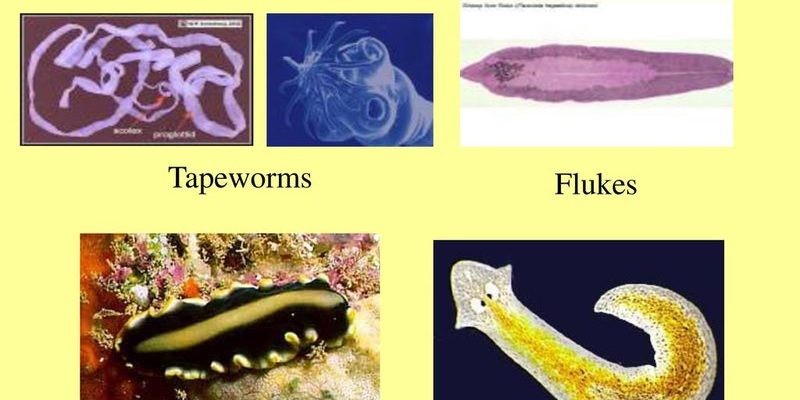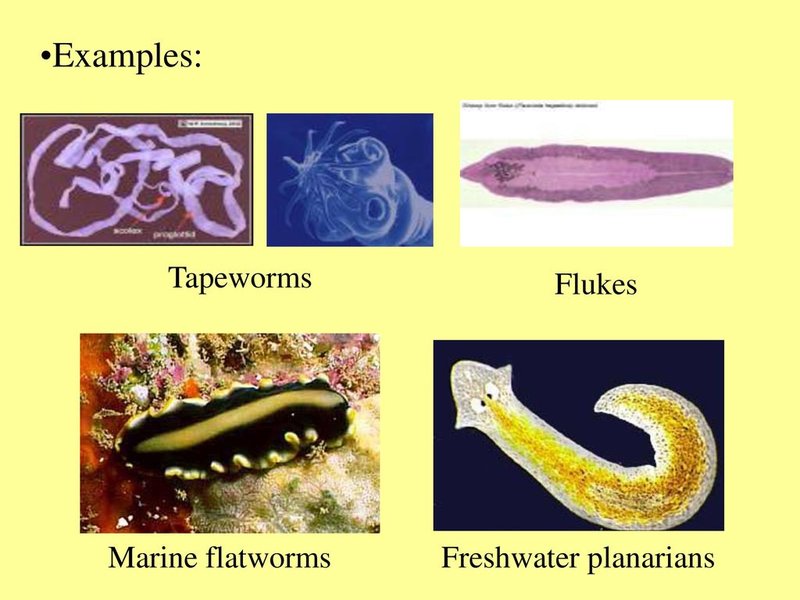
Bootlace worms (also known as *Lineus*, if you want to impress your friends with scientific terms) belong to a group that exhibits some remarkable features. Flatworms, on the other hand, encompass a diverse array of species, each with unique traits. The key is knowing what to look for, like how a barista knows the difference between an espresso and a latte. In this guide, I’ll walk you through the distinct characteristics of bootlace worms versus flatworms, so you’ll feel like a marine biologist on your next nature walk.
What Are Bootlace Worms?
Bootlace worms are fascinating creatures that can stretch up to 30 meters long—yes, you read that right. These elongated worms are mainly found in the oceans, particularly along the coasts of Europe. The name “bootlace” comes from their long, thin shape, resembling laces used in footwear. They belong to the group known as nemerteans and are known for their impressive regenerative abilities. If you think of a cut on your finger healing, imagine a bootlace worm regrowing a chunk of its body after being severed!
These worms are typically a bright yellow or orange color, which can be a helpful identifier when you spot them. They also move in a unique way by contracting and expanding their body, making their movements appear fluid and graceful. You’ll often find them hiding under rocks or in seaweed, so keep an eye out when you’re at the beach, as they can be quite elusive.
Characteristics of Bootlace Worms
– **Size**: They can reach incredible lengths, often making them the longest animals on Earth.
– **Coloration**: Usually bright hues like yellow or orange, which can help in identification.
– **Movement**: They move elegantly by contracting and expanding their body, distinguishing them from other worm types.
Understanding Flatworms
Flatworms are a diverse group that comes in numerous species, but they typically range from just a few millimeters to several meters long. They can be found in both freshwater and marine environments, which adds to your chance of spotting them on your next hike or beach trip. Flatworms have a distinctly flat body shape, as their name suggests. Unlike bootlace worms, they lack the elongated, ribbon-like appearance and often have a more uniform, flattened structure.
