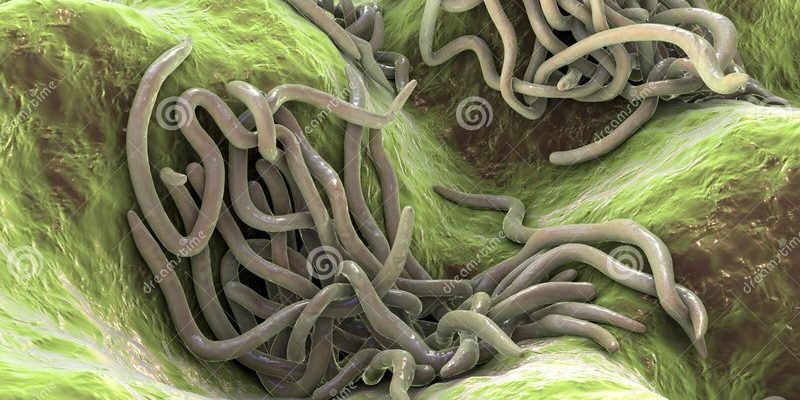
So, what exactly are wolf worms, and why should you care? Well, they might not be the most glamorous creatures in the animal kingdom, but these tiny invaders can tell us a lot about how ecosystems function. Their relationship with other organisms, including hosts and other parasites, plays a vital role in maintaining the balance of our natural world. Let’s dig deeper into the intriguing life of wolf worms and their ecosystem role.
What Are Wolf Worms?
Wolf worms are unique parasites primarily found in the larvae of certain insects, notably the *Hymenoptera* order, which includes wasps and bees. They’re not the kind of worms you might find in your garden; instead, they thrive as **internal parasites**. When we refer to wolf worms, we’re usually talking about the larvae of the bot fly species, which enter their host while they’re just getting started in life.
Once wolf worms manage to infiltrate their host, they embark on a rather gruesome journey. They burrow into the flesh, feeding on living tissue and causing quite a bit of discomfort for their unsuspecting hosts. Picture an unwelcome guest making themselves too comfortable in your living room. It’s not a pretty picture, right? But this behavior is essential for their survival, as they need nutrients to grow and eventually mature.
You might be wondering why we should care about these rather unseemly creatures. Wolf worms are part of a larger cycle of life, contributing to the parasitic dynamics that govern various ecosystems. In other words, they play a role in keeping populations of certain insects in check while providing nourishment for themselves.
The Lifecycle of Wolf Worms
Understanding the **lifecycle of wolf worms** is crucial to appreciate their role in ecology. They begin as eggs, laid by adult bot flies on specific host organisms. Once the eggs hatch, the tiny larvae penetrate the host’s skin, usually during the warmer months when the host is most active.
This initial stage is where the real fun begins for the wolf worms. They burrow into the host’s body, feeding off its tissue. It’s a bit like a parasite buffet! This phase can last several weeks to months, as the larvae grow larger and develop into mature parasites. Eventually, the wolf worms emerge from their host to pupate in the soil, ready to become adult flies themselves.
Interestingly, this lifecycle has an impact on the health of the host. While wolf worms can be harmful, causing infections or even death in extreme cases, their presence can help regulate insect populations. It’s a delicate balance, showcasing nature’s complex web of interactions.
Wolf Worms’ Impact on Hosts
You might think that wolf worms are nothing but bad news for their hosts, and you’d be right in many cases. However, there’s more to the story. While these parasites create significant health risks, such as infections and tissue damage, they also have some surprising ecological roles.
For instance, by targeting weaker individuals in a population, wolf worms can inadvertently promote healthier genetic pools. When sick or weak insects are out of the picture, it helps ensure that the remaining population is more robust and resilient. Thus, while wolf worms can cause problems, they also assist in maintaining the overall health of insect populations over time.
There’s also the aspect of *co-evolution*. Hosts develop defenses against their parasites, leading to an arms race of sorts. As wolf worms evolve, so too do the defenses of their hosts. This ongoing dynamic is crucial for the evolution of both the parasites and their hosts, influencing biodiversity.
Role of Wolf Worms in the Ecosystem
Now, let’s talk about the broader implications of wolf worms in ecosystems. Their presence is a reminder of how interconnected life can be; when one species thrives, it can influence many others. Wolf worms contribute to the intricate *food web* that sustains various organisms.
Besides controlling insect populations, wolf worms serve as a food source for other animals. Birds, for instance, may prey on infected insects, providing a natural balance in their ecosystems. This relationship demonstrates how one organism’s parasite can ultimately nourish another, showcasing the non-linear paths in nature.
Moreover, in some ways, wolf worms can help scientists study ecological health. By observing the prevalence of parasites like wolf worms, researchers can gauge the overall health of certain insect populations and ecosystems. Healthy ecosystems tend to have a balance of parasites and hosts, making these worms indicators of larger ecological trends.
Wolf Worms and Human Health
While wolf worms mainly target insects, their existence raises some questions about human health and safety. In some parts of the world, bot fly larvae can even infect humans, leading to a condition known as **myiasis**. Luckily, these instances are rare.
However, it’s essential to understand the implications of parasites like wolf worms in public health. They can carry diseases or trigger inflammatory responses in human hosts, leading to discomfort and sometimes requiring medical intervention. Awareness and education about such parasites are vital to help prevent infections in vulnerable populations.
Here’s the thing: while wolf worms may not directly affect our daily lives, they are part of the complex tapestry of life that includes us. Understanding their role helps in appreciating the delicate balance of ecosystems and the potential impacts on human health.
So, what do wolf worms really teach us? They remind us that every creature, no matter how small or seemingly insignificant, plays a role in the grand scheme of life. From their lifecycle to their impact on hosts and the ecosystem, wolf worms are a perfect example of the intricacies of **parasite ecology**.
These tiny invaders may cause distress, but they also contribute to the health and balance of the environments they inhabit. If we can learn to appreciate their role, we start to see the beauty in the chaotic dance of life—where parasites and hosts coexist, influencing one another in ways that are essential for the sustainability of life on Earth.
Understanding these dynamics not only deepens our appreciation for nature but also helps us advocate for healthy ecosystems. And who knows? Next time you come across a worm—likely squiggling in the soil—you might just think of the complex story it has to tell.