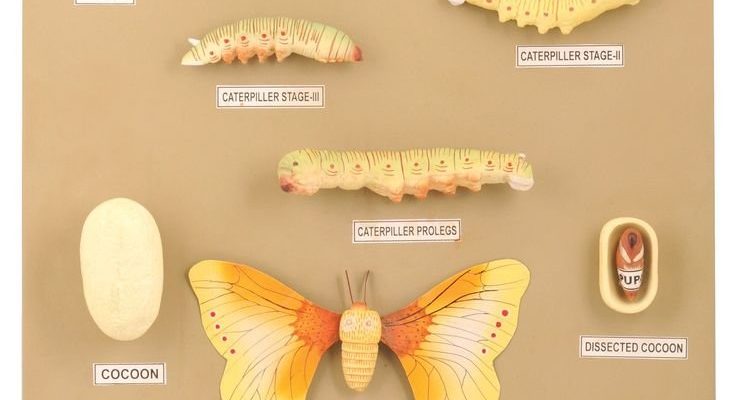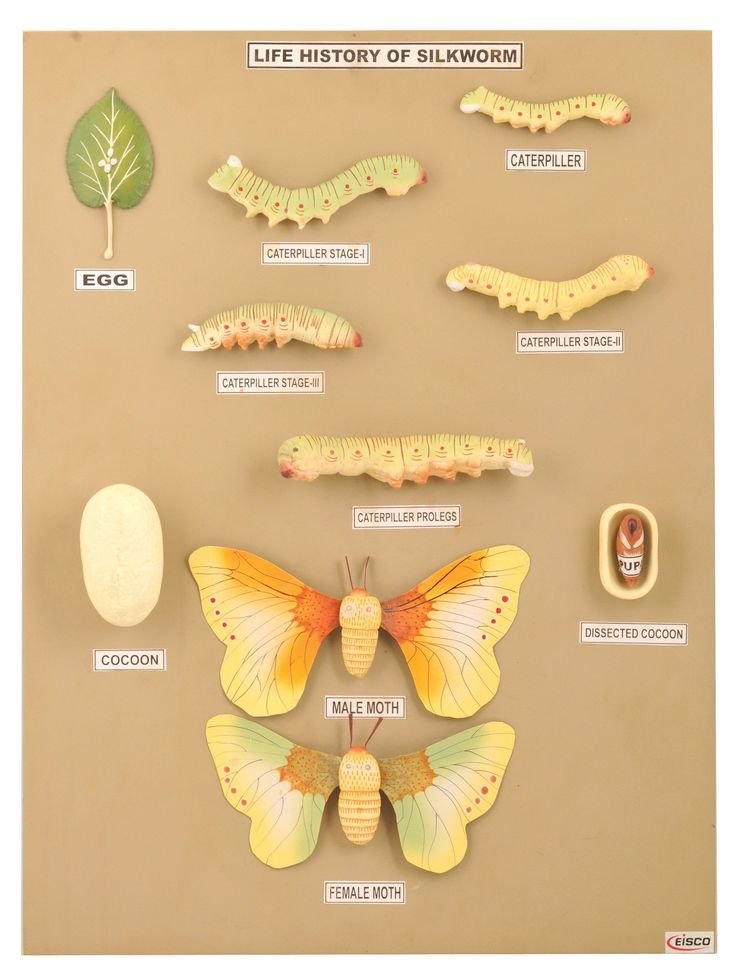
Imagine sitting down for a cozy chat, and I explain how these little creatures go from humble eggs to silk-producing machines. The journey isn’t just about becoming a moth; it’s about a series of transformations that are mesmerizing to watch. Let’s dive into the development stages of silkworms and explore it step by step, with some engaging visual charts along the way.
1. The Egg Stage
The first stage of the silkworm’s life begins as a tiny, delicate egg. These eggs are usually laid by the female moth on mulberry leaves, which serve as food for the young larvae. Picture them as the seeds of a garden, each waiting for the right moment to grow. Each egg is minuscule, about the size of a pinhead, often clustering together in small masses.
