure their survival and reproduction. It’s a masterclass in adaptability and resilience, showcasing how life can flourish even in challenging circumstances.
Impact on Host Health
Now you might be wondering, what does this mean for the host? The presence of wolf worms can lead to various health issues, depending on the severity of the infestation. The initial symptoms might be mild, like a small lump or swelling at the entry site. But as the larva grows and feeds, it can cause more serious complications.
Some common impacts include:
- Localized Infection: The host’s immune system may respond to the worm, leading to inflammation and infection.
- Pain and Discomfort: As the worm burrows deeper, it can cause significant pain, much like a thorn digging into your skin.
- Secondary Infections: Open wounds can become susceptible to other infections, complicating the host’s health further.
It’s essential for hosts (or pet owners) to pay attention to any unusual signs. Early intervention can make a huge difference, preventing any long-term harm.
How Do Hosts Defend Against Wolf Worms?
While the host’s body isn’t equipped to eliminate the wolf worms entirely, it does put up a fight. As mentioned earlier, the immune system tries to respond by sending white blood cells to the area, creating inflammation. But here’s the twist—the wolf worm’s ability to manipulate this response means the host often loses the battle, at least for some time.
However, there are some actions that hosts can take to defend against these invaders:
1. **Grooming**: Regular grooming helps to remove eggs or larvae before they can enter the skin.
2. **Avoiding High-Risk Areas**: Staying away from places known for high botfly populations can reduce the chances of infestation.
3. **Seeking Veterinary Care**: For pets, routine vet check-ups can catch issues early.
Taking proactive steps can make a world of difference in keeping these pesky worms at bay.
Exploring wolf worm behavior in host tissue offers a glimpse into the intricate dance of life and survival in nature. Understanding this relationship not only sheds light on the challenges that hosts face but also highlights the incredible adaptability of these little invaders.
While the notion of a creature living inside another can be unsettling, it’s a testament to how varied and fascinating life can be. Whether it’s a wild animal in the forest or a beloved pet, awareness and knowledge can make all the difference. Embrace the curiosity, and who knows? You might just find yourself captivated by the wonders of nature, even in its most unexpected forms!