You may have encountered them in various colors and patterns, from browns and blacks to vibrant, striking hues. Some flatworms even have eye spots, giving them a more interesting look. Their body structure adapts to a variety of environments, allowing them to thrive in many conditions.
Characteristics of Flatworms
– **Size and Shape**: They are generally flatter and can vary in size, but they don’t reach the extreme lengths of bootlace worms.
– **Color Variation**: Many species showcase intricate patterns and colors, making them visually appealing.
– **Habitat**: Flatworms can be found in diverse environments, from freshwater to marine ecosystems.
Key Differences in Appearance
Knowing how to spot the differences in appearance can make identifying these creatures much easier. While both bootlace worms and flatworms can be long and skinny, there are notable distinctions.
Bootlace worms often have a **smooth**, shiny surface, which contrasts with many flatworms that may feature a more textured body. Additionally, bootlace worms tend to be more vibrant in color. When you look closely, you might notice that flatworms have a **flattened** body with pointed ends, while bootlace worms are more consistent in their cylindrical shape.
Another significant difference is their movement. Bootlace worms undulate fluidly, while flatworms tend to glide more with a creeping motion. If you’re observing them, this can be an instant giveaway.
Comparison of Appearance
| Feature | Bootlace Worms | Flatworms |
|——————-|——————————-|—————————–|
| Body Shape | Long, cylindrical | Flat, leaf-like |
| Surface Texture | Smooth and shiny | Often textured |
| Movement | Fluid undulating | Creeping or gliding |
| Color Patterns | Bright, consistent colors | Variable, often patterned |
Habitat: Where They Live
Both bootlace worms and flatworms thrive in aquatic environments but can often be found in different types of habitats. Bootlace worms prefer **marine environments**, often residing in sandy or muddy substrates. They hide under rocks or in seagrass beds, making them less visible unless you’re specifically looking for them.
Flatworms, on the other hand, can be found in a broader range of habitats. They inhabit everything from freshwater ponds to brackish estuaries and even coastal waters. Some species are terrestrial, living in damp soils or leaf litter. Their adaptability to varied environments makes them easier to find compared to bootlace worms.
Common Habitats
– **Bootlace Worms**:
– Coastal marine areas
– Sandy or muddy substrates
– Under rocks and seaweeds
– **Flatworms**:
– Freshwater lakes and ponds
– Brackish estuaries
– Coastal waters and even terrestrial areas
Diet and Feeding Habits
When it comes to food, bootlace worms and flatworms have different dining habits. Bootlace worms are primarily carnivorous, often feeding on small fish, crustaceans, and occasionally, other worms. Their method of feeding is fascinating; they use a specialized structure called a proboscis to capture prey quickly. Imagine a tongue that can extend and retract at lightning speed!
Flatworms, in contrast, can be either carnivorous or herbivorous, depending on the species. Some hunt tiny aquatic creatures, while others graze on algae and detritus. Because of their diverse feeding approach, flatworms play various roles in their ecosystems.
Feeding Differences
– **Bootlace Worms**:
– Carnivorous
– Utilize a proboscis to capture prey
– **Flatworms**:
– Can be herbivorous or carnivorous
– Grazing or hunting depending on species
Why It Matters: Understanding Biodiversity
Being able to differentiate between bootlace worms and flatworms isn’t just a matter of curiosity—it’s crucial for understanding biodiversity. Each of these creatures plays a unique role in their respective ecosystems. Bootlace worms are vital in controlling prey populations, while flatworms contribute to nutrient cycling.
By learning about these creatures, you become a part of a larger conversation about our environment. Not only do you gain knowledge, but you also promote appreciation for the hidden wonders of the world around us. Plus, being able to discuss marine life confidently can make you the star of your next nature walk or aquarium visit!
The Importance of Biodiversity
– **Ecosystem Balance**: Knowing the roles of different species helps maintain ecological balance.
– **Conservation Awareness**: Understanding these organisms can lead to better conservation efforts.
– **Personal Connection**: Engaging with local wildlife fosters appreciation for nature.
In conclusion, when you’re next exploring coastal waters or aquatic environments, remember to keep an eye out for bootlace worms and flatworms. With this guide in hand, you’ll be able to spot the differences and appreciate the rich tapestry of life below the surface. Whether it’s their movement, habitat, or diet, each observation helps unravel the mysteries of our natural world. So, grab your boots, get out there, and happy worm-watching!