Velvet worms, belonging to the phylum Onychophora, have a unique and almost whimsical appearance that resembles a cross between a caterpillar and a worm. The way they move, with their soft, velvety bodies, can sometimes make them appear quite charming. But don’t let their cute looks fool you; they’re fierce predators that primarily feast on smaller insects. By hunting and feeding on these organisms, velvet worms help maintain a balanced ecosystem. But their importance doesn’t stop there—they also play a pivotal role in the breakdown of leaf litter, which is crucial for soil health and nutrient recycling.
The Role of Velvet Worms in Ecosystems
Understanding how velvet worms contribute to leaf litter decomposition starts with recognizing their role in the ecosystem. These fascinating creatures thrive in damp, leaf-litter-rich environments like tropical forests. Here, they hide beneath the fallen leaves and organic debris, ready to pounce on unsuspecting prey.
You might be wondering how this relates to decomposition. Well, as velvet worms consume insects, they also help regulate the populations of these pests. This balance aids the process of decomposition. Without such predators, certain insect populations could explode, leading to higher rates of decay that might overwhelm the system. By controlling these populations, velvet worms indirectly foster a more stable environment for leaf litter breakdown.
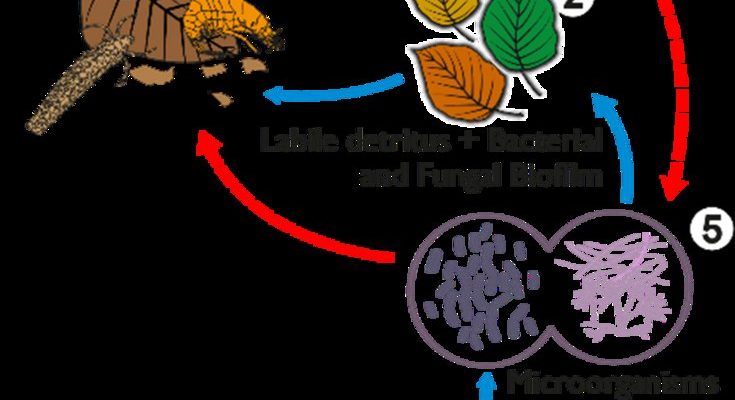
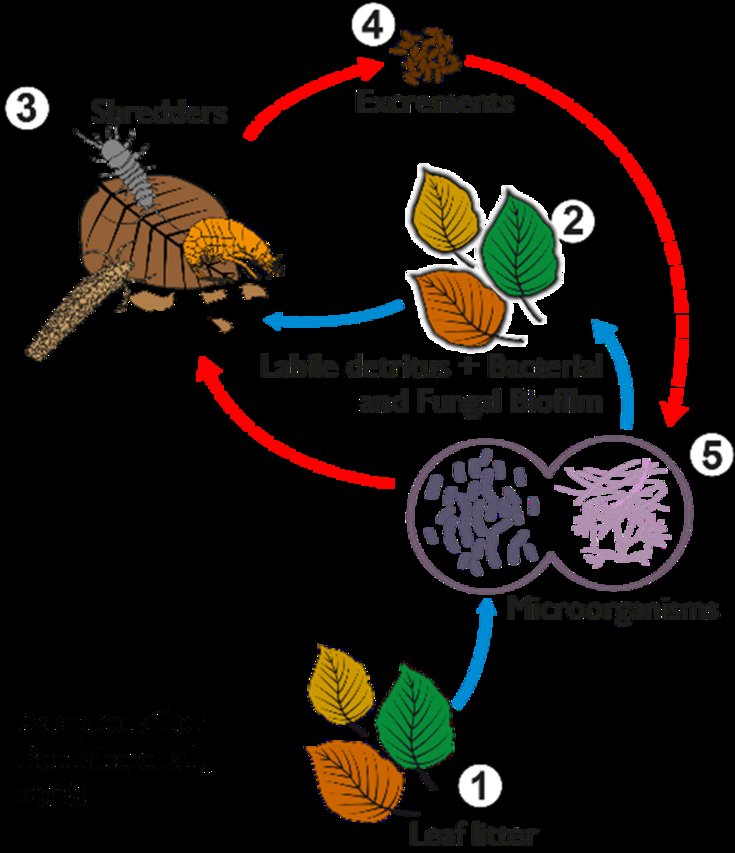
Additionally, when velvet worms prey on insects, they process organic matter in their own unique way. The waste produced by these creatures is rich in nutrients. This waste, known as frass, returns to the soil, enriching it and helping to break down leaf litter more effectively. It’s a beautiful cycle of life—velvet worms munch on insects, produce nutrient-dense frass, and create a healthier environment for the soil.
