Inchworms, belonging to the Geometridae family, have a unique way of moving that can make them look like they’re measuring the ground—hence the name. They’re not just fascinating to watch; they actually help maintain the balance in the environment. Although they might seem insignificant at first glance, inchworms contribute significantly to the food web, making them a vital part of forest ecosystems. You might be wondering, what exactly does that mean, and why should we care? Let me explain.
What Are Inchworms?
Inchworms are the larval stage of certain moths, primarily from the Geometridae family. You might notice them in your backyard or on hiking trails, often hanging out on leaves and branches. They’re typically green or brown, allowing them to blend into their surroundings like little magicians!
These caterpillars can grow anywhere from one inch to three inches long, and their unique movement—arching their bodies, then extending—gives them their “inchworm” nickname. But there’s more to them than just their charming antics. Inchworms go through several stages of growth, known as instars, before they pupate and emerge as adult moths. Each of these stages plays a part in their ecology, particularly in how they interact with their environment.
As inchworms munch on leaves, they not only use the plant for nourishment but also integrate into the food web. This brings us to our next point—why they matter so much in the forest ecosystem.
The Role of Inchworms in the Food Web
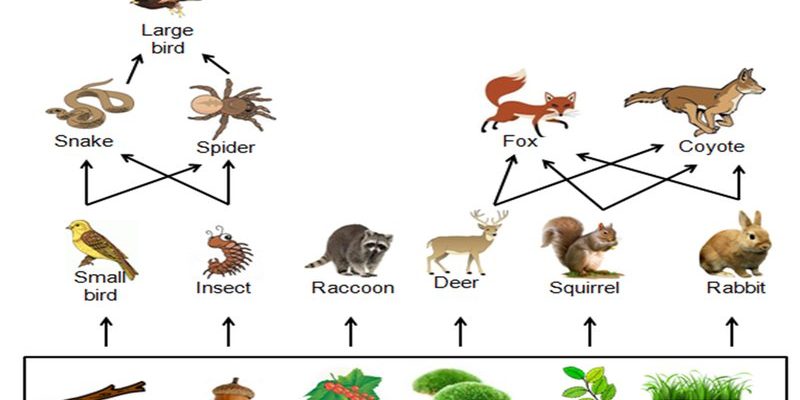
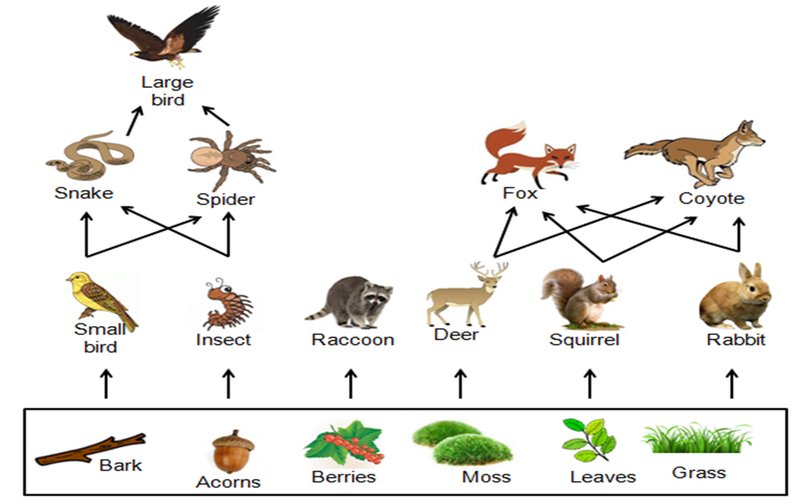
You might be surprised to learn that inchworms are more than just cute little critters. They serve as an important food source for a variety of forest animals. Birds, small mammals, and other insects rely on inchworms for nourishment. For example, during springtime, when food is scarce, birds are often seen hunting for these tasty larvae to feed their chicks.
Inchworms are also linked to the health of the plants around them. As they feed on leaves, they help in regulating plant growth. If there are too many inchworms, they can defoliate trees, but this can also lead to new growth when the trees recover. It’s like a natural way of pruning that can actually help trees thrive in the long run.
Ultimately, inchworms contribute to the delicate balance of the food web. When they eat, they support various creatures, allowing for rich biodiversity. If you think about it, they’re a bit like the glue that holds different parts of the ecosystem together.
Inchworms and Nutrient Cycling
Nutrient cycling is a fancy way of describing how nutrients move through the ecosystem. Inchworms play a surprisingly significant role in this cycle. When they consume leaves, they break down the plant material, making nutrients more available to the soil when they eventually drop off or get eaten by other animals.
When inchworms excrete waste, it adds organic matter to the soil, enriching it over time. This is essential for plant health, as it increases the nutrients available to other plants in the area. And as plants grow healthier, they can support a greater variety of species, including more inchworms. It’s a continuous cycle that keeps the forest alive.
So, inchworms don’t just contribute to the immediate food web; they also help maintain the long-term health of the ecosystem. It’s like they’re providing a service, nurturing the very ground they crawl upon.
Inchworms as Indicators of Ecosystem Health
Inchworms can also serve as a barometer for the health of their environment. Scientists often study populations of these caterpillars to gauge the overall health of forest ecosystems. A thriving inchworm population typically indicates a balanced environment, where predators, plants, and nutrients are all in sync.
However, if there’s a sudden spike or drop in inchworm numbers, it can signal changes in the ecosystem. For instance, a drop in populations could indicate issues like pollution, habitat loss, or climate change, which may threaten other species in the food web.
Just think of inchworms as little nature detectives, helping us understand how well our forests are functioning. When we see healthy inchworm numbers, it’s a good sign that the forest is thriving, supporting a rich variety of life.
Inchworms and Their Predators
Inchworms might be important in the food chain, but they’re not without their own vulnerabilities. Several predators target inchworms, making them an essential food source in the food web. Birds, such as warblers and sparrows, have adapted their hunting techniques to snatch these slow-moving caterpillars right off the branches.
Additionally, other insects like wasps and ants also hunt inchworms. This adds another layer to the ecosystem, showing how interconnected everything is. For instance, if inchworm populations decline due to increased predation or environmental changes, it directly impacts the animals that rely on them for food.
Understanding these relationships helps us see the bigger picture of forest health. It’s all about balance, and inchworms play a starring role in maintaining that equilibrium.
Preserving Inchworm Habitats
Given their importance, it’s essential to think about how we can help preserve inchworms and their habitats. Simple actions can make a big difference. For instance, planting native trees and shrubs can provide food and shelter for inchworms. You might also consider limiting pesticide use in your garden since chemicals can harm these creatures and their habitat.
Another effective way to support inchworm populations is to promote biodiversity. The more diverse a habitat is, the more resilient it becomes. By nurturing a variety of plants and insects, you’ll help enhance the overall stability of the ecosystem, benefiting inchworms and many other species.
In summary, supporting inchworm habitats is vital not just for them, but for the health of the entire forest ecosystem. Each little effort counts, leading to a more balanced environment.
Inchworms, while small and sometimes overlooked, play a significant role in forest ecology and the food web. From being a key food source for many animals to aiding nutrient cycling and indicating ecosystem health, they are essential players in maintaining the balance of nature.
The next time you’re out in the woods, take a moment to appreciate these fascinating little caterpillars. They may be inching along, but their impact on the environment is anything but small. By understanding their roles, we can take steps to preserve their habitats and the rich ecosystems they support. It’s a win-win for both inchworms and the environment!