Typically, the eggs take about **10 days to hatch**, depending on temperature and humidity. When they hatch, the tiny caterpillars, known as **larvae**, emerge. This moment is crucial, as it marks the beginning of a silkworm’s transformation. The larvae are ravenous, ready to devour mulberry leaves almost immediately. They need to eat a lot to grow quickly, almost like teenagers at an all-you-can-eat buffet!
2. The Larval Stage
Once the silkworm hatches, it enters the **larval stage**, which is the longest and most active phase of its life. It’s fascinating to watch the larva grow; it can increase its size over a thousand times in about **4 to 6 weeks**! Think of it as a rapid growth spurt, much like what we experience as kids. During this time, the silkworm will go through **five molts**, shedding its skin each time to accommodate its growing body.
The larval stage is all about munching and growing. The silkworm’s diet consists mainly of fresh mulberry leaves. As they eat, they store energy for the next stage of their lifecycle. It’s like filling up a gas tank for a long road trip; they need the fuel to keep moving forward. At each molting, you can see the skin left behind; it’s a bit creepy but a crucial part of their development.
3. The Pupal Stage
After the larval stage, the silkworm transitions into the **pupal stage**, or the cocoon phase. This is where things get pretty exciting! The silkworm finds a safe spot, usually on a branch or a stable surface, and begins to spin a cocoon around itself. Using a special fluid from its salivary glands, it creates a protective casing—essentially a silk sleeping bag. This process can take anywhere from **2 to 3 days**.
Inside the cocoon, the silkworm undergoes a remarkable transformation called **pupation**. Think of it as a magical makeover. During this time, the larva is changing into a moth. While it may appear like nothing is happening on the outside, there’s a lot of action happening inside! If you look closely, you might see the outline of the moth forming. This stage is one of the most crucial in the development of the silkworm, as it readies them for their emergence into the world.
4. The Adult Moth Stage
Finally, after spending several weeks inside the cocoon, the silkworm emerges as a fully grown moth. This **adult stage** is short-lived compared to the previous ones. Moths typically live only about **two weeks**, just long enough to mate and lay eggs, continuing the cycle. They don’t even eat during this stage; their sole purpose is to reproduce.
When you see these adult moths, they might look a bit drab compared to their colorful caterpillar counterparts. However, they are incredibly important for silk production. From one cocoon, you can get about **1,000 meters of silk thread**! It’s amazing how something so delicate plays such a vital role in the textile industry.
5. Visual Charts of Silkworm Development
Visual aids can make understanding the stages of silkworm development much clearer. Creating charts to illustrate the journey from egg to adult moth can be incredibly helpful. Here’s a simple breakdown you might envision:
| Stage | Description | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Egg | Laid on mulberry leaves; hatches into a larva. | ~10 days |
| Larva | Active growth phase; molts five times. | 4-6 weeks |
| Pupa | Cocoon formation; transformation into a moth. | 2-3 days |
| Adult Moth | Mating and laying eggs to start the cycle over. | ~2 weeks |
This chart summarizes the stages beautifully, showing how each phase is essential for the next. You can even create a visual timeline to trace their development, like a storybook for silkworms!
6. Why Understanding Silkworm Development Matters
You might be wondering why it’s important to understand the stages of silkworm development beyond just curiosity. For one, silk production is a massive industry. Knowing about these stages can help farmers improve yield and efficiency. By optimizing conditions during each phase, they can ensure a healthier crop of silkworms.
Additionally, understanding this process can inspire sustainable practices. As consumers become more eco-conscious, knowing how silk is harvested can lead to choices that support better farming practices. If you’re into crafts or fashion, you might also appreciate the artistry behind silk creation, which ties directly back to the life cycle we’ve just explored.
The journey of a silkworm from egg to adult moth is nothing short of incredible. Each stage plays a pivotal role in ensuring the survival and continuation of the species. By understanding the **stages of silkworm development** through visual charts and detailed explanations, we gain insight into not just their life cycle but also the broader implications for agriculture and sustainability. So, the next time you see a silk garment or read about silk production, you’ll have a deeper appreciation for the tiny creatures that make it possible. Let’s celebrate these unsung heroes of nature!

