Think of ribbon worms as the behind-the-scenes workers of the ocean. Just like the roots of a tree help it thrive by holding soil in place and providing nutrients, ribbon worms contribute to the marine ecosystem by participating in various food webs and helping decompose organic matter. In this article, we’re going to explore just how important these creatures are and what roles they play in our coasts and oceans.
What Are Ribbon Worms?
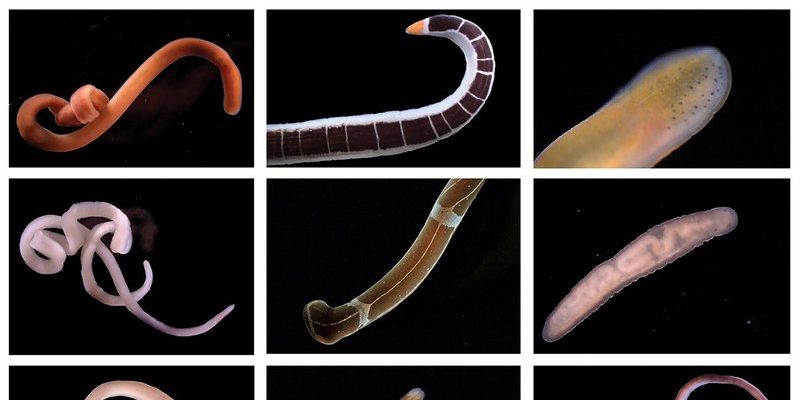
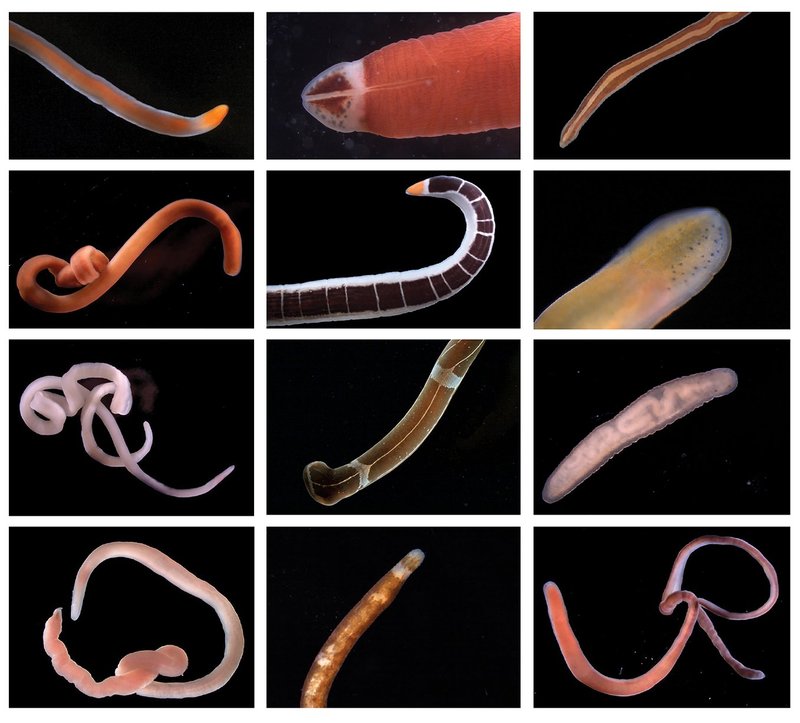
Ribbon worms, or *Nemertea*, are a diverse group of marine organisms known for their elongated, flat bodies. Some species can stretch to impressive lengths—up to 30 meters! They typically live in sandy or muddy substrates along coastlines and are often found in tidal zones. With a variety of colors and textures, they can blend seamlessly into their surroundings, making them a bit tricky to spot.
These worms are unique in their physical structure, featuring a specialized organ called a proboscis. This organ can be extended to catch prey, which often includes small crustaceans and other soft-bodied animals. Imagine a tiny, underwater ninja, stealthily catching its dinner! This predatory behavior not only helps the ribbon worms thrive but also helps control populations of their prey, maintaining a balanced ecosystem.
