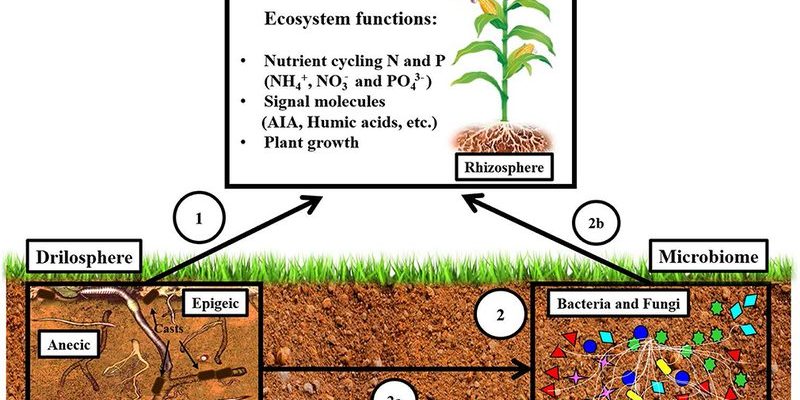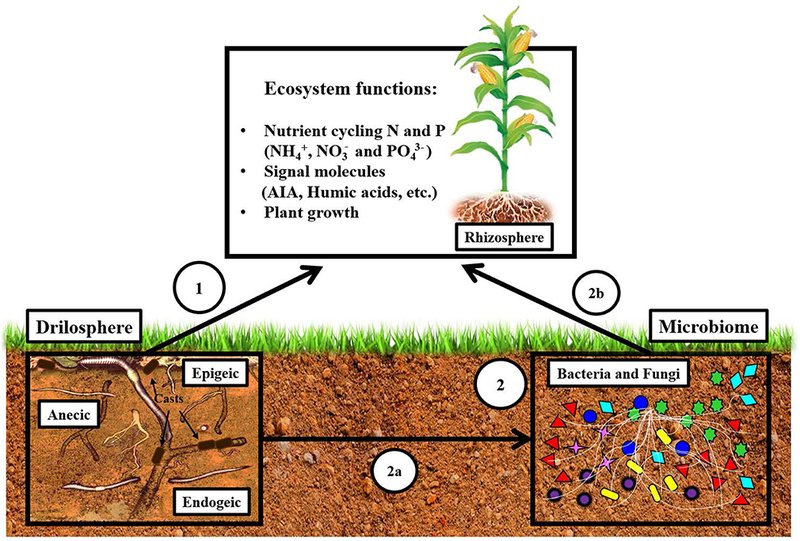
When you dig into the ground and disturb the soil, it’s easy to forget what’s happening down there. Earthworms are busy munching on organic material, aerating the soil, and promoting a bustling community of microbes. These microbes are like the unsung heroes of plant health. They break down nutrients and help plants absorb what they need to thrive. So, understanding the impact of earthworms on soil microbial life isn’t just a science project; it’s crucial for anyone who cares about gardening, farming, or even just enjoying a lush backyard.
In this article, we’ll explore the fascinating relationship between earthworms and the microorganisms that call the soil home. From their benefits in enhancing soil fertility to how they affect the ecosystem, I’ll break it all down for you. Ready? Let’s dig in!
What Are Earthworms and Why Do They Matter?
At first glance, earthworms might not seem that important. After all, they’re just squirming little creatures, right? But here’s the thing: they’re nature’s recyclers. Earthworms consume dead plant material, leaves, and other organic matter, turning that waste into nutrient-rich castings. This process not only enriches the soil but also creates a fantastic environment for soil microbes.
These castings are packed with essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium—key ingredients for plant growth. When earthworms burrow through the soil, they create channels that help improve soil structure. This allows air, water, and nutrients to move more freely, which is crucial for both plant roots and microbial life.
Moreover, earthworms promote a healthy microbial environment. They don’t just provide nutrients; their movement helps mix organic matter into the soil, ensuring that the microbes have access to food and oxygen. The more earthworms there are, the better the microbial community thrives.
How Earthworms Enhance Soil Microbial Diversity
One of the coolest things about earthworms is how they contribute to soil microbial diversity. Imagine a bustling city full of different people, each doing their own thing. That’s what a healthy soil ecosystem looks like. Earthworms help create habitats for diverse microbial life, which includes bacteria, fungi, and protozoa.
