Hornworms, particularly the species known as the *Manduca sexta*, undergo fascinating transformations as they transition from caterpillars to moths. Just like how we all go through stages in life—learning, growing, and transforming—hornworms experience their own journey. Let’s break down this lifecycle and see how hornworms fit into the larger picture.
What Are Hornworms?
Hornworms are the larval stage of certain moths, specifically the *Hawkmoths*. They get their name from the prominent horn-like structure on their rear end, which can look pretty intimidating for such a small creature. But don’t worry! These little guys are more about munching on plants than causing a ruckus.
Typically, hornworms are green, which helps them blend in with the leaves of the plants they eat. This camouflage is essential for avoiding predators, just as we might hide to avoid an awkward conversation at a party. However, their color makes them a favorite treat for larger animals, like birds and wasps, who are always on the lookout for a meal.
So, what do hornworms eat? Well, they primarily munch on the leaves of tobacco and tomato plants. You might have heard about gardeners battling these pests, as they can quickly destroy a garden by devouring the foliage. But they’re not just pests; they play a vital role in the ecosystem.
Life Stages of Hornworms
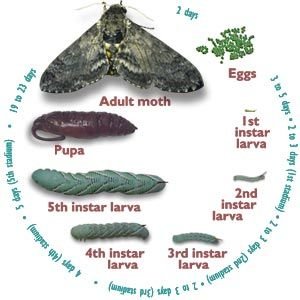
Hornworms go through several life stages before becoming moths. Think of it like a video game where each level presents new challenges and opportunities. Let’s break it down:
1. **Egg Stage**: The lifecycle begins when a female moth lays eggs on the host plant. These eggs are tiny and often blend seamlessly with the leaves, making them hard to spot.
2. **Caterpillar Stage**: Once the eggs hatch, tiny hornworms emerge and start munching away. As they grow, they’ll shed their skin multiple times—a process known as molting. Each time they molt, they grow larger and take on a slightly different appearance.
3. **Pupal Stage**: After reaching their maximum size, hornworms will find a safe spot to pupate. Here, they go into a sort of suspended animation, undergoing intense changes. This stage is akin to a teenager figuring out who they want to be, preparing to emerge as an adult.
4. **Adult Moth Stage**: Finally, the adult moth breaks free from the pupal casing, ready to take on the world. They’ll spend the next few weeks searching for mates and laying eggs, continuing the cycle.
This transformation highlights the idea of change and growth. Just as we learn and adapt throughout life, hornworms undergo significant changes on their journey to becoming moths.
The Importance of Hornworms in the Ecosystem
Hornworms might seem like mere garden nuisances, but they’re more important than we think. They serve several roles in the ecosystem:
– **Food Source**: Hornworms are a food source for various predators, including birds and beneficial insects. By supporting these animals, hornworms contribute to the balance of the ecosystem.
– **Pollination**: Once they become moths, they can help pollinate flowers while they feed on nectar. Just as a friend might help bring together people at a party, moths play a role in connecting plants and their pollinators.
– **Soil Enrichment**: When hornworms and other larvae decomposed, they contribute organic material to the soil. As they break down, they enhance soil quality, benefiting plants and the entire ecosystem.
Understanding the role of hornworms helps us appreciate the delicate balance of nature, where each creature, big or small, plays a part in the bigger picture.
Challenges Faced by Hornworms
Despite their crucial role, hornworms face challenges, much like we do in our lives. Some of these challenges include:
– **Predation**: As we mentioned earlier, hornworms are preyed upon by birds, wasps, and other animals. Their green coloration helps them hide, but it’s not foolproof.
– **Diseases and Parasites**: Hornworms can fall victim to various diseases and parasites, including bacteria and viruses. For example, parasitic wasps lay their eggs inside hornworms, and when the larvae hatch, they consume the caterpillar from the inside out.
– **Environmental Changes**: Just like we’re affected by climate change, hornworms are also impacted by changes in their environment. Extreme weather, habitat destruction, and pesticide use can drastically reduce their populations, impacting the entire lifecycle.
By exploring these challenges, we can better understand and appreciate these creatures and the struggles they face in their journey to adulthood.
The journey of hornworms encapsulates the essence of transformation and growth. From tiny eggs to voracious caterpillars and then to majestic moths, each stage plays a critical role in the overall lifecycle.
By understanding the role of hornworms in the moth lifecycle, we can cultivate a deeper appreciation for nature and all its intricacies. Just like in our lives, every stage is essential, whether it’s the beginning, the growth, or the transformation into something beautiful. Let’s cherish these remarkable creatures and the essential roles they play in our ecosystems.
