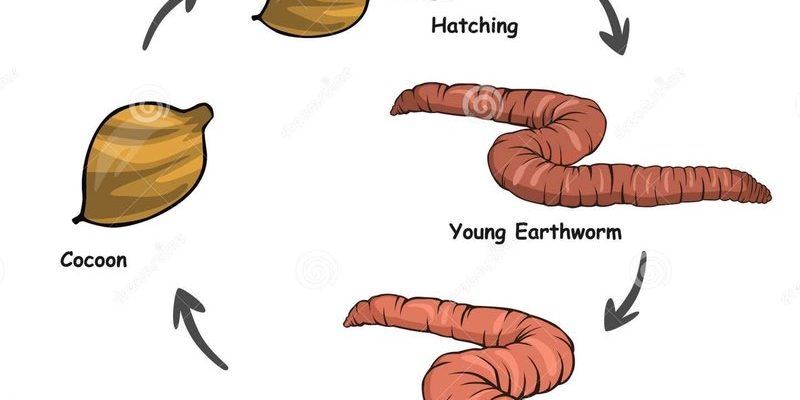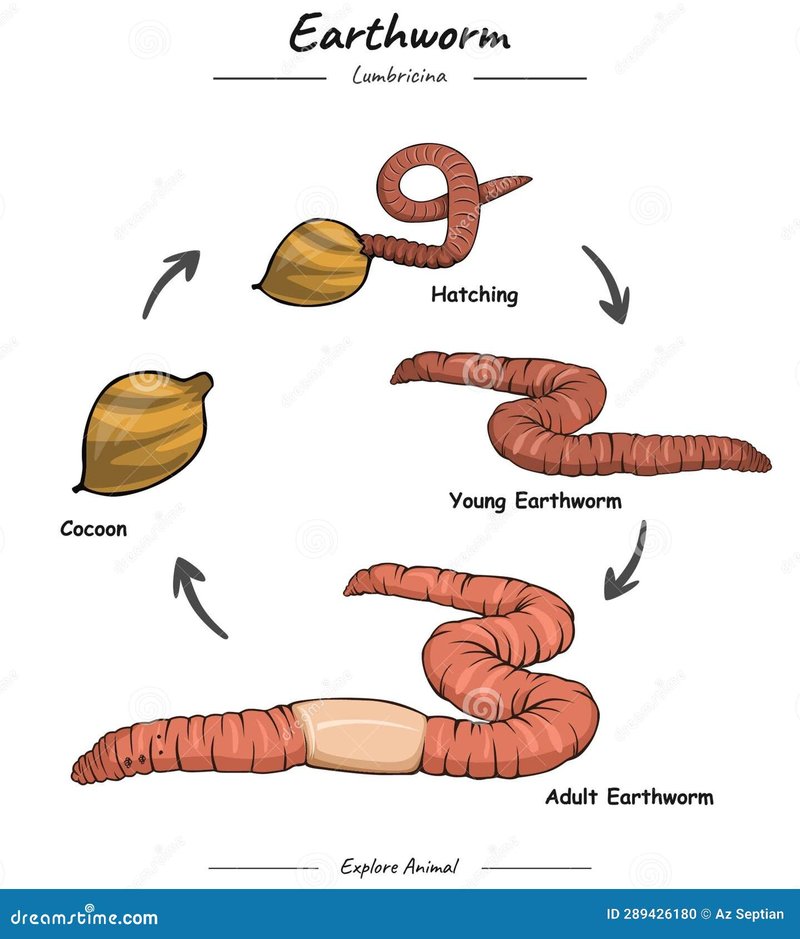
The lifecycle of a common earthworm is a journey of transformation, resilience, and essential ecological roles. Just like us, earthworms go through stages, from tiny hatchlings to robust adults. Let’s dig into their lifecycle and see why these squishy little allies are so important for our environment!
1. The Earthworm’s World
Before diving into the lifecycle, it’s helpful to understand where earthworms thrive. These creatures inhabit moist, nutrient-rich soil, often in gardens, forests, and fields. They play a vital role in maintaining soil health by aerating it and promoting plant growth.
Earthworms prefer dark, damp environments and can be found anywhere with organic material to consume. Picture them as the unsung heroes of your garden, working tirelessly beneath the surface. They consume decaying leaves, vegetables, and organic matter, breaking it down into nutrient-rich compost. So, when you see an earthworm, think of it as a mini gardener helping plants grow strong!