How Leaf Litter Decomposition Works
To appreciate the contribution of velvet worms fully, it’s essential to understand what leaf litter decomposition entails. Leaf litter is made up of fallen leaves, twigs, and other organic material that accumulates on the forest floor. Over time, this matter breaks down, returning vital nutrients to the soil, which plants need to grow.
The decomposition process involves a variety of organisms, including bacteria, fungi, and invertebrates. These tiny creatures work together, breaking down complex organic materials into simpler compounds. You can visualize it like a team of workers, each with a specific role: bacteria break down the smaller particles, fungi help decompose tougher materials, and invertebrates, including our velvet worms, shift and enrich the soil as they feed and move about.
In simple terms, leaf litter decomposition is nature’s recycling program. Without this process, our forests would be buried under a mountain of leaves, and nutrients would remain locked away instead of being available to plants. This process is crucial not only for plant life but for the entire ecosystem. It creates a fertile ground for new growth and supports the food chain.
Velvet Worms and Bacterial Activity
One fascinating aspect of velvet worms is how they affect bacterial activity in leaf litter. Bacteria are essential for breaking down organic matter, but their efficiency can vary based on the environment. Velvet worms contribute to a healthier microbial community in a few ways.
Firstly, their frass provides an additional nutrient source for bacteria. By feeding on insects and recycling those nutrients back into the soil, velvet worms help create an environment where bacteria can thrive. When the frass decomposes, it releases nutrients that fuel bacterial growth, which in turn enhances decomposition.
Secondly, the way velvet worms move through the leaf litter can disturb the soil, creating more oxygen and helping bacteria access organic matter more easily. Just think of it as stirring a pot while cooking; when you mix the ingredients, they cook more evenly. This mixing helps break down the leaf litter more effectively, ensuring that nutrients are released faster.
Ultimately, velvet worms act like tiny gardeners, enhancing the conditions in which beneficial bacteria flourish. This relationship between velvet worms and bacteria might seem small, but it’s a vital part of the larger picture regarding leaf litter decomposition.
Interactions with Other Decomposers
In the world of decomposition, velvet worms don’t work alone. They interact with various decomposers, forming a crucial part of the ecosystem’s complex web. As we discussed earlier, bacteria and fungi play significant roles in breaking down dead plant matter, but invertebrates like earthworms, millipedes, and even slugs also participate.
When velvet worms move through leaf litter, they can help mix the layers, making it easier for other decomposers to access nutrients. This interaction is vital because it promotes collaboration among all the organisms involved. Each type of decomposer has its strengths, like how different tools serve unique purposes in a toolbox. Together, they create a more efficient decomposing process.
Moreover, velvet worms can also serve as food for other predators, like birds or larger insects. By being a part of this food chain, they help sustain a diverse ecosystem. So, in a way, velvet worms not only help break down leaf litter but also help support the broader community of organisms that depend on decomposition for survival.
Why Velvet Worms Matter in Conservation
Now, you might be wondering why all this matters. As environmental concerns grow, scientists and conservationists are looking more closely at the roles of various organisms in ecosystems. Velvet worms may not be the most famous critters, but their contribution to leaf litter decomposition makes them important players in maintaining healthy forests.
Healthy ecosystems help regulate climate, filter water, and support biodiversity. When leaf litter decomposes efficiently, it ensures plants can access the nutrients they need to thrive. This, in turn, supports the animals that depend on those plants and the entire food web. If velvet worms and other decomposers were to decline, the ripple effect could disrupt this balance.
Conservation efforts often focus on preserving larger, more recognizable species, but the tiny ones like velvet worms deserve attention too. Protecting their habitats ensures that these creatures can continue their important work in decomposition and nutrient cycling.
Final Thoughts: Celebrating the Velvet Worm
In the grand scheme of the forest ecosystem, velvet worms may be small, but their contributions are huge. From controlling insect populations to enriching the soil with their frass, they play a vital role in leaf litter decomposition. This process is essential for the health of the ecosystem, supporting both plant and animal life.
Next time you stroll through a forest, take a moment to appreciate the hidden heroes working beneath your feet. Velvet worms might not be the first thing that comes to mind, but they are crucial links in the intricate chain of life. By understanding their role, we not only celebrate these fascinating creatures but also recognize the interconnectedness of all life on our planet. So, here’s to the velvet worm—a small but mighty contributor to the cycle of life!