Silkworms, scientifically known as *Bombyx mori*, are primarily known for their role in silk production. But before they become the fantastic moths we recognize, they start their lives in the most unassuming way—with a tiny egg. If you’ve ever been curious about how they grow and change, you’re in the right place. Buckle up as we explore the incredible journey of the silkworm!
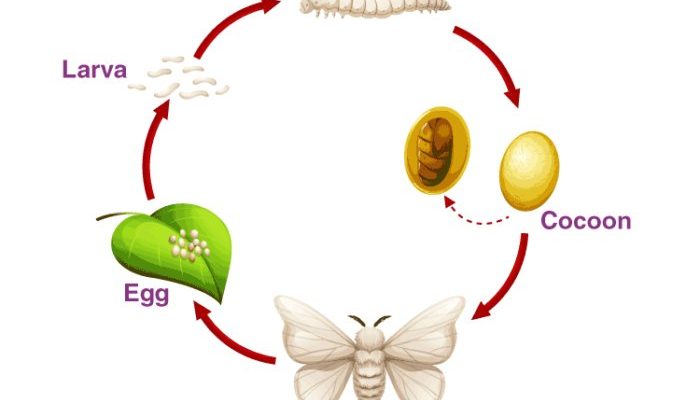
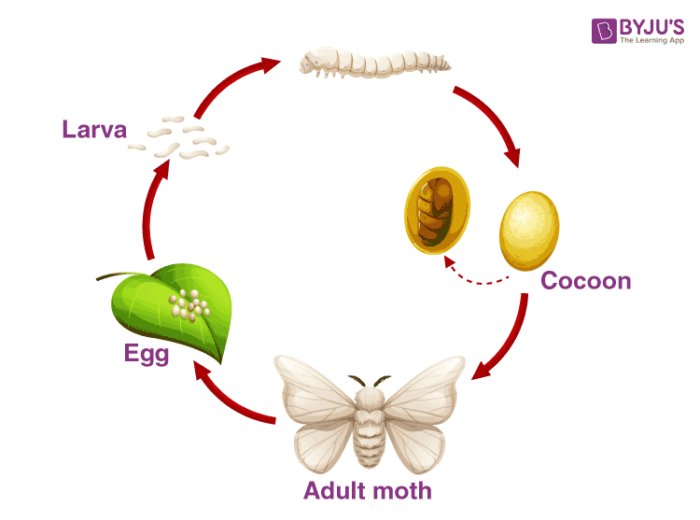
Stage 1: The Egg
The lifecycle of a silkworm begins with the **egg** stage. These eggs are incredibly small and usually laid in clusters. When a female moth is ready to lay her eggs, she chooses a cozy spot—often on mulberry leaves, which are the main food source for silkworms. You might be wondering how long it takes for these little eggs to hatch. Well, it typically takes about 10 days, depending on the temperature and humidity.
Each silkworm egg is dot-sized and can appear a pale yellow or brown. Once they hatch, the tiny caterpillars—or larvae—emerge, ready to eat and grow. Here’s a fun fact: a single female moth can lay as many as 500 eggs! That’s a lot of potential silkworms.
Stage 2: The Larva
Once the eggs hatch, the silkworms enter the **larval stage**, which is when they really start to eat. These little caterpillars are ravenous! Their diet mainly consists of mulberry leaves, and they can eat up to 80 times their weight in just a few weeks. This stage lasts about 4-6 weeks, during which they go through several molts, shedding their skin as they grow.
You might be asking, “What’s the point of all this eating?” Well, during this period, silkworms are busy gathering energy for the next phase of their life. It’s fascinating how their bodies transform—growing in size and changing color as they prepare for the big change ahead. If you look closely, you can see the growth happening before your eyes!
Stage 3: The Pupa (Cocoon Stage)
After the larval stage, the silkworm enters the **pupal stage**. This is when they begin to spin their protective cocoons. It’s like wrapping themselves in a cozy blanket! The silk they produce is made from a protein that they secrete through their salivary glands.
The process of spinning a cocoon can take about 2-3 days, during which the silkworm will create a silky structure that’s not just beautiful but also serves as a safeguard against predators. Inside this cocoon, the silkworm undergoes a magical transformation called **metamorphosis**. It’s like a hidden world where the caterpillar is turning into a moth—a real-life version of a superhero changing in the shadows!
Stage 4: The Adult Moth
After spending about 10-14 days in the cocoon as a pupa, the silkworm finally emerges as an **adult moth**. This stage is amazing but short-lived. Adult silkworm moths usually have a lifespan of about 5-10 days, during which their primary goal is to reproduce.
Interestingly enough, the adult moths don’t eat. They rely on the energy stored in their bodies from the larval stage. When they emerge from their cocoons, they have stunning wings that are often white and fluffy—a stark contrast to their previous caterpillar form. As they flutter around, searching for mates, their primary job is to keep the cycle going, laying more eggs and starting the whole process over again.
The Role of Temperature and Environment
You may be curious about how important **temperature** and **environment** are in the silkworm lifecycle. The truth is, they play a crucial role! Silkworms thrive in warm, humid conditions. Ideal temperatures are usually between 20°C to 30°C (68°F to 86°F).
If temperatures dip too low or jump too high, it can affect their growth, feeding, and even the quality of the silk they produce. For example, too much humidity can lead to mold growth on the mulberry leaves, which can harm the larvae. Farmers pay close attention to these factors to ensure a healthy silkworm population.
The Significance of Silkworms to Humans
Silkworms are not just fascinating creatures—they also hold a special place in human history. For centuries, we’ve relied on them for silk production, a luxurious fabric that has been treasured across cultures. The **silk** harvested from cocoons is woven into garments, accessories, and decorative items.
Beyond silk, silkworms are also used in traditional medicine and as a source of protein in some cultures. Silkworm larvae can be enjoyed as a snack or added to dishes. Isn’t it incredible how a creature that starts as a tiny egg can contribute so much to our lives?
So there you have it! The lifecycle of a silkworm is a captivating journey filled with changes, challenges, and beautiful transformations. From a delicate egg to a mesmerizing moth, each stage plays a vital role in the continuation of this remarkable species.
Next time you come across silk fabrics, remember the small creatures that made it possible. Silkworms are nature’s little miracle workers, turning leaves into luxurious silk. They remind us of how interconnected everything is in the web of life. Whether you’re a budding enthusiast or just curious, understanding the silkworm lifecycle opens up a whole new appreciation for this incredible insect!