2. The Beginning: Eggs and Hatchlings
The lifecycle of an earthworm begins with reproduction. Most common earthworms are **hermaphrodites**, meaning each worm has both male and female reproductive organs. During mating, two earthworms exchange sperm. After this, each worm produces a cocoon, which is a small, transparent pouch that holds the eggs.
Inside this cocoon, the fertilized eggs develop. It typically takes about two to three weeks for the eggs to hatch, depending on environmental conditions like temperature and moisture. When they emerge, the baby earthworms are incredibly tiny—only a few millimeters long! Can you imagine being born that small?
Hatchlings are initially white and soft, gradually darkening as they mature. They begin eating organic material and burrowing into the soil almost immediately. This is their first step into a life filled with adventure below the ground!
3. Growing Up: Juvenile Stage
After hatching, earthworms enter the juvenile stage, which lasts for several months. During this time, they grow rapidly, feeding on organic matter and soil as they dig their burrows. Think of this phase as a toddler exploring their surroundings, constantly learning and developing.
Juvenile earthworms grow by shedding their skin in a process called *ecdysis*. As they grow, they become more adept at absorbing nutrients from the soil, helping them build strength and size. They also start to develop their reproductive organs, preparing for adulthood.
Here’s the thing: the growth rate of earthworms can be influenced by several factors, including soil type, temperature, and moisture levels. In ideal conditions, an earthworm can grow quite quickly, sometimes reaching full size in just a few months!
4. The Adult Earthworm: Reproductive Stage
Once earthworms reach maturity, usually between 6 to 12 months, they are ready to reproduce. Adult earthworms can live for several years, depending on their environment and predators. They reach a length of about 4 to 8 inches, with some species growing even longer!
In this stage, earthworms are on the lookout for partners to mate with. As they engage in mating rituals, they exchange sperm and create those precious cocoons for the next generation. It’s a cycle that keeps on giving.
Interestingly, while some earthworms can survive in harsh conditions, their ideal environment is moist and nutrient-rich. If the soil dries out, they can become inactive or even die. This is why gardeners often find them after heavy rains—they’re not just moving around; they’re also actively searching for food in damp soil!
5. The Importance of Earthworms in Ecosystems
Earthworms may seem small, but their impact on the environment is enormous. They help break down organic matter, improve soil structure, and enhance nutrient availability for plants. This makes them crucial players in our ecosystems.
In fact, healthy soil ecosystems are teeming with life, and earthworms significantly contribute to soil fertility. By aerating the soil through their burrowing, they allow air and water to reach plant roots more easily. This process prevents compaction and helps sustain healthy plant life.
When you think about why healthy gardens grow well, remember earthworms! They’re like tiny tillers working away, ensuring that plants have what they need to thrive.
6. Common Threats to Earthworm Populations
Despite their resilience and adaptability, earthworms face several threats. One of the biggest is habitat loss due to urbanization and agricultural practices. Pesticides and fertilizers can also harm their populations, leading to declines in soil health.
Invasive species pose another challenge, often outcompeting native earthworms for resources. Additionally, climate change can disrupt the delicate balance of soil ecosystems, affecting earthworm survival.
It’s essential to protect these little creatures as they play such a vital role in our environment. Simple actions, like planting native plants and reducing chemical use in gardens, can help create a safe haven for earthworms and promote a healthy ecosystem.
7. Fascinating Facts About Earthworms
Earthworms are full of surprises. Here are some fun facts that might just make you appreciate these slimy beings even more:
- Earthworms can regenerate: If an earthworm loses its tail, it can grow back!
- They breathe through their skin: Earthworms don’t have lungs; they absorb oxygen through their moist skin.
- Some can live for several years: In the right conditions, earthworms can live up to eight years!
- They can eat their own weight: An adult earthworm can consume about its own weight in organic matter each day.
These little facts reveal just how quirky and interesting earthworms really are.
The lifecycle of a common earthworm is a remarkable journey full of growth, adaptation, and ecological importance. From hatching tiny eggs to becoming vital players in soil health, these creatures remind us of the interconnectedness of life.
So, the next time you spot an earthworm in your garden or during a nature walk, take a moment to appreciate the incredible journey this small creature has taken. They may seem simple, but their role in our ecosystems is anything but! By understanding and valuing earthworms, we contribute to a healthier planet for ourselves and future generations.
Whether you’re a gardener, a student, or simply someone curious about nature, earthworms offer a fascinating glimpse into the natural world. So let’s give them a little love—after all, they’re working hard beneath our feet!