The Role of Ribbon Worms in the Food Web
You might be wondering, “What does all this mean for coastal ecosystems?” Well, ribbon worms are key players in the coastal food web. They serve as both predators and prey, making them vital for the survival of various marine species.
- Predators: As hunters, ribbon worms help keep the populations of their prey in check. By consuming small animals, they play a part in controlling species that could otherwise become too abundant.
- Prey: In turn, these worms are also food for larger predators like fish, birds, and crabs. So, when you think of ribbon worms, think of them as a tasty snack for those higher up in the food chain.
In this way, ribbon worms help maintain the balance of the ecosystem, ensuring that no single species dominates the area. This balance is crucial for the health of coastal and marine environments. If ribbon worm populations were to decline, it could lead to an overpopulation of their prey, which might harm vegetation and other species that rely on a stable ecosystem.
The Contribution to Nutrient Cycling
One of the *less obvious* but equally important roles of ribbon worms is their contribution to nutrient cycling. As they consume organic matter, they help break it down and recycle nutrients back into the ecosystem. This process is essential for maintaining soil and water quality.
When ribbon worms feed, they often consume decaying plant material or dead organisms. By breaking these materials down, they help release nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus back into the water and sediment. These nutrients are vital for the growth of algae and plants, which serve as the foundation for the entire marine food web.
Imagine a recycling system in the ocean, where ribbon worms act as the workers that break down and repurpose waste for use by other species. Without them, the ocean would struggle to maintain its nutrient balance, affecting everything from tiny plankton to larger marine animals.
Impact on Coastal Habitats
In addition to their role in food webs and nutrient cycling, ribbon worms also impact the physical environment of coastal habitats. Their burrowing activities can help aerate the sediment, making it easier for other organisms to thrive.
The Burrowing Behavior
When ribbon worms dig into the sand or mud, they create spaces that allow water and nutrients to circulate more freely. This aeration is beneficial for other organisms, such as fish and invertebrates, that rely on healthy sediment for survival. It’s like turning over a garden bed to ensure that every plant gets the nutrients it needs to grow.
This behavior can also help create a more stable environment overall. By mixing up the sediments, ribbon worms contribute to preventing erosion and maintaining the integrity of coastal habitats. Their activities can even encourage the growth of beneficial microorganisms that further support the ecosystem.
Threats to Ribbon Worm Populations
Despite their importance, ribbon worms face several threats in today’s changing environment. From pollution to habitat destruction, these factors can severely impact their populations.
One major concern is **pollution**. Chemicals from agricultural runoff, plastic waste, and other pollutants can harm ribbon worms and their habitats. Since they live in the sediments where pollutants accumulate, they are often some of the first species to show signs of distress.
Another significant threat is **habitat destruction**. Coastal development, such as the construction of marinas or overfishing, can disrupt the places where ribbon worms thrive. When their habitats are damaged, it’s not just the ribbon worms that suffer—many other marine species also feel the impact.
Conservation Efforts for Coastal Ecosystems
Given the crucial role that ribbon worms play, it’s essential to understand how we can help protect them and the ecosystems they support. Many conservation efforts focus on preserving coastal habitats and reducing pollution.
- Establishing marine protected areas: These protected zones can help maintain healthy habitats where ribbon worms and other marine species can thrive without the pressures of human activity.
- Reducing pollution: Initiatives aimed at reducing plastic waste, controlling agricultural runoff, and improving waste management can help improve the overall health of coastal ecosystems.
By taking these steps, we can ensure that ribbon worms continue to play their vital role in our oceans for generations to come.
In conclusion, ribbon worms are not just fascinating creatures to observe; they are vital players in our coastal ecosystems. From their roles in the food web to their contributions to nutrient cycling and the physical environment, these worms help maintain the delicate balance of marine life.
By understanding and protecting ribbon worms and their habitats, we can contribute to the health of our oceans and the many species that rely on these ecosystems. So, the next time you’re near the coast and spot one of these long, squiggly creatures, take a moment to appreciate the essential role they play in the underwater world. Together, we can help ensure that they continue to thrive and support the vibrant life around them.