When earthworms break down organic matter, they make nutrients available to various microbes in a form that’s easy for them to use. Different types of microorganisms prefer different conditions, and earthworms help create a mix of environments by aerating the soil and increasing moisture levels. This means there’s a niche for everyone, whether it’s bacteria that thrive in high nitrogen or fungi that prefer slightly acidic conditions.
Furthermore, as earthworms move through the soil, they bring organic matter down from the surface into deeper layers. This mixing action supports a wider variety of microorganisms, which can lead to greater resilience in the soil ecosystem. A diverse microbial community can better withstand diseases and environmental stressors, just like a diverse team can tackle challenges more effectively.
The Role of Microbes in Soil Health
Now that you understand how earthworms contribute to microbial diversity, let’s dive into the roles these microbes play. Microorganisms in the soil are not just passive residents; they are active participants in the ecosystem. They help decompose organic matter, breaking it down into simpler compounds plants can absorb.
Bacteria, for example, are incredible at breaking down complex organic materials into simpler nutrients. They also play a key role in the nitrogen cycle, converting atmospheric nitrogen into forms plants can use. Fungi, on the other hand, form partnerships with plant roots, enhancing nutrient uptake and improving plant health.
Additionally, microbes help suppress plant diseases by outcompeting harmful pathogens. When the microbial community is healthy and diverse, it creates a balanced environment that supports plant growth and reduces the chances of disease outbreaks. This is particularly important for farmers and gardeners looking to maintain healthy plants without relying too heavily on chemical fertilizers or pesticides.
Earthworms and Nutrient Cycling
When we talk about the impact of earthworms on soil microbial life, we can’t ignore their role in nutrient cycling. Nutrient cycling is the process by which nutrients are returned to the soil, making them available for plants again. Earthworms play a critical part in this process.
By consuming organic materials and excreting nutrient-rich castings, earthworms help redistribute essential elements back into the soil. Their activities support the transformation of nutrients through decomposition, making it easier for microbes to access and utilize these nutrients.
This cycle is particularly important in agricultural systems where nutrient depletion can lead to reduced soil fertility over time. By encouraging earthworm populations, farmers can enhance their soil’s productive capacity and overall health, leading to better crop yields and more sustainable practices.
Challenges Facing Earthworms and Microbial Life
Despite their importance, earthworms and the microorganisms that thrive because of them face several challenges. One major threat is soil degradation caused by intensive farming practices, which can lead to compaction and loss of organic matter. When soil is compacted, it becomes harder for earthworms to move through and for microbes to thrive.
Another threat is the use of chemicals, such as pesticides and herbicides, which can negatively impact both earthworm and microbial populations. These substances can kill beneficial soil organisms, disrupting the delicate balance that exists in healthy soils.
Climate change is also a significant factor. Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can affect earthworm populations and the microorganisms they support. Warmer temperatures can lead to increased microbial activity, which, if not matched by an adequate supply of organic matter, could deplete soil nutrients over time.
How to Encourage Earthworm Populations in Your Soil
If you’re eager to promote healthy soil and support earthworms, there are several simple steps you can take. Here’s where you can really make a difference:
- Avoid Over-Tilling: Excessive tilling disrupts the soil structure and can harm earthworms. Limit tillage to preserve their habitats.
- Provide Organic Matter: Incorporate compost, leaf litter, and other organic materials into the soil to give earthworms plenty to eat.
- Use Chemical-Free Practices: Minimize or eliminate the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides that can harm beneficial soil organisms.
- Retain Moisture: Maintain soil moisture to create a favorable environment for earthworms. Mulching can help keep the soil damp.
- Practice Crop Rotation: Rotating your crops can help maintain soil health and support diverse microbial communities.
By taking these steps, you’ll not only support earthworm populations but also foster a thriving microbial community that contributes to healthier plants and improved soil quality.
In summary, earthworms are not just humble creatures burrowing in the ground. They play a significant role in enhancing soil microbial life, which is essential for plant health and overall ecosystem balance. By enriching the soil, promoting microbial diversity, and supporting nutrient cycling, earthworms help create a thriving environment for all living things.
So the next time you see an earthworm wiggling by, remember: it’s not just a squishy worm. It’s a vital player in the interconnected web of life beneath our feet. By understanding their impact on soil microbial life, we can learn to appreciate and protect these fascinating creatures, ensuring healthier soils for the future.