In this article, we’ll break down the stages of silkworm development and illustrate them with visual charts. This not only makes it easier to understand but also gives you a clearer picture of each stage, from egg to mature moth. Whether you’re studying this for school or just curious about the silkworm lifecycle, I’ll walk you through step-by-step. So, grab a cup of coffee, sit back, and let’s dive into the world of silkworms!
The Life Cycle of Silkworms: An Overview
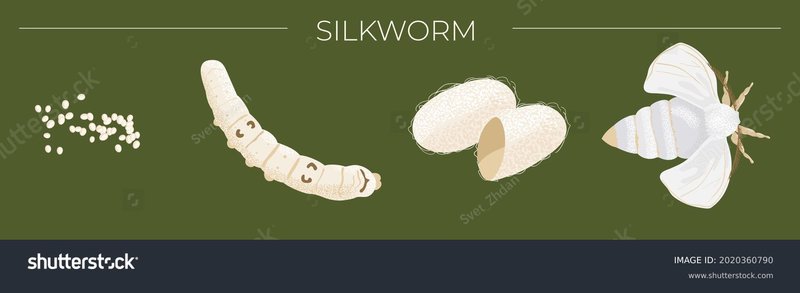
Silkworms follow a unique life cycle that includes four main stages: egg, larva (caterpillar), pupa (cocoon), and adult moth. Each stage is critical for their development and ultimately affects the quality of silk they produce. To simplify, think of it like a video game where each level presents new challenges and rewards. Just like how you can’t rush through levels without gathering skills, silkworms must go through each life stage before becoming the beautiful moths that lay more eggs.
Here’s a quick overview of what happens in each stage:
- Egg: Tiny, often laid on mulberry leaves.
- Larva: This is the caterpillar stage where they munch on leaves, growing rapidly.
- Pupa: The stage where they spin their cocoons and undergo metamorphosis.
- Adult Moth: The finally emerged moth, ready to reproduce.
Each stage is unique and comes with its own characteristics and challenges, leading us to the first phase.
Stage 1: The Egg Stage
Silkworm eggs are tiny, about the size of a pinhead, and can be laid in clusters of hundreds on mulberry leaves. When they’re laid, these eggs are typically yellowish-white. They need specific conditions to hatch, including the right temperature and humidity. If you were to compare silkworm eggs to seeds, they require the perfect environment to sprout into lively larva.
Once conditions are just right, which usually takes around 10 days, the eggs will hatch into tiny larvae. You might be wondering what happens if the environment isn’t suitable? Well, if it’s too cold or too damp, the eggs might not hatch at all. So, it’s like waiting for the right moment to plant a garden. Timing is everything!
Stage 2: The Larval Stage
After hatching, the larval stage is where the fun begins. Think of this phase as the hungry teenager of the silkworm’s life. These little creatures will eat practically nonstop, munching on mulberry leaves, which are their primary food source. In fact, they can consume up to 20,000 times their body weight by the time they’re ready to pupate. That’s equivalent to a person eating several tons of food!
During this stage, they’ll undergo a series of molts—up to five times—shedding their old skin to grow bigger. This is similar to how you might outgrow a favorite pair of shoes. Each molt is essential for their development and signifies growth. And, let me tell you, the transformation is quick! The entire larval stage lasts about 4 to 6 weeks.
Stage 3: The Pupal Stage
Once they’ve reached their full size, it’s time for the pupal stage. This is where the real magic happens, as the larvae spin a protective cocoon around themselves. Picture them as tiny artists, carefully weaving intricate silk threads to create a safe haven. It can take anywhere from 2 to 3 days to finish spinning, and the cocoon is made from a single thread that can be up to a mile long!
Inside the cocoon, the silkworm undergoes metamorphosis, changing from a caterpillar to a moth. It’s like going to sleep and waking up as a completely different person. During this time, they are extremely vulnerable, much like a baby wrapped snug in a blanket. The pupal stage can last anywhere from a week to several weeks, depending on the conditions and species.
Stage 4: The Adult Moth
After the pupal stage, it’s showtime! The adult moth emerges from the cocoon, ready to make its mark on the world. Interestingly, male silkworm moths have larger, bushier antennae than females, helping them locate mates through scent. You might say it’s their way of flirting!
Once they emerge, they don’t eat anything; their only goal is to find a mate and lay eggs. The female can lay up to 500 eggs, starting the cycle all over again. It’s a bit like a relay race, where each generation passes on its legacy. The adult moth stage typically lasts around 5 to 7 days. This short lifespan emphasizes the urgency of their quest for reproduction.
Visual Charts of Silkworm Development
To help visualize silkworm development, charts can be incredibly useful. Here’s a simple depiction of each stage:
| Stage | Description | Time Frame |
|---|---|---|
| Egg | Small, yellowish-white eggs laid on mulberry leaves. | About 10 days |
| Larva | Hungry caterpillars that grow rapidly. | 4 to 6 weeks |
| Pupa | Caterpillars spinning cocoons and undergoing metamorphosis. | 1-3 weeks |
| Adult Moth | Emerging moths focused on mating and laying eggs. | 5 to 7 days |
Each stage flows into the next, forming a continuous cycle. This chart not only summarizes the stages but also gives you a quick reference for studying.
Why Understanding Silkworm Stages Matters
Understanding the stages of silkworm development is crucial for several reasons. For one, it highlights the importance of silk production in the textile industry. Without awareness of their life cycle, we couldn’t effectively cultivate silkworms for their silk. It’s essential for farmers and businesses to know when to harvest or manage the silkworms for optimal silk quality.
Additionally, this knowledge can help in scientific research as well. Studying their growth patterns and environmental needs can lead to better farming practices and sustainability efforts. Plus, it opens the door to understanding other insects and their life cycles, enhancing our overall understanding of ecosystems.
Considering the ongoing importance of silk in clothing and textiles, this small creature plays a huge role in day-to-day life. So next time you see silk, remember the journey these little silkworms took to get there!
In conclusion, the stages of silkworm development—from egg to larva to pupa to adult moth—reflect a remarkable transformation. Each phase not only contributes to the lifecycle but also plays a vital role in silk production. With this visual guide, I hope you feel more connected to the world of silkworms and appreciate the beauty of their development. Who knew such a tiny creature could have such a big impact?
