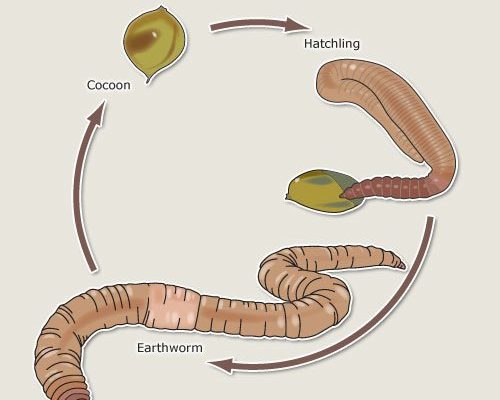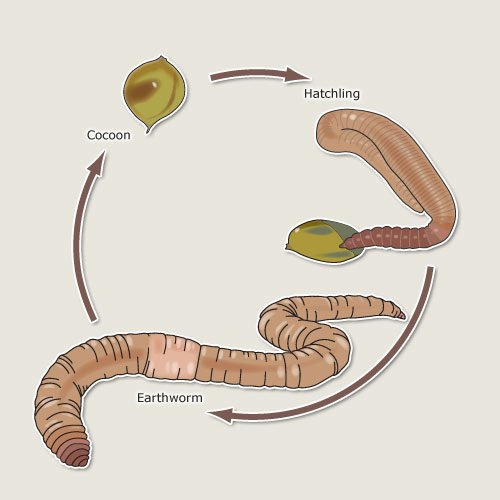
In this article, we’ll explore the cool journey of earthworm reproduction. From the moment they mate to the time hatchlings emerge, this process is a bit like a hidden life cycle, waiting to be uncovered. Whether you’re an aspiring gardener curious about soil health or just someone who loves nature, understanding this process is pretty fascinating. So grab your favorite drink, sit back, and let’s dig in!
The Basics of Earthworm Anatomy
Before we dive into reproduction, it’s helpful to understand a bit about earthworm anatomy. Earthworms are unique creatures, equipped with a few special features that aid in their reproduction. For starters, they have both male and female reproductive organs, which means they are hermaphrodites. This is pretty handy when it comes to mating, as two earthworms can exchange sperm to fertilize each other’s eggs.
One of the key parts of an earthworm is the clitellum. This thickened, glandular section of the worm’s body is crucial during reproduction. It’s like a cocoon factory, producing a protective casing for the eggs. You might think of it as the earthworm’s equivalent of a nursery—it’s where the magic begins.
As they move through the soil, earthworms contribute to a healthy ecosystem. They recycle nutrients, aerate the soil, and create spaces for plant roots to grow. So, it’s clear that these creatures play a big role in our environment, and understanding how they reproduce helps us appreciate their contribution even more.
How Earthworms Mate
When it comes to mating, earthworms engage in a rather interesting dance. During mating season, two worms will come together and align their bodies. They exchange sperm in a process that might seem a bit like a romantic rendezvous. Here’s how it works:
1. Alignment: The worms will position themselves side by side.
2. Sperm Exchange: They exchange spermatophores, which are small packets of sperm. This allows both worms to collect sperm from each other, which they’ll store for later use.
3. Cloacal openings: After the exchange, they will separate, each now equipped with sperm to fertilize their eggs.
Honestly, it’s quite a fascinating process when you think about it. It’s like they’re preparing for a future generation while working together, forming a bond over their shared journey.
The Role of the Clitellum in Egg Production
Once earthworms have mated, the next step is egg production. The clitellum plays a key role here! After a period of time, the clitellum secretes a mucus ring, which acts as a protective casing for the eggs. This is where the magic of reproduction really happens.
Here’s how it unfolds:
– The earthworm will move forward, leaving behind a trail of mucus.
– As they do this, they deposit their fertilized eggs into the mucus ring, which then constricts to form a cocoon.
– Each cocoon can contain several eggs, and after a few weeks, it will be ready to hatch.
This cocoon is like a safe haven for the developing eggs—it protects them from predators and environmental conditions, giving the hatchlings a better chance of survival. It’s nature’s version of a cozy nest!
The Development Inside the Cocoon
After the cocoon is formed, the developing embryos take center stage. Inside this protective casing, fertilized eggs undergo a remarkable transformation. The young earthworms, known as hatchlings, are developing and growing.
– Timing: Depending on the species and environmental conditions, it typically takes about 2 to 3 weeks for the eggs to hatch.
– Nutritional Support: The yolk sac of each egg provides essential nutrients during this time, ensuring that the hatchlings have what they need to grow.
– Survival Strategy: This phase is crucial. With protection from the cocoon, the hatchlings can develop in relatively safe conditions, which is vital for their survival.
It’s fascinating to think about how these little beings are maturing out of sight, just waiting for the right moment to break free into the world.
Hatching: The Emergence of the Young Earthworms
Once the hatching time arrives, the earthworm babies are ready to make their grand entrance. They wiggle their way out of the cocoon and into the soil, which is their new home. But what does this process look like?
– Emergence: As they break free, these hatchlings are tiny—just a few centimeters long. They resemble miniature versions of adult worms, equipped with everything they need to start their lives.
– Finding Their Food: Right away, they begin to burrow into the soil, looking for organic material to eat. This could be decaying leaves or other plant matter. They’re instinctively drawn to nutrient-rich areas, which helps them grow.
– Growth Journey: Over time, these small worms will continue to grow and eventually become adults themselves, ready to start the reproductive cycle all over again.
It’s a cycle that feels almost poetic, don’t you think? They come from the earth, and in their life’s journey, they will return to it, continuing the circle of life.
The Impact of Earthworm Reproduction on Soil Health
Understanding how earthworms reproduce goes beyond mere curiosity—it has significant implications for gardening and agriculture. Earthworms are vital for maintaining soil health, and their reproduction plays a direct role in this.
– Soil Aeration: As earthworms burrow, they create channels in the soil. This helps with aeration, allowing air and water to reach plant roots more efficiently.
– Nutrient Cycling: Their waste, known as castings, is rich in nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium—essential for plant growth. As a result, the presence of earthworms increases soil fertility.
– Decomposition: Earthworms help break down organic matter, returning nutrients back to the soil. Their reproduction ensures a steady population to keep this cycle going.
This means that the more earthworms you have in your garden, the healthier your soil will be! It’s like having nature’s little gardeners at work.
Protecting Earthworms for Future Generations
Now that we know how these little creatures reproduce and contribute to our ecosystem, it’s essential to think about how we can protect them. Earthworm populations can be threatened by factors like chemical pesticides, habitat loss, and pollution. Here are some ways we can help:
- Reduce Pesticide Use: Instead of chemicals, try natural pest control methods to keep your garden healthy.
- Practice Composting: This creates a rich habitat for earthworms and provides them with plenty of organic matter to munch on.
- Avoid Tilling: Excessive soil disturbance can harm earthworm populations. Try no-till gardening methods instead.
- Educate Others: Share what you’ve learned about earthworm reproduction and their role in the ecosystem—it can inspire others to protect them too!
By taking these steps, we can help ensure that future generations of earthworms thrive, continuing their essential work in our soil.
In conclusion, the journey from cocoon to hatchling is a remarkable part of the life cycle of earthworms. Their ability to reproduce, thrive, and contribute to a healthy ecosystem is a reminder of the intricate connections in nature. Understanding how they reproduce not only enhances our appreciation for these creatures but also encourages us to care for our environment. So next time you see an earthworm, remember this little life cycle dance happening right beneath our feet!